Catharanthus roseus-derived Exosome Research and Application
Introduction Uniqueness Capabilities Methodology Platform Strengths Deliverables Reviews FAQs
Introduction: Exploring Vesicle Complexity in Catharanthus roseus
Catharanthus roseus, widely known as Madagascar periwinkle, has long been valued in botanical science for its secondary metabolites. More recently, its extracellular vesicles—specifically exosomes—have emerged as a new focal point for plant-based nanovesicle research. At Creative Biolabs, we offer a comprehensive platform for the investigation and application of Catharanthus roseus-derived exosomes (CRDEs), aimed at academic and industrial researchers focused on foundational exosome biology.
CRDEs are attracting interest due to their structural resilience, molecular richness, and potential for scale-up. With specialized profiling techniques and deep domain expertise, Creative Biolabs supports scientific exploration across characterization, biosynthesis pathways, immune modulation, and vesicle engineering. Our work on CRDEs advances the broader understanding of plant-derived extracellular vesicles while reinforcing our reputation for scientific rigor and custom project support.
Our Focus: What Makes Catharanthus roseus-Derived Vesicles Unique
CRDEs possess several remarkable biological and physical features:
-
Exceptional Stability: CRDEs resist enzymatic degradation (nucleases and proteases) and maintain membrane integrity even in acidic or basic environments.
-
Distinct Lipid Profile: Ether phospholipids dominate CRDE lipidomics, potentially contributing to vesicle longevity and bioactivity.
-
Immune Modulation: In vitro data suggest CRDEs activate the TNF-α/NF-κB/PU.1 axis in immune cells, stimulating cytokine production and lymphocyte proliferation.
-
Organ-Specific Distribution: CRDEs localize to immune organs post intraperitoneal injection and show survivability in the digestive tract upon oral administration.
Our characterization pipeline at Creative Biolabs has confirmed the unique proteomic signature of CRDEs, including enrichment in polycystin-associated proteins, which may indicate their multivesicular body (MVB) origin—a noteworthy insight for plant exosome studies.
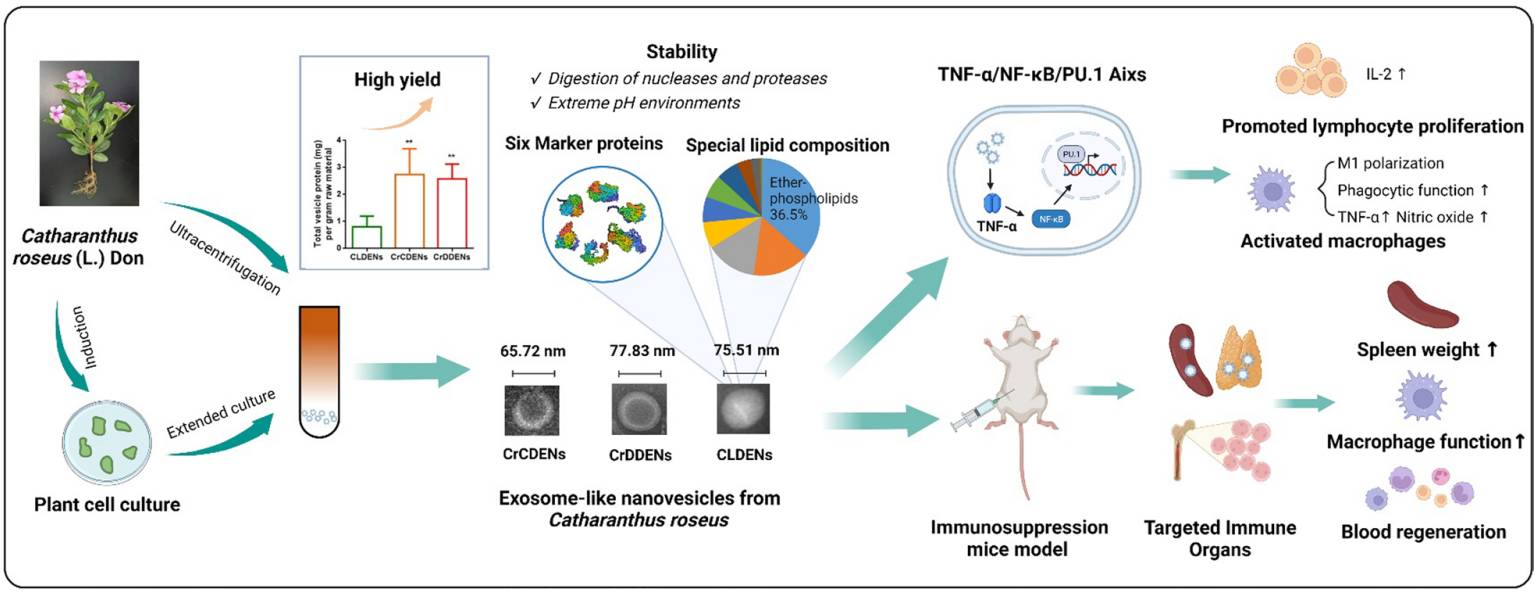 Fig. 1 Isolation and analytical studies of CRDE.1
Fig. 1 Isolation and analytical studies of CRDE.1
Research Capabilities: Tailored Solutions for CRDE Exploration
At Creative Biolabs, we provide a suite of services that enable targeted CRDE research:
-
Source Material Optimization: We work with authenticated C. roseus tissues and dedifferentiated cell cultures.
-
Custom Isolation Protocols: Tailored methods to isolate high-purity vesicles without solvent-based contamination.
-
Molecular Profiling: Full suite of lipidomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and small RNA analysis.
-
Immunological Assays: Quantitative assays to test immune activation and suppression reversal.
-
Scale-Up Feasibility: Suspension culture platforms achieving >1 g vesicles from tens of liters of supernatant.
Our scientists collaborate with your team to align technical designs with specific research questions, delivering meaningful data with contextual interpretation.
Our Methodology: From Leaves to Functional Particles
Creative Biolabs' standard workflow for CRDE projects:
-
Tissue Sourcing & Authentication
-
Controlled Cell Culture of stem-forming and dedifferentiated systems
-
Sequential Centrifugation and Ultrafiltration
-
Vesicle Validation using TEM, NTA, and zeta potential analysis
-
Functional Testing, including cytokine response and lymphocyte proliferation assays (Optional)
-
Omics Integration: Lipid, protein, and metabolite data correlated to biological function (Optional)
Our strict adherence to plant tissue handling and cleanroom protocols ensures high reproducibility and sample quality across batches.
Analytical Platform: Tools that Drive Discovery
Creative Biolabs' CRDE analytical capabilities are powered by cutting-edge tools:
-
TEM and AFM for membrane morphology
-
UPLC-MS/MS for deep lipid and metabolite profiling
-
NTA (Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis) for size/concentration assessment
-
High-sensitivity Proteomics and RT-qPCR platforms
-
Custom Reporter Assays to evaluate immunostimulatory properties
We continually refine our platform to meet emerging needs in exosome systems biology.
Scientific Strengths: Why Researchers Choose Creative Biolabs
-
Botanical Cell Engineering Expertise: Plant-based vesicle systems require knowledge of both tissue culture and nanovesicle dynamics—Creative Biolabs offers both.
-
Multi-Omics Precision: We deliver data-rich profiles to enable cross-analysis and hypothesis generation.
-
High-Yield Production Models: Our suspension cell systems allow feasible scale-up for exploratory projects.
-
Low Contaminant, Solvent-Free Protocols: Especially critical for immune or metabolic pathway assays.
-
Reliable Data, Publication-Ready Outputs: All deliverables include clear documentation, raw data access, and method transparency.
What You Will Receive from Creative Biolabs
Each Catharanthus roseus exosome research project includes:
-
TEM and NTA reports with morphological and concentration metrics
-
Omics-level lipid, protein, and metabolite data (optional)
-
Vesicle stability and response profiles (optional)
-
Immunomodulation assay results (optional)
-
Customized SOPs for sample isolation and processing
-
Batch records for repeatability and reproducibility (optional)
What Our Clients Say
"Our experience with Creative Biolabs on Catharanthus roseus-derived vesicles was seamless from consultation to data delivery. Their team identified key lipid biomarkers we hadn't considered, and their immunological analysis supported our new hypothesis in innate immune training."
— Dr. HanXXXX
"Creative Biolabs' scale-up service for CRDE allowed us to move from proof-of-concept to a consistent production model. Their vesicle data were essential for our internal feasibility report."
— Prof. EmiXXXX
Catharanthus roseus-derived exosomes represent a resilient, information-rich system for exploring plant biology, immune modulation, and vesicle biosynthesis. Creative Biolabs provides a complete scientific infrastructure to turn exploratory interest into high-quality, actionable data. Reach out to begin your customized CRDE research project.
FAQs
Q: Why is Catharanthus roseus a focus for exosome research?
A: Catharanthus roseus is known for its rich secondary metabolite production, including valuable alkaloids. Researching its exosomes can provide insights into their role in plant biology, such as stress responses and intercellular signaling, potentially leading to innovative biotechnological applications.
Q: How are exosomes from Catharanthus roseus produced for research purposes?
A: Exosomes can be isolated from the culture medium of Catharanthus roseus cell cultures or tissues. Techniques such as differential centrifugation, ultrafiltration, and polyethylene glycol (PEG) precipitation are commonly used to purify exosomes for subsequent analysis and research.
Q: What are the key functions of Catharanthus roseus-derived exosomes?
A: Exosomes from Catharanthus roseus are believed to play critical roles in:
-
Cell signaling: Mediating communication between plant cells.
-
Stress response: Helping the plant to adapt to environmental stressors.
-
Transporting bioactive compounds: Carrying secondary metabolites that can influence neighboring cells and tissues.
Q: What are the potential applications of Catharanthus roseus-derived exosomes?
A: Potential applications include:
-
Agricultural biotechnology: Enhancing stress resistance in crops by utilizing the signaling properties of these exosomes.
-
Natural product discovery: Using the exosomes to facilitate the bioavailability and targeted delivery of secondary metabolites for various industrial applications, such as cosmetics or food industries.
-
Biotechnological tools: Developing transgenic plants that harness exosomes for improved traits or as delivery vehicles for beneficial genes.
Q: Are there any challenges in studying Catharanthus roseus-derived exosomes?
A: Yes, some challenges include:
-
Isolation and purification: Obtaining pure exosomes without contamination from other cellular components can be technically demanding.
-
Standardization: Developing standardized methods for exosome characterization and quantification remains a hurdle.
-
Understanding function: Elucidating the precise mechanisms through which exosomes exert their effects is an ongoing area of research.
Q: What are the future directions for research on Catharanthus roseus-derived exosomes?
A: Future research could focus on:
-
Characterizing the molecular composition of exosomes to understand their specific roles.
-
Exploring their interactions with other cells and environmental factors.
-
Investigating their potential in bioremediation or enhancing plant growth under suboptimal conditions.
-
Developing innovative biotechnological applications in crop improvement and sustainable agriculture.
Reference
-
Ou, Xiaozheng, et al. "Novel plant-derived exosome-like nanovesicles from Catharanthus roseus: preparation, characterization, and immunostimulatory effect via TNF-α/NF-κB/PU. 1 axis." Journal of Nanobiotechnology 21.1 (2023): 1-22. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by adding the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Isolation and analytical studies of CRDE.1
Fig. 1 Isolation and analytical studies of CRDE.1









