Extracellular Vesicle Modification Services
Overview Services Features FAQs
Overview
Extracellular Vesicle Engineering
As one of the important media of intercellular communication, extracellular vesicles (EVs) have the characteristics of high stability, strong ability to enter tissue cells, and good biocompatibility, and have inherent advantages in disease treatment. However, native EVs are poorly targeted and easily cleared from circulation. A large number of studies have shown that engineering transformation is expected to improve the targeting and anti-phagocytosis capabilities of EV and enhance the internalization of target cells.
EV engineering strategies mainly include two aspects:
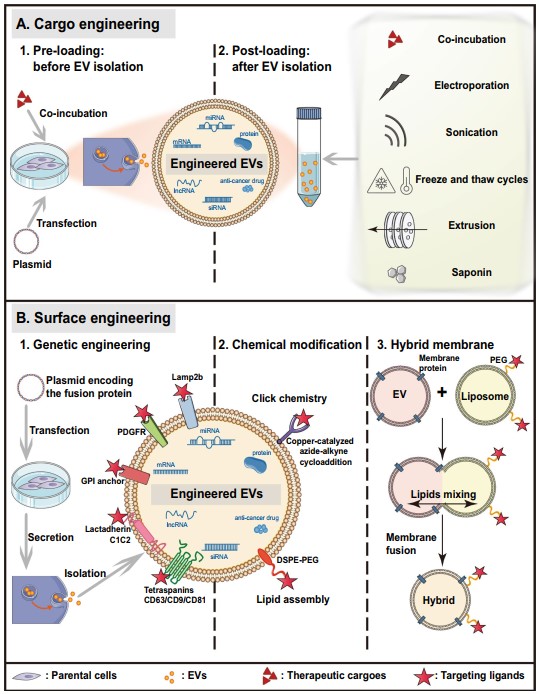 Fig.1 Current technologies for EV bioengineering.1,2
Fig.1 Current technologies for EV bioengineering.1,2
Engineered EV can perform a variety of functions, including targeted delivery of drugs, regulation of specific gene expression, promotion of immune responses, and combination of multiple therapeutic methods, etc., and have broad clinical application prospects.
Creative Biolabs has been paying attention to the research progress of engineered EVs, and has been continuously improving technology and equipment, and is willing to work with customers to develop the therapeutic potential of EV.
Services
Therapeutic Molecular Loading Services for Extracellular Vesicle
We can provide EV loading service to load nucleic acids (including mRNA, miRNA, circRNA, siRNA, etc.), proteins, and drugs into EV. The loading techniques we use include genetic loading and physicochemical loading. Genetic loading refers to the overexpression of therapeutic small molecules in parental cells, relying on the cell's own sorting system to complete the loading. Physicochemical loading refers to the loading of therapeutic small molecules into EVs by physical or chemical means after the isolation and purification of EV.
Surface Modification Services for Extracellular Vesicle
The EV surface modification services we can provide include targeting service (endowing EV tissue or cell targeting, anti-phagocytosis, and internalization capabilities) and labeling service (in vivo or in vitro tracking). The modification techniques we use are divided into the genetic modification and chemical modification. Genetic modification refers to the genetic recombination of parental cells to produce EV with modified peptides or proteins. Chemical modification refers to the modification of functional molecules on the surface of EV by chemical methods after the isolation and purification of EV.
Features
-
Customized Drug Loading Solutions
-
Advanced Surface Modification Techniques
-
High Quality and Purity Assurance
-
Scalable and Reproducible Production
Creative Biolabs has been focusing on the development of cell-free therapy. In addition to EV modification services, we can provide global customers with EV one-stop services including isolation and purification services for EV, characterization and quantification services for EV, EV profiling services, EV manufacturing service, and EV functional research and verification services. If you want to get engineered EV with more comprehensive functions, please contact us. Our professional team will formulate the most rigorous experimental plan for you.
FAQs
Q: How do you ensure the stability of extracellular vesicles after drug loading or surface modification?
A: Clients can choose from various stability tests, including size distribution analysis, zeta potential measurement, and storage condition assessment, to ensure that extracellular vesicles maintain their integrity, functionality, and stability after drug loading or surface modification.
Q: What experiments can you perform to confirm that the target molecule has been successfully modified on the surface of exosomes?
A: Typically, nano-flow cytometry or ELISA is used to detect engineered surface targets on extracellular vesicles, confirming successful surface modification.
Q: How do you handle potential issues with the targeting specificity of modified extracellular vesicles?
A: To address potential issues with targeting specificity, we can conduct thorough in vitro and in vivo testing to evaluate the selectivity of surface-modified extracellular vesicles for the desired target cells or tissues. Based on the test results, we can further refine the modification strategy to enhance targeting specificity and minimize off-target effects.
References
-
Weng, Z.; et al. Therapeutic roles of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in cancer. Journal of Hematology & Oncology. 2021, 14(1):136.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Current technologies for EV bioengineering.1,2
Fig.1 Current technologies for EV bioengineering.1,2









