Rose-derived Exosome Research and Application
Overview Services Workflow Platform Advantages Deliverables Testimonials FAQs
Botanical Nanocarriers: A Closer Look at Rose-Derived Vesicles
The discovery that plant cells secrete nanovesicles—functionally similar to animal exosomes—has opened an exciting frontier in botanical research. Among various plant species, the common rose (Rosa spp.) offers promising prospects due to its rich phytochemical profile and long-standing use in dermatological preparations. At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in the extraction, characterization, and analysis of rose-derived exosomes, providing high-quality support to academic researchers exploring their biological roles and material applications.
Unlike simple plant extracts, rose-derived exosomes (RDEs) offer a highly structured lipid bilayer that encases bioactive molecules such as microRNAs, proteins, and plant-specific signaling compounds. These vesicles play a role in intercellular communication and are being investigated for their ability to modulate cell behaviors in vitro, particularly in skin models. Creative Biolabs is at the forefront of providing standardized and customizable workflows that respect the complexity of rose-derived systems.
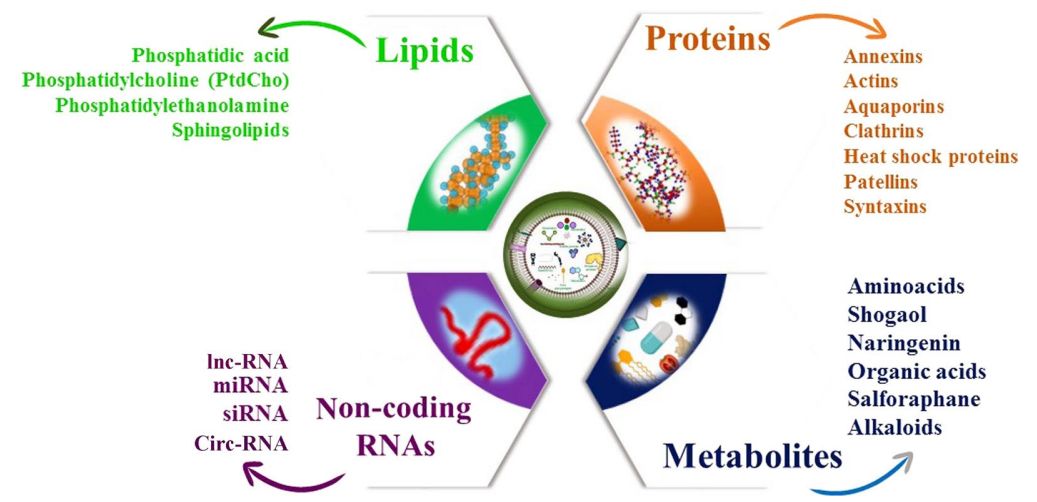 Fig.1 Biological composition of plant-derived exosomes.1
Fig.1 Biological composition of plant-derived exosomes.1
Tailored Capabilities: What Creative Biolabs Offers in Rose Vesicle Research
At Creative Biolabs, we provide a full suite of services to support rose-derived exosome research:
-
Tissue Source Verification: Selection of rose petals or whole flower biomass based on bioactivity benchmarks.
-
Specialized Isolation Protocols: Viscous botanical homogenates require nuanced pre-clearing and filtration techniques, which Creative Biolabs provides using tangential flow filtration and size exclusion chromatography.
-
Physicochemical Characterization: From size and morphology (via NTA and TEM) to charge profiling and vesicle purity assessment, we ensure robust dataset generation.
-
Bioactive Component Analysis: LC-MS profiling of antioxidant phenolics, lipidomic profiling of vesicle membranes, and RNA content mapping.
-
Cytocompatibility Testing: We evaluate RDEs in various skin-derived cell lines, measuring endpoints such as viability, ROS response, and collagen synthesis.
From Harvest to Data: Our Methodical Approach
Our rose exosome platform is structured around a reproducible, research-grade workflow:
-
Biomass Processing: Petals or full flower tissues are washed and homogenized under chilled PBS conditions to preserve vesicle structures.
-
Filtration & Pre-Clearance: Removal of fibrous material and cell debris through multistep centrifugation and microfiltration.
-
Vesicle Concentration: Ultrafiltration or size exclusion chromatography enriches RDEs for downstream use.
-
Compositional Validation: Using analytical tools, we characterize vesicle-associated lipids, RNAs, and phenolics. (Optional)
-
Biological Testing: Optional assays assess cell proliferation effects, inflammatory modulation, and oxidative response. (Optional)
-
Data Compilation: Clients receive comprehensive reports, including yield, size distribution, purity metrics, and biochemical fingerprints (Optional).
Analytical Depth: Inside the Creative Biolabs Technology Platform
Our research infrastructure supports high-resolution analysis of rose exosomes:
-
UPLC-MS/MS for phytochemical and antioxidant quantification (Optional)
-
TEM & DLS for morphology and stability verification
-
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) for vesicle size/concentration
-
Zeta Potential Assessment for vesicle surface charge (Optional)
-
Gene Expression & Uptake Studies using qPCR and live-cell imaging (Optional)
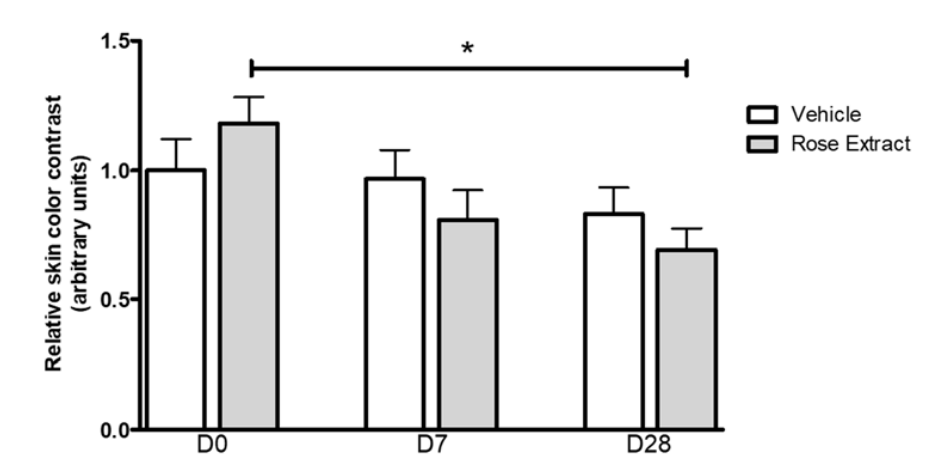 Fig.2 Detection of rose extract efficacy on dark eye circles.2
Fig.2 Detection of rose extract efficacy on dark eye circles.2
Why Creative Biolabs? Distinctive Strengths in Plant Vesicle Research
-
Specialization in Floral Vesicles: Creative Biolabs offers validated protocols for roses and other ornamental botanicals.
-
Transparent Data Workflow: Every result includes traceable SOPs, quality controls, and analytic reproducibility.
-
Non-clinical Focus: We support foundational science, mechanism discovery, and functional profiling—no therapeutic claims.
-
Scalable Research Design: Creative Biolabs adapts projects from initial feasibility to expanded biological testing.
Your Research Package: What's Included
Every Creative Biolabs project on rose-derived exosomes includes:
-
TEM/NTA-based morphology and quantitation
-
Bioactive cargo composition (lipidomics, phenolics, and RNA) (Optional)
-
Cytocompatibility and ROS modulation studies (Optional)
-
Extraction and enrichment SOPs
-
Batch consistency data and documentation (Optional)
-
Customizable reporting formats for publication or grant use
What Clients Say
"Creative Biolabs' profiling of rose exosomes allowed us to see unique antioxidant payloads we couldn't isolate using traditional extracts. Their team was incredibly responsive and offered reliable comparative data."
— Dr. EmiXXXX
"We partnered with Creative Biolabs to test rose vesicle effects on fibroblasts, and the results were robust and reproducible. Their SOPs were well-documented and easy to replicate in-house."
— Dr. AntXXXX
Rose-derived exosomes are more than just a novel skincare ingredient—they are a molecular system rich with research potential. With Creative Biolabs' rigorous scientific approach, expert protocols, and cross-disciplinary insight, your lab can explore this botanical vesicle frontier with clarity and confidence. Connect with Creative Biolabs to launch your rose exosome project today.
FAQs
Q: What unique properties make rose-derived exosomes make them suitable for research?
A: Rose-derived exosomes are known for their rich bioactive compounds. These components contribute to their ability to mediate cellular communication and influence various biological processes. Their unique biochemical profile supports their application in cosmetic research, particularly in enhancing skin health and rejuvenation.
Q: How do rose-derived exosomes contribute to skin health according to recent studies?
A: Research indicates that rose-derived exosomes can promote skin hydration, improve elasticity, and enhance barrier function. Their antioxidant properties help mitigate oxidative stress, which is often linked to skin aging. Additionally, studies suggest that they may stimulate fibroblast activity, leading to increased collagen production, which is critical for maintaining youthful skin.
Q: What specific applications of rose-derived exosomes are being explored in the field of cosmetology?
A: In cosmetology, rose-derived exosomes are being studied for their potential in formulating serums and creams that target skin rejuvenation, pigmentation issues, and wound healing. Their natural origin and biocompatibility make them ideal candidates for developing innovative cosmetic products that aim to enhance skin appearance and health.
Q: Are there any research findings on the anti-inflammatory effects of rose-derived exosomes?
A: Yes, preliminary research suggests that rose-derived exosomes possess anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe irritated skin and reduce redness and inflammation. For sensitive skin or disorders like rosacea and eczema, where inflammation is a major problem, they are a potential element.
Q: How does the extraction process of rose-derived exosomes affect their activity and efficacy?
A: The method of extraction is crucial as it can affect the integrity and bioactivity of the exosomes. Techniques such as ultrafiltration or precipitation are commonly employed, and optimizing these processes ensures the preservation of their functional attributes. The optimal extraction techniques that optimize activity and yield are still being investigated.
Q: What challenges exist in the research and application of rose-derived exosomes?
A: Challenges in this field include standardization of extraction techniques, variability in composition due to different rose species and cultivation conditions, and the need for extensive characterization to fully understand their mechanisms of action.
References
-
Nemati, Mohadeseh, et al. "Plant-derived extracellular vesicles: a novel nanomedicine approach with advantages and challenges." Cell Communication and Signaling 20.1 (2022): 69.
-
Duroux, Romain, et al. "A rose extract protects the skin against stress mediators: A potential role of olfactory receptors." Molecules 25.20 (2020): 4743.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Biological composition of plant-derived exosomes.1
Fig.1 Biological composition of plant-derived exosomes.1
 Fig.2 Detection of rose extract efficacy on dark eye circles.2
Fig.2 Detection of rose extract efficacy on dark eye circles.2









