Cardiovascular Disease Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes
Overview Services Features FAQs
Liquid biopsy based on blood circulating exosomes provides a promising platform for accurately diagnosing and predicting cardiovascular disease (CVD). To help address the research limitations of exosomes in CVD diagnosis, Creative Biolabs has leveraged its resources to create a "one-stop" service system for exosome research, including extraction and identification, tracing, functional molecular validation, and histological analysis. Our research services related to the application of exosomes in CVD diagnosis provide a new vision for the application of exosomes in CVD diagnosis.
Exosomes as CVD Diagnostic Biomarkers
Traditional biomarkers for CVD, such as total cholesterol levels and low-density lipoprotein, can only roughly assess the risk of disease onset and progression, but cannot accurately predict the stage of the pathological process. With the demand for new methods of disease diagnosis such as liquid biopsy in precision medicine, exosomes, mediating intercellular communication in multiple physiopathological states, can be easily isolated from body fluids such as blood and urine as a new source of CVD diagnostic markers.
There is strong evidence that exosomes, as bilayer lipid vesicles secreted by most cells, carry bioactive factors and signaling molecules related to multiple CVD pathophysiologies with involvement in cardiovascular system development and injury by regulating the expression of related genes.
Investigation of epicardial adipose tissue-derived exosomes (eFat-EXO) revealed their high secretion under ventricular fibrillation-promoting (AF) conditions and their pro-inflammatory, pro-fibrotic, and pro-arrhythmic components. Furthermore, the role of circulating exosomes and their cargoes has been suggested to be promising in the diagnostic and prognostic strategies of several CVD pathological processes.
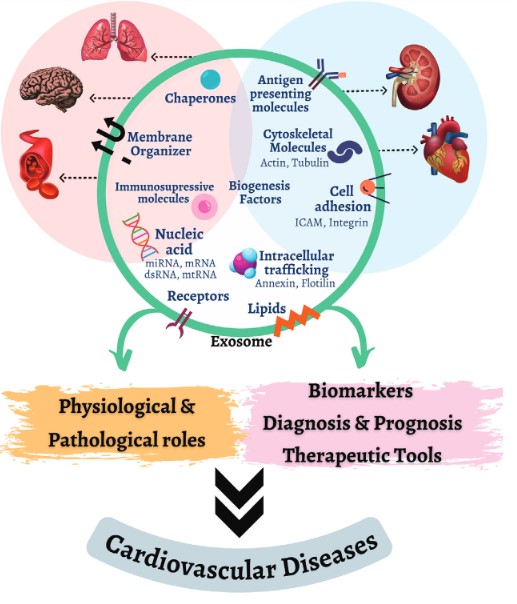 Fig.1 Exosomes' role in cardiovascular health and disease.1, 3
Fig.1 Exosomes' role in cardiovascular health and disease.1, 3
Application of Exosomes in CVD Diagnosis Research Service at Creative Biolabs
Exosomes have shown great potential as novel markers for liquid biopsy in the diagnosis of several CVDs, such as coronary artery disease (ACD) and heart failure (HF) disease. Creative Biolabs applied exosome profiling service for CVD diagnosis aims to inspire new ideas for exosomes as markers in future precision medicine and to improve the research progress of exosomes in CVD diagnosis.
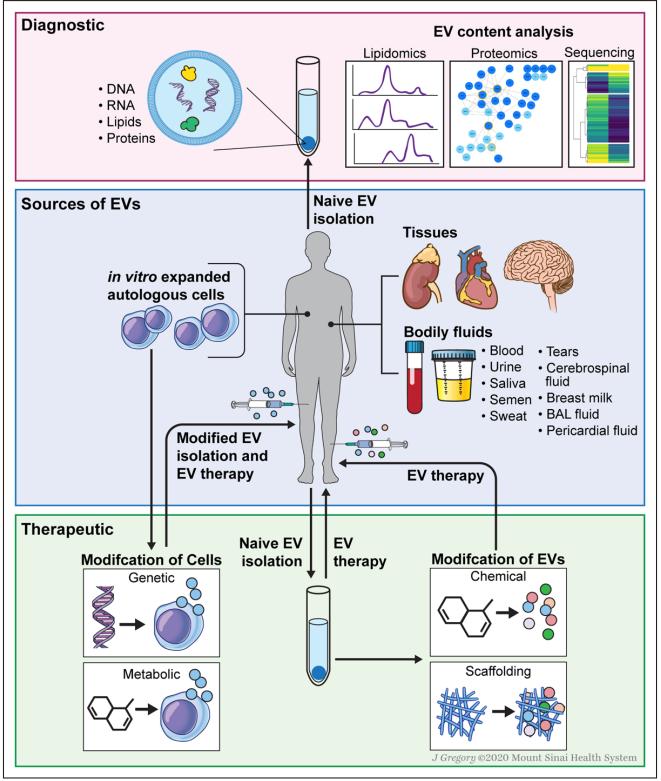 Fig.2 EV diagnostics and various strategies for EV-based therapies.2, 3
Fig.2 EV diagnostics and various strategies for EV-based therapies.2, 3
-
Discovery of Exosomal miRNAs for CVD Diagnosis
Exosomes secreted from damaged myocardium and dead cardiomyocytes in ACD found down-regulated expression of miR-939-5p, which is involved in the pathological process of inhibition of angiogenesis by nitric oxide signaling pathway, while up-regulated levels of exosomal miR-133a expression allow for assessment of the extent of myocardial injury and attack cell death. eFat-EXO encapsulated miR-3064-5p was identified as closely associated with the regulation of lipogenic differentiation functions in CVD. miR-192, miR-194, and miR34a showed predictive tasks for the development of heart failure and ventricular remodeling.
In addition to being used for the prediction of early stages of myocardial infarction, exosomal miRNAs can also serve as candidates for the prognosis of late stages of AVD. For example, the circulating endothelial cell-derived exosome miR-92a-3p has been recognized in the regulation of endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypes in ACD. Exosomal overexpression of miR-22, miR-320a, miR-423-5p and miR-92b in HF-associated serum and blood serve as specific biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of systolic heart failure.
-
Discovery of Exosomal Proteins and Cytokines for CVD diagnosis
Several exosomal proteins are upregulated under CVD conditions that have been identified, with significant enrichment of plasma exosome-carrying proteins including C7, C8, C5, complement factor I, complement factor B, and complement factor H components of the complement system, while P-selectin-expressing particles, CD3+/CD45+, S-MA-α+ circulating exosome levels, and exosome-carrying Cystatin C, Serpin F2, and CD14 levels may be important for assessing CVD risk and mortality. In addition, elevated secretion of eFat-EXO and carriage of high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukins and tumor necrosis factor are targets for AF diagnosis.
Features
-
Advanced Diagnostic Capabilities: Exosomes can be utilized to detect biomarkers associated with CVDs. Their use in diagnosis offers an extremely sensitive, non-invasive technique for early detection.
-
Non-Invasive Sampling: The use of exosomes allows for the analysis of biomarkers through easily accessible body fluids. This lessens discomfort and the necessity for intrusive procedures.
-
High Specificity and Sensitivity: Exosomes can carry a range of molecular signals, which are specific to cardiovascular diseases. This allows for the development of highly specific and sensitive diagnostic assays.
-
Early Detection and Prognosis: Exosome-based diagnostics can identify early changes in cardiovascular health before symptoms appear. This facilitates timely intervention and personalized treatment plans, potentially improving outcomes.
-
Integration with Emerging Technologies: Exosome diagnostics can be integrated with advanced technologies such as machine learning and genomic analyses, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of cardiovascular disease diagnosis.
At Creative Biolabs, our experts keep abreast of the latest developments in exosomes in diagnostic applications and aim to support research on exosomes in CVD diagnostic applications in a multifaceted manner, with our most advanced and comprehensive technology platform. Please contact us to discuss your project.
FAQs
Q: How are exosomes collected for diagnostic purposes?
A: Saliva, urine, and blood are examples of bodily fluids from which exosomes can be isolated. The collection process is non-invasive and involves standard procedures for obtaining these fluids, followed by isolation and analysis of exosomes using specialized techniques.
Q: What advantages do exosome-based diagnostics offer over traditional methods?
A: Exosome-based diagnostics enable early detection of cardiovascular diseases before symptoms manifest and can be integrated with advanced technologies for more accurate results.
Q: Can exosome-based diagnostics be used for all types of cardiovascular diseases?
A: Indeed, a variety of cardiovascular diseases can be diagnosed using exosome-based diagnostics. Research is ongoing to enhance their effectiveness across different types of cardiovascular diseases, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, and hypertension.
Q: Does exosome-based diagnostics have any drawbacks or difficulties?
A: Some challenges include the need for standardized protocols for exosome isolation and analysis, as well as the need for further validation studies to confirm the utility of exosome-based biomarkers.
References
-
Neves, Karla B., et al. "Exosomes and the cardiovascular system: Role in cardiovascular health and disease." The Journal of Physiology 601.22 (2023): 4923-4936.
-
Sahoo, Susmita, et al. "Therapeutic and diagnostic translation of extracellular vesicles in cardiovascular diseases: roadmap to the clinic." Circulation 143.14 (2021): 1426-1449.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Exosomes' role in cardiovascular health and disease.1, 3
Fig.1 Exosomes' role in cardiovascular health and disease.1, 3
 Fig.2 EV diagnostics and various strategies for EV-based therapies.2, 3
Fig.2 EV diagnostics and various strategies for EV-based therapies.2, 3









