Flower-derived Exosome Research & Applications
Overview Highlights Services Workflow Platform Advantages Deliverables Reviews FAQs
Scientific Discovery Rooted in Botanical Vesicles
In recent years, the scientific spotlight has increasingly turned toward the biological potential of plant-derived nanovesicles, with flower-derived exosomes (FDEs) becoming a compelling focus for foundational research. These nanometer-sized extracellular vesicles, secreted by floral tissues such as petals, pollen, stems, and sometimes even nectar glands, offer an intricate biochemical landscape rich in secondary metabolites and regulatory molecules. Unlike exosomes from fruits or roots, floral exosomes are often more diverse in their lipid, protein, and RNA cargo, reflecting the dynamic metabolic environment of flowering tissues. At Creative Biolabs, we have built a dedicated and modular research infrastructure to support in-depth investigations into these vesicles, offering customized services that integrate isolation, profiling, and functional characterization to illuminate their scientific value. Through our collaborative approach, we aim to empower academic, industrial, and institutional researchers to uncover new pathways, mechanisms, and applications anchored in the unique attributes of flower-derived exosomes.
To help researchers explore the unique characteristics of different floral species, we also offer targeted pages that delve into specific types of flower-derived exosomes. These include:
Each category highlights distinct chemical profiles, isolation strategies, and potential research applications, providing a valuable extension to this core overview.
What Makes Flower Vesicles Unique?
Exosomes derived from floral sources show a diverse and potent composition of bioactive molecules such as flavonoids, terpenes, alkaloids, microRNAs, and specialized lipids. Unlike fruit- or root-derived exosomes, flower-derived vesicles often exhibit high levels of aromatic secondary metabolites, contributing to their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities.
Recent research has linked flower exosomes to a wide range of biological interactions, including:
-
Oxidative Stress Reduction: Natural antioxidants present in floral vesicles can modulate oxidative stress pathways.
-
Intercellular Communication: FDEs exhibit strong potential in facilitating cross-kingdom messaging.
-
Bioactive Delivery: Due to their low immunogenicity and permeability, flower exosomes are ideal for carrying complex cargos in vitro.
-
Agricultural Applications: Some floral vesicles show promise in enhancing plant resistance and promoting pollination or nutrient absorption.
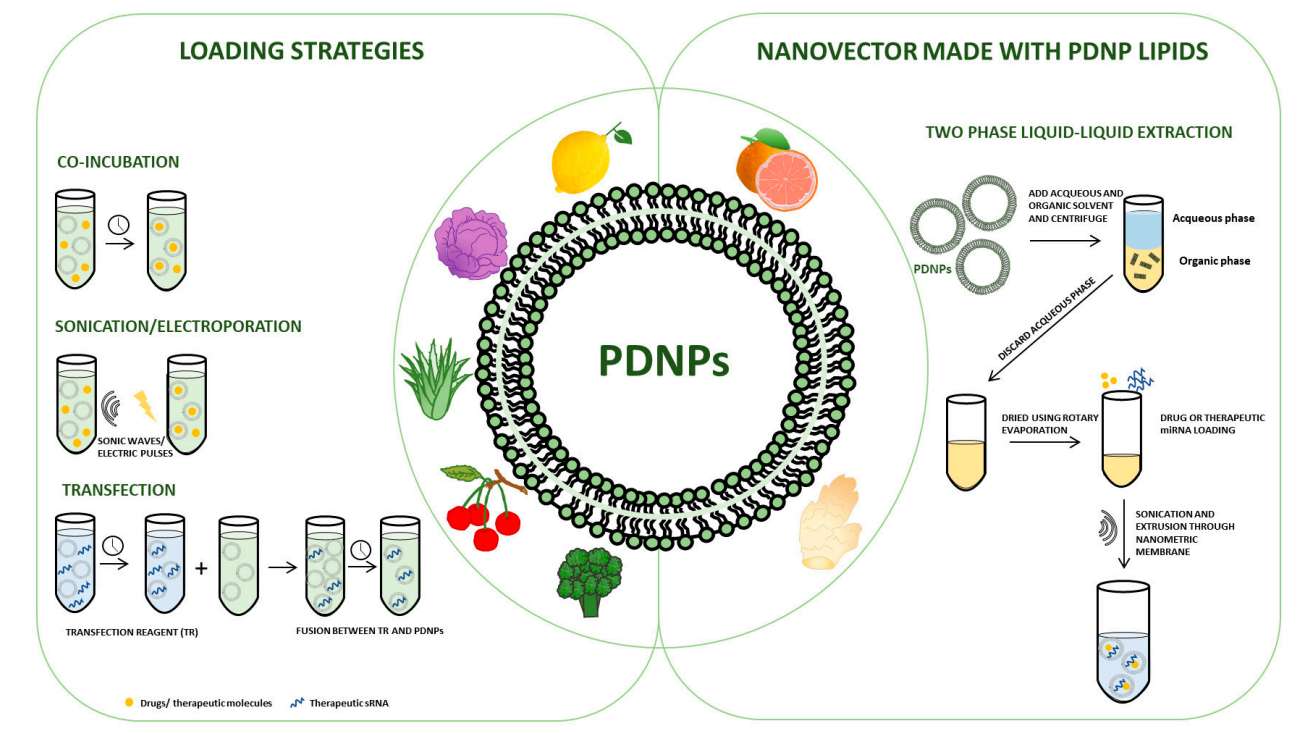 Fig.1 Strategies used for plant-derived nanovesicle loading.1
Fig.1 Strategies used for plant-derived nanovesicle loading.1
Creative Biolabs' Core Capabilities in Flower Exosome Research
Creative Biolabs' integrated services for flower-derived exosome studies are designed to meet the needs of academic labs, botanical institutes, and biotech innovators. Our portfolio includes:
-
Species-Specific Isolation: From rose, jasmine, chamomile, tea flower, to aloe and Centella, we tailor protocols for specific floral species.
-
Comprehensive Profiling: Morphological (TEM), particle analysis (NTA), proteomics, RNA-seq, and lipidomics.
-
Bioactivity Evaluation: Including antioxidant potential, fibroblast stimulation, and epithelial modulation.
-
Customized Studies: Client-specified endpoints, vesicle engineering, or floral comparative analytics.
From Petal to Data: Our Workflow
Creative Biolabs ensures rigorous, reproducible workflows to generate high-purity flower exosomes:
-
Source Selection: Ethically and sustainably sourced flower tissues.
-
Tissue Homogenization: Gentle physical disruption to preserve vesicle integrity.
-
Differential Centrifugation: Removing large debris and concentrating vesicle-rich fractions.
-
Ultracentrifugation & Filtration: Density-based separation and size exclusion purification.
-
Characterization & Validation: Particle size distribution, zeta potential, morphology, and cargo content.
-
Biofunctional Screening: Optional in vitro assays to assess vesicle behavior.
Infrastructure That Supports Results
At Creative Biolabs, scientific integrity begins with infrastructure. We maintain advanced tools dedicated to plant nanovesicle research:
-
TEM for nanoscale structure imaging
-
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) for vesicle quantification
-
RT-qPCR and miRNA microarrays for RNA cargo profiling (Optional)
-
UPLC-MS/MS for small molecule composition and metabolomics (Optional)
-
Custom vesicle-labeling solutions for uptake tracking (Optional)
Why Choose Creative Biolabs for Flower Exosome Research?
Our clients choose Creative Biolabs for our technical precision, biological insight, and scientific collaboration. Key advantages include:
-
High Purity, Low Contaminant Preparations
-
Custom Protocol Design for rare or exotic floral sources
-
Non-Toxic Processing Pipelines free from harsh solvents
-
Grant and Publication Support with full protocol transparency
-
Batch-to-Batch Reproducibility guaranteed through rigorous QC
What You Receive
Your collaboration with Creative Biolabs yields:
-
Well-characterized, pure flower exosome samples
-
Complete analytical reports: NTA, TEM, protein/RNA profiles (Optional)
-
Project-specific documentation: isolation parameters, SOPs, and stability data
-
Optional: in vitro function reports and vesicle engineering summaries (Optional)
Feedback from Our Clients
"Creative Biolabs helped us explore the bioactivity of Centella-derived vesicles in dermal fibroblasts. Their results supported our cosmetic formulation hypothesis and gave us reliable experimental ground. The communication throughout the project was timely and clear, and their team was proactive in providing valuable insights that improved our study design."
— Dr. LinXXXX
"With Creative Biolabs's help, we were able to isolate stable rose-derived vesicles that exhibited strong antioxidant activity. Their methodological clarity and result reproducibility were top-notch. Our internal validation confirmed their data quality, and we're now preparing a publication using the results. Creative Biolabs exceeded our expectations in both scientific support and technical execution."
— Prof. AndrXXXX
Whether you are just starting a feasibility study or scaling up a comparative project, Creative Biolabs is your partner in unlocking the biological potential of flower-derived vesicles. Contact Creative Biolabs to accelerate your floral exosome research.
FAQs
Q: What are some potential applications of flower-derived exosomes in cosmetics and skincare?
A: Flower-derived exosomes are gaining attention for their potential in skincare formulations. They may contain bioactive molecules promoting skin hydration, enhancing anti-aging effects, and facilitating skin repair. Research is ongoing to explore their roles in improving skin barrier function and delivering essential nutrients to skin cells.
Q: How do flower-derived exosomes compare to exosomes from other plant sources?
A: Flower-derived exosomes are unique due to their composition, which may include specific bioactive compounds not found in other plant-derived exosomes. This distinctive profile could enhance their effectiveness in various applications, particularly in cosmetics and personal care products, where specific phytochemicals may provide unique benefits for skin health.
Q: How does the protein composition of flower-derived exosomes contribute to their biological functions?
A: The protein content of flower-derived exosomes is crucial, as it includes enzymes, growth factors, and signaling molecules that can influence cellular behavior. Understanding the protein landscape can help identify specific functions related to plant interactions and potential mechanisms for benefits in skincare and other applications.
Q: Can flower-derived exosomes be used in nanocarrier systems for bioactive delivery?
A: Yes, flower-derived exosomes have the potential to serve as nanocarriers for delivering bioactive compounds. Their natural origin and ability to encapsulate various molecules make them ideal candidates for targeted delivery systems, enhancing the bioavailability and efficacy of active ingredients in cosmetic formulations.
Q: What are the research directions currently being explored in flower-derived exosome studies?
A: Current research is exploring the molecular mechanisms behind the bioactivity of flower-derived exosomes, including their roles in promoting cellular regeneration, modulating inflammation, and contributing to plant stress responses. Investigations are also focusing on their applications in developing novel materials for skincare and cosmetic products, understanding their environmental interactions, and harnessing their potential in biotechnological innovations.
Reference
-
Tinnirello, Vincenza, et al. "Exploiting the opportunity to use plant-derived nanoparticles as delivery vehicles." Plants 12.6 (2023): 1207. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Strategies used for plant-derived nanovesicle loading.1
Fig.1 Strategies used for plant-derived nanovesicle loading.1









