Virus Infections Diagnosis-Applied Exosomes
Exosomes are vesicles released after the fusion of multivesicular bodies with the plasma membrane of cells. Carrying functional proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids derived from donor cells, they mediate intercellular communication and play an important role in the pathogenic process of the organism. At present, the research on the mechanism of exosomes in viral infection and the potential markers of exosomes in the diagnosis and treatment of viral infections is still in its infancy. More and more studies are continuously elucidating the mechanism of exosomes in viral infection, especially their role in immune regulation. This provides a research basis for the possibility of exosomes as potential markers for the diagnosis of viral infections and their application prospects. Creative Biolabs can provide the most comprehensive exosome sequencing services, including exosomal proteome sequencing, exosomal whole transcriptome sequencing, exosomal miRNA sequencing, exosomal lncRNA sequencing, exosomal circRNA sequencing, etc., to help you mine the most valuable information in exosomes.
The Role of Exosomes in the Virus Infections
-
Viruses manipulate the exosome synthesis pathway. Viruses that enter cells through endocytosis can use the formation of exosomes to assist in their replication. These viruses can enter the late endosome, which integrates the viral genome into the cytoplasm. Late endosomes eventually form multivesicular bodies (MVBs). After MVB fuses with the cell membrane, it releases its internal intraluminal vesicles (i.e., exosomes) into the extracellular environment. For example, the Gag of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) interacts with transmembrane proteins (CD63 and CD81) to facilitate viral import.
-
Exosomes mediate the transmission and spread of viruses. The material transport of exosomes can lead to virus transmission. Studies have shown that exosomes can package viral mRNA and protein through ubiquitination and ESCRT recruitment mechanisms. The release of these exosomes facilitates further transmission and spread of the virus.
-
Exosomes regulate the host immune system. Exosomes produced by virus-infected cells carry virus-encoded genetic information and can transmit this viral information to immune cells, thereby inducing or inhibiting the host's innate immunity.
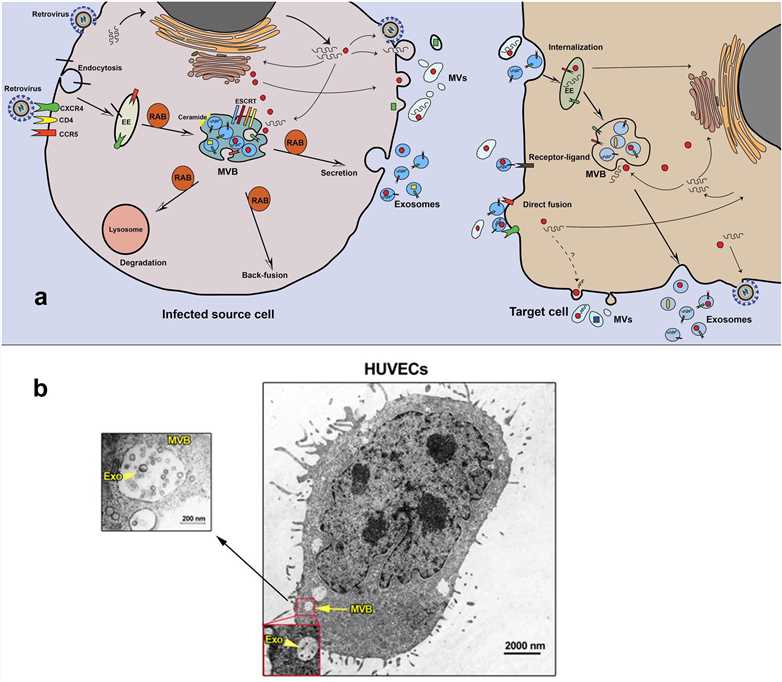 Fig.1 Biogenesis, trafficking, and uptake of exosomes from virus-infected cells.1,2
Fig.1 Biogenesis, trafficking, and uptake of exosomes from virus-infected cells.1,2
Potential of Exosomes as Diagnostic Markers for Viral Infection
Screening and identifying biomarkers that can be used for the diagnosis and prognosis of viral infection will be very beneficial to patients. Exosomes can be widely and stably present in biological fluids, such as blood, urine, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, ascites, amniotic fluid, and even breast milk. Thus, exosomes released from host cells or the immune system can carry a wealth of information about the disease state, which can alter the host's response to viral infection positively or negatively. For example, miRNAs in trophoblast-derived exosomes have been shown to attenuate vaccinia virus replication in recipient cells by inducing autophagy. vmiR99 and vmiR88 in serum exosomes from HIV-1-infected patients have been shown to stimulate signaling pathways in macrophages that lead to the massive secretion of TNFα through activation of endosomal TLR8. Viral components in semen-derived exosomes from patients with reticuloendotheliosis virus (REV) infection can evade REV-specific neutralizing antibodies, contributing to REV impairing the potency of host immune responses. Therefore, the information in exosomes has very good clinical application ability in the early diagnosis and prognosis of viral infection and related diseases.
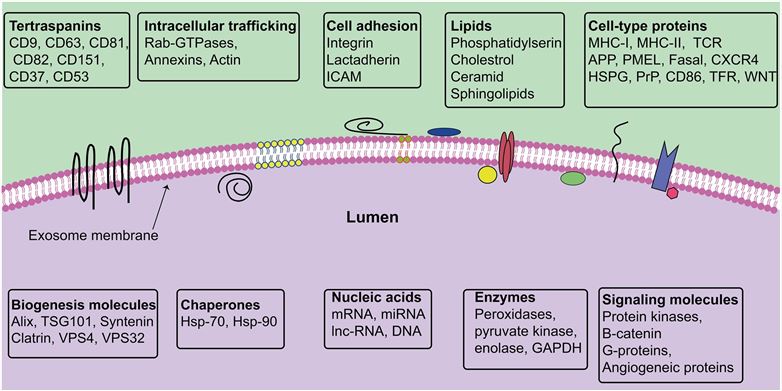 Fig.2 Exosomes contain different types of components both on their surface and lumen and this content can vary widely between cells and conditions.1,2
Fig.2 Exosomes contain different types of components both on their surface and lumen and this content can vary widely between cells and conditions.1,2
At Creative Biolabs, experienced technicians and scientific consultants can provide you with exosome extraction services, exosome identification services, exosome profiling services, and exosome NGS services to help you discover the most potential biomarkers in exosomes for the diagnosis of viral infectious diseases. Please do not hesitate to contact us to formulate the most rigorous experimental plan and provide the most reliable exosome technical services for you.
References
-
Rezaie, J.; et al. The versatile role of exosomes in human retroviral infections: from immunopathogenesis to clinical application. Cell and Bioscience. 2021, 11(1):19.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Biogenesis, trafficking, and uptake of exosomes from virus-infected cells.1,2
Fig.1 Biogenesis, trafficking, and uptake of exosomes from virus-infected cells.1,2
 Fig.2 Exosomes contain different types of components both on their surface and lumen and this content can vary widely between cells and conditions.1,2
Fig.2 Exosomes contain different types of components both on their surface and lumen and this content can vary widely between cells and conditions.1,2









