Liver Disease Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes
Exosomes are products that are released outside the cell through exocytosis after the fusion of intracellular multivesicular bodies and the plasma membrane. These products are nanoscale vesicles surrounded by biomembranes, which are mainly responsible for intercellular communication and participate in the regulation of metabolism, immunity, and other functions. In the field of disease diagnosis, exosomal contents are emerging as key players in the pathogenesis of various diseases. In recent years, a large number of relevant studies have shown that diseased liver cells release a lot of exosomes, which are involved in the key pathobiological processes of liver diseases. As a consequence, based on body fluid-based liquid biopsy, exosomes have great application prospects in the development of new diagnostic and prognostic molecular biomarkers for liver diseases. Creative Biolabs has been making every effort to build a professional "one-stop" research service platform for exosomes. We have established a comprehensive technical system including exosome extraction, exosome identification, exosome labeling, exosome proteomics sequencing, exosome transcriptomic sequencing, etc., to provide all-around support and convenience for research scientists.
The Pivotal Role of Exosomes in Liver Diseases
Exosomes participate in the information exchange between liver cells and liver cells, between liver cells and other liver tissue cells, and between the liver and other tissues. Exosome-mediated signaling leads to diverse pathological changes such as proliferation, angiogenesis, inflammation, and tissue remodeling. Therefore, exosomes play an important role in various liver diseases, such as liver injury, liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Since the liver is the only organ in the human body without pain-sensing nerves, it is difficult to detect the chronic damage of viruses, alcohol, and drugs in the early stage. Therefore, it is difficult for people to detect early liver disease. Usually, the exacerbation of the liver disease is carried out imperceptibly. By the time pain occurs, the condition is often already serious. Therefore, there is an urgent need for noninvasive or minimally invasive liquid biopsy markers for early diagnosis of liver diseases.
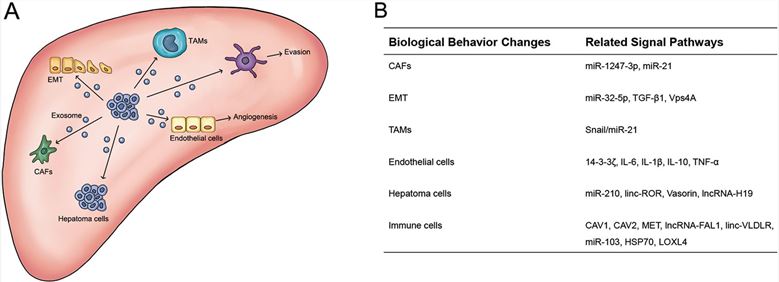 Fig.1 Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells can affect biological behavior changes of many types of cells by releasing exosomes.1,3
Fig.1 Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells can affect biological behavior changes of many types of cells by releasing exosomes.1,3
Potential Application of Exosome Contents in the Diagnosis of Liver Diseases
The importance of liquid biopsy for early diagnosis of diseases, medication monitoring, and prognosis judgment has become increasingly clear. It is currently believed that exosomes from urine (non-invasive) and blood (minimally invasive) can be used as sources of molecular biomarkers for disease diagnosis, early detection, and prognosis of different liver diseases. This is because exosomes in blood and urine contain specific molecules from the liver, such as miRNAs, lncRNAs, and protein, and the exosomal contents may be associated with different liver diseases. For example, by measuring 9 miRNAs (miR-1225-5p, miR-1275, miR-638, miR-762, miR-320c, miR- 451, miR-1974, miR-1207-5p, miR-1246), the results showed that the expression of these 9 miRNAs had a screening accuracy of 96.59% for hepatitis C patients and normal people, suggesting that specific miRNAs could expression to distinguish hepatitis C patients from a normal population. The level of lncRNA-H19 in serum exosomes of patients with liver cirrhosis was significantly higher than that of healthy people and was positively correlated with the degree of disease. Alcohol increased exosome secretion, and miR-27a in exosomes could polarize primitive monocytes into M2 macrophages. Therefore, miR-27a in patient exosomes is also a potential target for the diagnosis of alcoholic fatty liver. These data demonstrate that exosomes can serve as a promising diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for liver diseases.
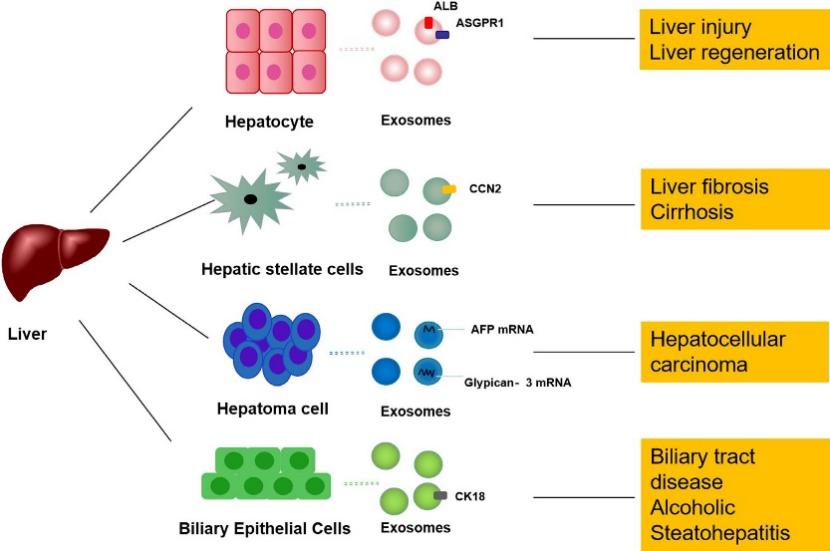 Fig.2 Exosomes derived from liver cells are involved in the pathogenesis of liver diseases and may serve as diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets.2,3
Fig.2 Exosomes derived from liver cells are involved in the pathogenesis of liver diseases and may serve as diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets.2,3
Starting from the enrichment and isolation of exosomes, Creative Biolabs guarantees high-quality exosome output and conducts quality control at every level during the research process. We will choose the optimal exosome isolation method and library construction method, combined with the analysis algorithm that meets the characteristics of exosomes, customize the analysis plan for customers, and provide the best solution for the overall study of exosome contents. If you have an idea to discover biomarkers in exosomes that can diagnose liver disease, please contact us to provide you with the most comprehensive exosome sequencing service.
References
-
Wang, H.; et al. Tumorigenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic potential of exosomes in liver cancer. Journal of Hematology & Oncology. 2019, 12(1):133.
-
Jiao, Y.; et al. Advances on liver cell-derived exosomes in liver diseases. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 2021, 25(1):15-26.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells can affect biological behavior changes of many types of cells by releasing exosomes.1,3
Fig.1 Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells can affect biological behavior changes of many types of cells by releasing exosomes.1,3
 Fig.2 Exosomes derived from liver cells are involved in the pathogenesis of liver diseases and may serve as diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets.2,3
Fig.2 Exosomes derived from liver cells are involved in the pathogenesis of liver diseases and may serve as diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets.2,3









