Tartary Buckwheat derived Exosome Research & Application
Introduction Development Support Workflow Key Findings Infrastructure Why us Deliverables Testimonials FAQs
Introduction to Tartary Buckwheat Nanovesicles
Tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum), recognized for its dual role as a nutrient-rich grain and traditional medicinal food, is gaining increasing attention in exosome research. Its naturally high levels of flavonoids, phenolic acids, rutin, and quercetin contribute to multiple physiological functions. Recent studies have isolated nano-sized extracellular vesicles—resembling exosomes—from Tartary buckwheat, revealing their stability in gastrointestinal conditions and potential in modulating starch digestion and gut microbiota. Creative Biolabs, a professional service provider in the exosome research space, offers customized development solutions to facilitate pioneering work on Tartary buckwheat-derived exosomes (TBDEs).
Tailored Exosome Development Support
At Creative Biolabs, we focus on the custom development of Tartary buckwheat-derived exosomes for foundational scientific research. Our exosome development services are designed to meet the needs of academic and industrial researchers seeking robust, reproducible exosome preparations from Tartary buckwheat.
-
Our baseline service includes customized isolation and enrichment of TBDEs, with optional lyophilization as needed, tailored to specific downstream applications.
-
Optional Services: Upon request, we offer additional analyses such as molecular profiling (proteomics, miRNA, lipidomics), surface marker identification, and particle size distribution analysis using NTA and TEM
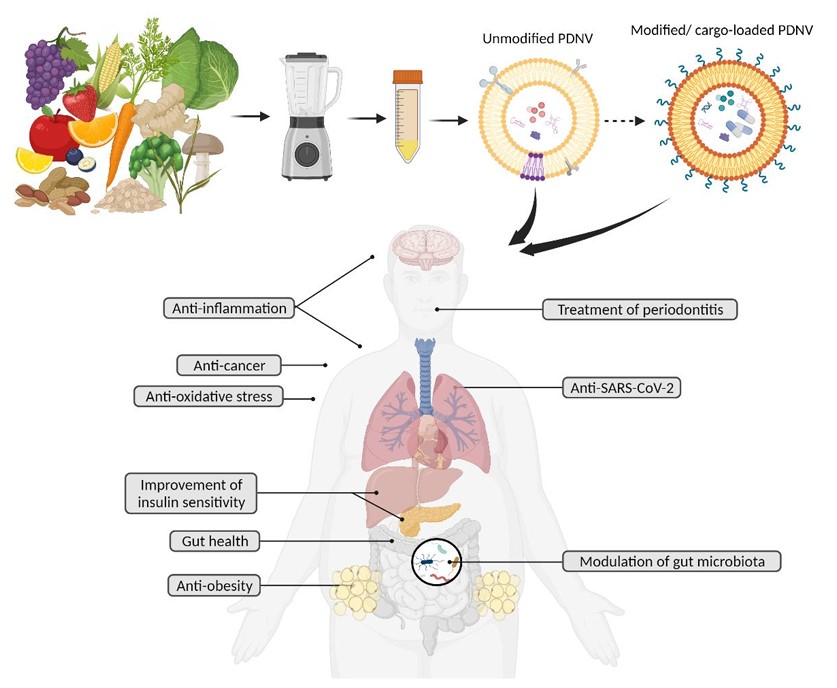 Fig.1 Unmodified PDNVs and modified PDNVs possess various potential health benefits.1
Fig.1 Unmodified PDNVs and modified PDNVs possess various potential health benefits.1
Isolation Strategy & Workflow Overview
Our streamlined, plant vesicle-focused workflow ensures efficient TBDE production while preserving functional integrity:
-
Raw Material Processing: Homogenization of tartary buckwheat material in buffer.
-
Pre-Cleaning: Low-speed centrifugation and filtration to remove cellular debris.
-
Vesicle Concentration: Sequential differential centrifugation to isolate crude vesicle fractions.
-
Density-Based Separation (Optional): Gradient centrifugation to enrich vesicle populations from sucrose interfaces.
-
Resuspension & Quality Check: Final suspension in PBS and optional purity assessments.
This workflow is scalable and adjustable based on yield requirements and vesicle type.
Key Research Progress on Tartary Buckwheat-Derived Vesicles
Researchers have uncovered several distinctive biological features of TBDEs:
|
Research Focus
|
Findings and Conclusions
|
|
Structural Identity
|
TBDEs exhibit a typical cup-shaped morphology of exosomes, with particle sizes ranging from 30 to 200 nm and a negative surface charge, indicating efficient cellular interaction capabilities.
|
|
Gastrointestinal Stability
|
TBDEs maintain structural integrity and surface potential when exposed to simulated gastrointestinal fluids, demonstrating promise for oral delivery applications.
|
|
Impact on Starch Metabolism
|
-
TBDEs significantly increase the proportion of resistant starch in wheat starch, reducing digestibility.
-
Hydrogen bonding between TBDEs and starch molecules promotes a more ordered, less digestible complex.
-
TBDEs act as competitive inhibitors of α-amylase and α-glucosidase, thereby reducing the rate of enzymatic starch digestion.
|
|
Modulation of Gut Microbiota
|
-
Oral administration of TBDEs leads to their accumulation in intestinal and liver tissues.
-
miRNA cargo, including miR482 variants and novel sequences, plays a role in reshaping microbiota composition and regulating bacterial gene expression.
-
Enhanced probiotic diversity and increased short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) levels contribute to improved intestinal homeostasis.
|
Specialized Infrastructure & Tools
Creative Biolabs leverages a suite of cutting-edge technologies and cleanroom lab conditions to support reliable TBDE development:
-
High-speed and ultracentrifugation systems
-
Density gradient separators
-
Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) platforms (optional)
-
Transmission electron microscopy (optional)
-
Microfluidics and filtration modules (optional)
-
RNA/protein analytical pipelines (optional)
Why Researchers Choose Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs distinguishes itself in the plant-derived exosome sector through:
|
Years of experience in botanical nanovesicle projects.
|
Protocols optimized for consistency, purity, and yield.
|
|
Clients benefit from a modular service format that allows selection tailored to your specific needs.
|
Strong data protection and project-specific NDAs.
|
What You Receive from Creative Biolabs
Our standard deliverables for Tartary buckwheat-derived exosome projects include:
-
A defined quantity of purified TBDEs
-
Protocol summary and quality report
Optional Deliverables:
-
NTA/TEM characterization reports
-
Molecular content analysis results
-
Stability profile under storage and digestion-mimicking conditions
Feedback from Our Partners
"Creative Biolabs provided invaluable support in our study of Tartary buckwheat vesicles. Their team was professional and responsive, and their vesicle preparations were consistently high-quality. We will definitely work with them again."
— Academic Research Group, Asia
"The modular design of Creative Biolabs' services allowed us to focus on our goals without overspending. Their optional analysis reports also helped us publish more confidently."
— University Lab, Europe
Tartary buckwheat-derived exosomes present a versatile and underexplored area in plant nanovesicle science. Creative Biolabs is committed to accelerating your discoveries with high-quality, customizable service offerings. Contact us to discuss your project requirements and begin your journey into TBDE research.
FAQs
Q: Why are exosomes generated from tartary buckwheat important for research?
A: Tartary Buckwheat-derived exosomes are nano-sized vesicles secreted by the Tartary Buckwheat plant, rich in bioactive compounds, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Their significance lies in their ability to facilitate intercellular communication and transfer bioactive molecules, making them valuable tools in studying plant defense mechanisms, stress responses, and potential applications in various fields, including beauty and cosmetics.
Q: What functions do Tartary Buckwheat exosomes perform in plant biology?
A: In plant biology, Tartary Buckwheat exosomes are believed to play roles in mediating stress responses, enhancing nutrient uptake, and promoting interactions with other plants or microorganisms. They can transmit signals that help buffer against environmental stressors, which may contribute to the overall resilience of the plant.
Q: How can Tartary Buckwheat exosomes be beneficial in skincare and beauty applications?
A: The bioactive components found in Tartary Buckwheat exosomes, such as antioxidants, polysaccharides, and flavonoids, provide promising attributes for skin care. They can strengthen the skin barrier, increase skin moisture, and fight oxidative stress. Research into their incorporation into cosmetics may yield innovative products that offer protective and rejuvenating benefits for the skin.
Q: Are there any research efforts focused on the extraction and characterization of Tartary Buckwheat exosomes?
A: Yes, researchers are actively developing methods for the isolation and characterization of Tartary Buckwheat exosomes. These studies often involve various techniques, including ultrafiltration and differential centrifugation, to purify the exosomes, followed by analysis methods such as NTA and electron microscopy to confirm their size, structure, and composition.
Q: What potential applications are being explored for Tartary Buckwheat exosomes beyond skincare?
A: Exosomes from Tartary Buckwheat are being investigated for potential uses in agriculture, including boosting plant growth, increasing stress tolerance, and strengthening soil quality, in addition to cosmetics. Moreover, their unique properties could be harnessed in food technology, functional foods, and natural preservatives, lending to sustainability and novelty in these sectors.
Q: What are the challenges associated with studying Tartary Buckwheat-derived exosomes?
A: Challenges in researching Tartary Buckwheat-derived exosomes include the complexity of their composition, variability in isolation methods, and the need for sophisticated analytical techniques to fully understand their functions. Further research is required to standardize methodologies and elucidate mechanisms of action at a molecular level.
Q: How can researchers contribute to the understanding of Tartary Buckwheat exosomes?
A: Researchers can contribute by conducting fundamental studies that explore the molecular composition and biological activities of Tartary Buckwheat exosomes. Collaborative efforts that bridge disciplines—such as plant biology, materials science, and cosmetic formulation—can accelerate innovation and application of these exosomes in various fields.
Q: What are the potential avenues for further investigation into exosomes generated from Tartary Buckwheat?
A: Future research directions may include deeper investigations into the mechanisms of action of Tartary Buckwheat exosomes, exploration of their synergistic effects when combined with other bioactive ingredients, and advancing technology for large-scale isolation and application.
Reference
-
Kim, Sora Q, and Kee-Hong Kim. "Emergence of Edible Plant-Derived Nanovesicles as Functional Food Components and Nanocarriers for Therapeutics Delivery: Potentials in Human Health and Disease." Cells vol. 11,14 2232. 18 Jul. 2022, doi:10.3390/cells11142232. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Unmodified PDNVs and modified PDNVs possess various potential health benefits.1
Fig.1 Unmodified PDNVs and modified PDNVs possess various potential health benefits.1









