Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived Exosome Research & Application
Background Workflow Research Progress Support Platform Why Choose Us Testimonials FAQs
Background and Significance
Pediococcus pentosaceus is a Gram-positive lactic acid bacterium widely recognized for its role in fermentation processes that enhance flavor, safety, and nutritional profiles of foods such as vegetables, dairy, and meats. Beyond its contributions to food preservation, an emerging research frontier has revealed that this bacterium can release nanosized extracellular vesicles (EVs), often referred to as exosome-like structures. These vesicles are increasingly studied as mediators of bacterial communication and modulators of host–microbe interactions.
At Creative Biolabs, we have established expertise in supporting the study of exosomes derived from Gram-positive bacteria, including Pediococcus pentosaceus. Our services are tailored to researchers aiming to dissect the biological characteristics, molecular composition, and functional properties of these vesicles. Unlike generic bacterial EV studies, Creative Biolabs places a strong emphasis on reproducible workflows, transparent reporting, and flexible optional add-ons to match the scope of each customer 's research project.
Standardized Workflow for Vesicle Preparation
To investigate Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes, reproducibility in sample preparation is essential. Creative Biolabs employs a core workflow that ensures consistent vesicle isolation. This streamlined protocol forms the foundation of our service portfolio, while additional characterization and molecular profiling remain available as optional extensions, depending on project needs and data library availability.
-
Core Isolation Workflow
-
Culture initiation – Pediococcus pentosaceus is cultured under controlled conditions to ensure optimal vesicle release.
-
Clarification – Culture supernatants are subjected to sequential low-speed centrifugation and filtration to remove cellular debris.
-
Ultracentrifugation – High-speed ultracentrifugation is applied multiple times to pellet vesicular fractions.
-
Resuspension & storage – Vesicles are resuspended in sterile PBS and preserved under frozen conditions to maintain structural integrity.
-
Optional Services (project-dependent)
-
Size distribution analysis (e.g., NTA, DLS)
-
Electron microscopy imaging
-
Proteomic and lipidomic profiling
-
RNA cargo investigation
-
Functional assays in in vitro systems
Creative Biolabs emphasizes that the feasibility of certain advanced assays depends on the availability of validated genomic or proteomic resources for this species.
Research Progress on Pediococcus pentosaceus-Derived Exosomes
|
Study Focus
|
Key Findings
|
|
Physical characterization
|
Vesicles derived from Pediococcus pentosaceus are typically larger than those from Gram-negative bacteria such as E. coli. They display high surface electronegativity, which may influence interactions with host cells.
|
|
Liver fibrosis & vaccine models
|
Experimental models suggest that these vesicles may help reduce hepatic fibrosis. In vaccination studies, they showed the capacity to suppress excessive Th1-driven responses.
|
|
Immune cell modulation
|
In vivo data indicate that the vesicles can promote the differentiation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells, drive macrophages toward an M2-like phenotype, inhibit T-cell activation, and stimulate the expression of anti-inflammatory mediators such as IL-10 and PD-L1.
|
|
Inflammation and wound repair
|
In murine models, vesicle treatment reduced neutrophil infiltration during acute peritonitis, alleviated colitis symptoms, and improved wound healing by enhancing recruitment of regulatory immune cells.
|
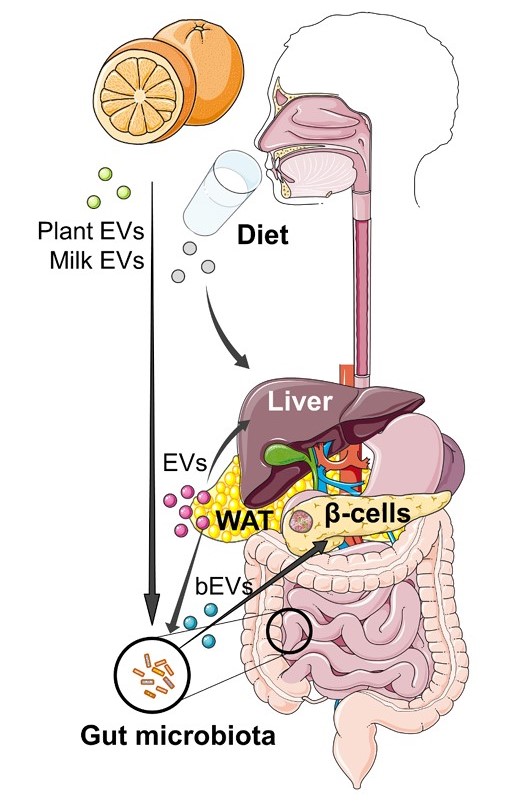 Fig. 1 EVs released by the gut microbiota participate in a multi-directional, inter-kingdom crosstalk.1
Fig. 1 EVs released by the gut microbiota participate in a multi-directional, inter-kingdom crosstalk.1
Research Support Platform at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs has developed a dedicated platform for bacterial exosome research that integrates expertise in microbiology, nanotechnology, and biomolecular characterization. For Pediococcus pentosaceus, our platform is adaptable to diverse research goals:
-
Customized vesicle generation from specific bacterial strains or growth conditions
-
Flexible downstream analyses (optional) such as proteome or metabolome profiling
-
In vitro functional evaluation using immune and epithelial cell models (optional)
-
Comparative studies across Gram-positive vs. Gram-negative vesicles
By leveraging this modular system, Creative Biolabs ensures that every project is aligned with the client 's research scope, budget, and publication goals.
Why Researchers Choose Creative Biolabs
Researchers collaborating with Creative Biolabs consistently highlight several distinguishing advantages:

Scientific depth
A team with extensive expertise in both exosome biology and Gram-positive microbiology.

Transparency
Clear distinction between standard workflows and optional advanced analyses.

Flexibility
Tailored service packages that match early-stage feasibility studies as well as comprehensive characterization projects.

Customer-centered approach
Close communication and adaptability to evolving project requirements.
Voices from the Research Community
"Partnering with Creative Biolabs for bacterial exosome isolation has greatly accelerated our project. Their transparent breakdown of essential workflow versus optional services allowed us to allocate our budget efficiently while ensuring we received reliable, high-quality data."
— Research Scientist, European University
"The Creative Biolabs team showed a deep understanding of both bacterial culture requirements and vesicle biology. Their transparent communication built confidence at every step of the process."
— Principal Investigator, North American Research Institute
These testimonials reflect Creative Biolabs ' dedication to enabling scientific discovery rather than delivering off-the-shelf results.
The study of Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes is still unfolding, yet the available findings point to their relevance in microbial ecology, host–microbe communication, and immunomodulation. At Creative Biolabs, we anticipate that further exploration will clarify how these vesicles can be leveraged in food science, microbiome research, and broader biological studies. By choosing Creative Biolabs as your research partner, you gain access to a structured workflow, optional high-resolution analyses, and a collaborative team dedicated to ensuring that your projects yield meaningful insights. Contact us to discuss your project requirements, and let us support your next step in Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosome research.
FAQs
Q: What are the key functional properties of Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes?
A: Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes have been shown to possess several functional properties, including antimicrobial activity, modulation of immune responses, and enhancing the stability of bioactive compounds. These exosomes can influence gut microbiota composition and contribute to the overall health of host organisms by delivering bioactive molecules.
Q: How can Pediococcus pentosaceus exosomes be utilized in microbial fermentation processes?
A: The exosomes derived from Pediococcus pentosaceus can be utilized in microbial fermentation to enhance probiotic viability and activity. Their ability to encapsulate and transport peptides and metabolites may improve fermentation efficiency and product quality in various food applications, potentially leading to the development of novel functional foods.
Q: What is the significance of studying the cargo of Pediococcus pentosaceus exosomes?
A: Understanding the cargo of Pediococcus pentosaceus exosomes is critical for uncovering their biological roles. The diverse molecules encapsulated can provide insights into intercellular communication, stress responses, and potential biotechnological applications. This knowledge can inform future research on harnessing these exosomes for various industrial applications.
Q: Are there any challenges associated with isolating and characterizing exosomes from Pediococcus pentosaceus?
A: Isolating and characterizing exosomes from Pediococcus pentosaceus presents several challenges, such as ensuring the purity and yield of the exosomes, as well as the need for precise characterization techniques to analyze their size, composition, and functionality. Standardization of these methodologies is necessary for reliable research outcomes.
Q: How does the study of Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes contribute to the field of microbiome research?
A: Research on Pediococcus pentosaceus-derived exosomes contributes significantly to the understanding of the gut microbiome by providing insights into microbial interactions and their ecological roles. These exosomes may mediate beneficial effects on the host 's health and help decipher the complex relationships within the microbiome, paving the way for innovative strategies in microbial ecology.
Q: What are the potential avenues for future research on Pediococcus pentosaceus exosomes?
A: Future studies may aim to clarify how exosomal components influence host cell function, examine their contribution to stress tolerance and environmental adaptation, and explore applications in agriculture and food biotechnology. There is also growing interest in engineering these exosomes to enhance or tailor their properties for innovative uses.
Reference
-
Castaño, Carlos et al. "An Overview of Inter-Tissue and Inter-Kingdom Communication Mediated by Extracellular Vesicles in the Regulation of Mammalian Metabolism." International journal of molecular sciences vol. 24,3 2071. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24032071
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 EVs released by the gut microbiota participate in a multi-directional, inter-kingdom crosstalk.1
Fig. 1 EVs released by the gut microbiota participate in a multi-directional, inter-kingdom crosstalk.1













