Aspergillus flavus-derived Exosome Research & Application
Stepwise Isolation Flavus Exosomes Distinctive Traits Biological Insights Advantages Client Viewpoints FAQs
Aspergillus flavus is one of the most extensively studied filamentous fungi, known for its dual biological nature-serving as both an industrially useful species and an opportunistic pathogen. In recent years, exosomes derived from A. flavus have emerged as promising subjects in fungal biology, revealing complex communication mechanisms between fungal cells and host systems.
At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in providing professional exosome research solutions tailored to Aspergillus flavus-derived exosomes. With comprehensive experience in fungal exosome isolation, analysis, and custom development, Creative Biolabs supports global researchers seeking reliable and reproducible data to advance basic and translational studies in fungal biology.
Stepwise Exosome Isolation Workflow
Creative Biolabs employs a modular and research-oriented workflow for isolating A. flavus-derived exosomes. Our platform emphasizes reproducibility and customization, ensuring the highest-quality vesicle recovery across various sample types.
Standard Workflow – Custom Exosome Development
-
Culture Establishment: Optimize fungal growth under controlled environmental and nutritional conditions to stimulate exosome secretion.
-
Supernatant Collection: Obtain clarified culture supernatants post fungal growth for exosome enrichment.
-
Concentration & Pre-purification: Perform ultrafiltration and gradient-based pre-purification to concentrate exosome-rich fractions.
-
Ultracentrifugation: Apply differential ultracentrifugation to isolate A. flavus-derived exosomes of consistent size and purity.
-
Quantification & Quality Control: Assess vesicle particle concentration, morphology, and integrity through nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) and electron microscopy.
Optional Analytical Services (based on species library availability):
-
Proteomic & Lipidomic Profiling: Characterize cargo proteins, enzymes, and metabolites unique to A. flavus vesicles.
-
RNA Sequencing & Bioinformatics: Identify and annotate exosomal RNA species for gene expression or regulatory pathway analysis.
-
Functional Assays: Explore the role of exosomes in fungal communication, host immune modulation, or stress adaptation.
-
Labeling & Imaging: Fluorescent labeling and visualization for uptake or distribution studies.
Reach out to Creative Biolabs for a customized isolation plan suited to your fungal model.
Current Studies on Aspergillus flavus-Derived Exosomes
|
Research Focus
|
Findings and Outcomes
|
|
Study of exosome production capability in A. flavus.
|
Culturing under spore-inducing conditions followed by ultrafiltration and ultracentrifugation successfully yielded A. flavus-derived vesicles. NTA confirmed particle sizes consistent with known fungal exosome ranges (40–400 nm).
|
|
Examination of immune modulation by A. flavus exosomes.
|
Bone marrow-derived macrophages exposed to fungal exosomes showed elevated secretion of TNF-α, IL-1β, and nitric oxide, indicating immunostimulatory potential.
|
|
Investigation of macrophage activity upon exosome treatment.
|
Exposure enhanced phagocytic and bactericidal activities of macrophages against fungal spores, suggesting exosome-mediated immune priming.
|
|
Analysis of polarization markers in exosome-treated macrophages.
|
Upregulation of iNOS transcripts indicated a shift toward M1-type macrophage polarization, while M2 markers remained unchanged.
|
|
In vivo evaluation of exosomal immune influence.
|
Pretreatment with A. flavus exosomes in Galleria mellonella larvae reduced CFU counts upon infection challenge, confirming immune activation and enhanced host resistance.
|
Contact Creative Biolabs to integrate published insights into your own fungal exosome project.
Distinctive Traits of A. flavus and Its Exosomes
|
Aspergillus flavus (Organism)
|
A. flavus-Derived Exosomes
|
-
A saprophytic mold prevalent in soil, crops, and food residues; known for its resilience under heat and dehydration.
-
Capable of producing aflatoxins, potent secondary metabolites associated with contamination of grains and nuts.
-
Exhibits both pathogenic and industrially useful strains; some are exploited for enzyme or organic acid production.
-
Acts as a model organism for studying fungal virulence, secondary metabolism, and stress response.
|
-
Secreted during active growth and metabolism, contributing to environmental adaptability and pathogenic interactions.
-
Typically range from 40-400 nm, encapsulating virulence-related proteins and signaling molecules.
-
Contain enzymes, surface antigens, and metabolites reflecting the parental cell's physiology and stress status.
-
Serve as carriers for virulence factors and communication mediators influencing host-pathogen interactions.
|
Consult Creative Biolabs for detailed exosome characterization tailored to your experimental objectives.
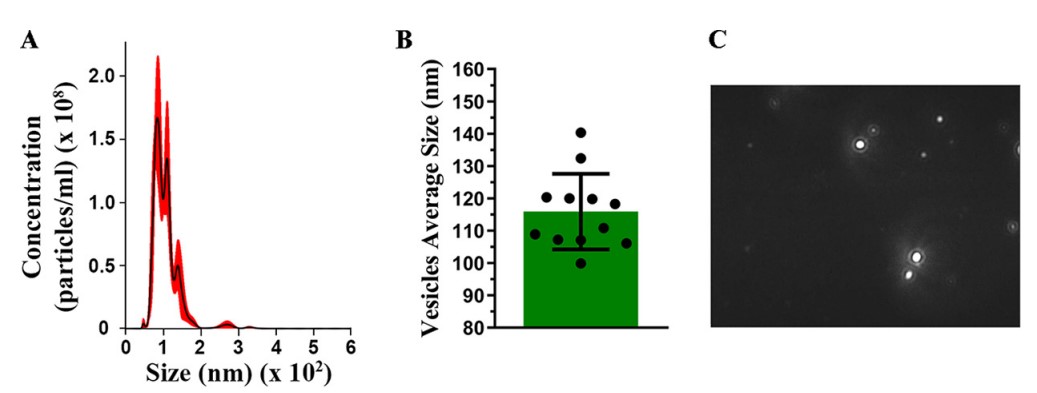 Fig.1 NTA characterization of Aspergillus flavus-derived Exosome.1
Fig.1 NTA characterization of Aspergillus flavus-derived Exosome.1
Key Biological Insights
Research on A. flavus exosomes contributes to broader fungal biology understanding:

Virulence Modulation
Exosomal proteins and lipids act as virulence modulators during host infection and environmental adaptation.

Host Interaction
Exosomes can influence innate immune pathways and shape the response of macrophages and epithelial cells.

Fungal Communication
Serve as intercellular messengers regulating colony development, spore formation, and antifungal resistance mechanisms.

Environmental Sensing
Reflect real-time physiological states of fungal cells under nutrient stress or toxin exposure.
Creative Biolabs' team can help you investigate these biological processes through tailored assays.
Advantages of Partnering with Creative Biolabs
Working with Creative Biolabs ensures that every fungal exosome study is conducted with precision, reproducibility, and full data transparency.
 Dedicated Fungal Exosome Expertise
Dedicated Fungal Exosome Expertise
Experienced in diverse fungal models beyond A. flavus, including Histoplasma and Malassezia.
 Comprehensive Customization
Comprehensive Customization
Adaptable workflows aligned with your unique strain and experimental needs.
 Transparent Data Delivery
Transparent Data Delivery
Detailed reports, raw data access, and QC documentation provided with every project.
 Research Partnership Mindset
Research Partnership Mindset
Creative Biolabs functions as an extension of your research team, not just a service provider.
Collaborate with Creative Biolabs to elevate your fungal exosome research.
Client Perspectives
"Our lab collaborated with Creative Biolabs for Aspergillus flavus exosome isolation and characterization, and the results exceeded expectations. Their team provided detailed project updates and transparent data, which made the entire process smooth and scientifically rigorous. We were especially impressed by the reproducibility of their NTA and proteomic results."
— Dr. L. HerXXX
"Working with Creative Biolabs gave us a strong technical foundation for studying fungal exosome-host interactions. The customized workflow they designed for our A. flavus strain saved us months of optimization. Their scientists clearly understand fungal biology, not just exosome technology."
— Dr. R. PatXXX
"We appreciated the professionalism and responsiveness of the Creative Biolabs team. Every stage — from culture preparation to optional molecular analysis — was handled with precision. The data package we received was publication-ready and matched our internal QC metrics."
— Dr. H. NakXXX
"Creative Biolabs offers more than a service — it's a partnership. They guided our team through technical decisions and provided insightful explanations about vesicle biogenesis in A. flavus. Their collaborative approach has made them our preferred partner for future exosome projects."
— Dr. E. WalXXX
Start your collaboration with Creative Biolabs and experience trusted scientific partnership.
The exploration of Aspergillus flavus-derived exosomes has opened a new window into fungal biology and intercellular communication. By leveraging Creative Biolabs' advanced isolation and analytical platform, researchers gain access to dependable results and customized technical insight that empower further discoveries in mycology, host-pathogen interaction, and environmental adaptation studies. Contact us to design your next fungal exosome research project.
FAQs
Q: What are the primary challenges in isolating exosomes from Aspergillus flavus, and how do you address them?
A: Isolating exosomes from A. flavus can be challenging due to the presence of cell debris and other extracellular vesicles. We utilize optimized ultracentrifugation techniques to enhance purity and yield, combined with advanced characterization methods.
Q: How do you characterize the protein composition of A. flavus-derived exosomes?
A: We employ mass spectrometry and Western blotting to analyze the protein content of the exosomes. Additionally, we utilize specific markers known to be enriched in fungal exosomes to validate our findings.
Q: Can exosomes from Aspergillus flavus influence plant-microbe interactions?
A: Yes, our preliminary studies indicate that A. flavus exosomes may play a significant role in modulating plant-microbe interactions, potentially influencing plant immunity and nutrient absorption. We conduct assays to assess their effects on various plant species.
Q: What potential applications do you see for A. flavus-derived exosomes in biotechnological fields?
A: The exosomes exhibit potential applications in biocontrol strategies against plant pathogens, as delivery vehicles for biopesticides, and as components in bioremediation techniques, leveraging their natural properties for environmental sustainability.
Q: How do external factors, such as nutrient availability or environmental stress, affect exosome production in Aspergillus flavus?
A: Nutrient availability and environmental stress conditions, such as temperature fluctuations or oxidative stress, have been shown to influence the quantity and composition of exosomes produced. We are currently investigating these effects to better understand their biological implications.
Reference
-
Brauer, Verônica S., et al. "Extracellular vesicles from Aspergillus flavus induce M1 polarization in vitro." Msphere 5.3 (2020): 10-1128. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title. https://doi.org/10.1128/msphere.00190-20.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 NTA characterization of Aspergillus flavus-derived Exosome.1
Fig.1 NTA characterization of Aspergillus flavus-derived Exosome.1













