Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived Exosome Research & Application
Background Isolation Research Insights Platform Advantages Testimonials FAQs
Scientific Background
Propionibacterium freudenreichii is a Gram-positive bacterium widely recognized for its probiotic properties and key role in food fermentation, particularly in dairy products such as Swiss-type cheeses. As a commensal organism in the human gastrointestinal tract, it contributes to the balance of gut microbiota and the maintenance of intestinal homeostasis. In addition to its fermentation-related applications, P. freudenreichii has attracted attention for the exosome-like vesicles it produces.
Recent research demonstrates that exosomes from P. freudenreichii carry a complex cargo of proteins capable of modulating immune pathways, interacting with host cells, and regulating inflammatory responses. While much of this research is preclinical and mechanistic in nature, it offers an exciting framework for understanding microbial-host interactions. Creative Biolabs utilizes our knowledge of bacterial exosomes to offer customized services for researchers studying vesicles derived from P. freudenreichii, highlighting stringent workflows, reproducibility, and optional advanced analyses.
Isolation Workflow for P. freudenreichii Vesicles
Creative Biolabs has designed a core workflow to generate high-quality exosomes from P. freudenreichii, focusing on reproducibility and scalability. All optional analyses, such as molecular profiling or detailed characterization, are performed upon request and depend on the availability of validated strain-specific libraries.
-
Standard Isolation Process
-
Cultivation – P. freudenreichii is grown under defined liquid culture conditions until reaching stationary phase to maximize exosome release.
-
Clarification – Cultures are centrifuged to remove bacterial cells, and the supernatant is carefully collected.
-
Filtration – Sequential filtration removes residual bacteria and large debris.
-
Concentration – Ultrafiltration is applied to concentrate vesicles from the culture supernatant.
-
Exosome Recovery – Vesicles are recovered into TBS buffer via serial ultracentrifugation steps.
-
Optional Purification – Size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) can be employed to further purify vesicles and eliminate protein contaminants.
-
Optional Add-Ons (project-dependent)
-
Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) for size distribution
-
Electron microscopy imaging for morphological assessment
-
Proteomic and metabolomic profiling of exosome cargo
-
Functional assays in cell culture systems
Creative Biolabs ' workflow ensures that all core isolation steps are standardized while providing flexibility for more in-depth investigations as required by research objectives.
Insights from Research on P. freudenreichii-Derived Exosomes
Scientific studies highlight several notable features of P. freudenreichii-derived exosomes, particularly their roles in immunomodulation and inflammation regulation. The following table summarizes key research findings reported by independent investigators:
|
Research Focus
|
Summary of Findings
|
|
Protein Cargo Analysis
|
MS studies revealed that P. freudenreichii exosomes carry a diverse set of proteins. Abundant immunomodulatory proteins include Surface layer protein SlpB, enolase 1, iron/manganese superoxide dismutase, and malate dehydrogenase. These proteins potentially contribute to host–microbe signaling.
|
|
Regulation of NF-κB Pathway
|
In vitro models using lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human intestinal epithelial cells showed dose-dependent inhibition of NF-κB activation, leading to attenuation of pro-inflammatory responses. IL-8 levels were reduced to baseline without cytotoxic effects, demonstrating regulatory activity rather than cell damage.
|
|
Role of Surface Layer Proteins
|
Comparative studies with mutant strains indicate that SlpB is a major effector mediating anti-inflammatory activity, although other vesicle components may also participate in regulating NF-κB signaling.
|
|
Applications in Microbial Ecology and Food Processing
|
Vesicles reflect the probiotic properties of their parent strain and may influence gut microbiota composition. Additionally, P. freudenreichii-derived vesicles may play a role in flavor modulation and biochemical processes during cheese maturation.
|
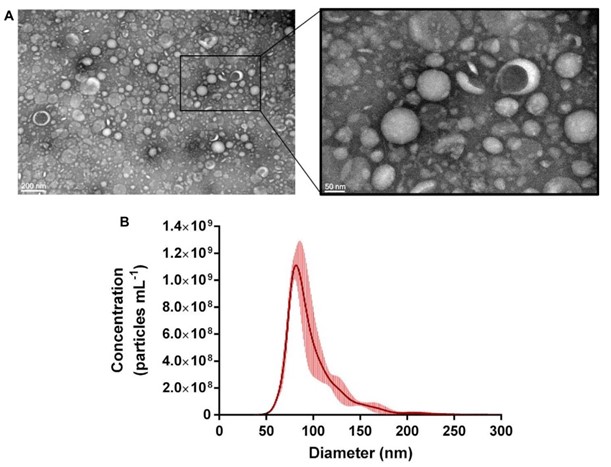 Fig.1 Characterization of the morphology and size for Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes.1
Fig.1 Characterization of the morphology and size for Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes.1
Creative Biolabs Research Support Platform
Creative Biolabs has developed a specialized platform that integrates microbiology, nanotechnology, and bioanalytical techniques to support research on P. freudenreichii-derived exosomes. Key components of this platform include:
Custom Exosome Production
Vesicle generation tailored to specific strains, culture conditions, or research objectives.
Flexible Downstream Analyses (Optional)
Proteomics, metabolomics, RNA content analysis, or lipidomic profiling can be incorporated depending on library availability and research goals.
Functional Assessment in Cell Models (Optional)
Immune or epithelial cell assays to explore immunomodulatory or anti-inflammatory properties.
Comparative Vesicle Studies
Enable side-by-side evaluation of exosomes from different Gram-positive species to understand unique functional profiles.
This modular platform allows Creative Biolabs to provide research-grade vesicles with consistent quality and traceability while accommodating varying project requirements.
Advantages of Collaborating with Creative Biolabs

Technical Expertise
Deep experience in Gram-positive bacterial vesicle biology and standardized isolation protocols.

Reproducibility
Strict quality control across all stages of vesicle preparation ensures consistent results.

Customizability
Flexible packages allow adaptation to early-stage feasibility studies or comprehensive characterization projects.

Collaborative Support
Dedicated scientific support for project design, troubleshooting, and data interpretation.
Creative Biolabs ' approach combines technical rigor with flexibility, enabling researchers to obtain vesicles suited to their specific experimental needs while retaining control over downstream analyses.
Testimonials from Scientific Collaborators
Creative Biolabs has worked with numerous academic and industrial research teams, who consistently emphasize our reliability and professionalism:
"Creative Biolabs provided high-quality Propionibacterium freudenreichii vesicles for our inflammation assays. Their clear workflow and optional characterization services allowed us to focus on hypothesis-driven experiments without concerns about variability."
— Senior Scientist, USA
"The Creative Biolabs team possesses a strong grasp of bacterial exosome biology. Their guidance on optional analyses helped us plan a cost-effective study while obtaining reproducible and meaningful data."
— Senior Scientist, Canada
The study of P. freudenreichii-derived exosomes remains in a rapidly evolving stage. Current evidence points to their potential as mediators of host–microbe communication, modulators of intestinal immune responses, and contributors to food fermentation dynamics. Creative Biolabs anticipates that ongoing research will expand understanding of these vesicles ' molecular cargo and functional roles, offering opportunities for mechanistic exploration and novel applications in microbial ecology studies. By utilizing Creative Biolabs' platform, researchers benefit from a well-organized workflow, optional advanced analyses, and scientific consultation, enhancing your projects for dependable and insightful outcomes. Contact us with your interest.
FAQs
Q: What are the primary functions of exosomes derived from Propionibacterium freudenreichii?
A: Exosomes from Propionibacterium freudenreichii play a significant role in intercellular communication. They are known to carry bioactive molecules such as proteins, lipids, and RNA that can influence recipient cells. Research indicates these exosomes may modulate immune responses, enhance gut barrier function, and influence microbiota composition.
Q: How do Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes interact with the gut microbiome?
A: These exosomes can facilitate communication among gut microbial communities by transferring genetic material and proteins that may alter microbial behavior and composition. This interaction has implications for gut health, as it may promote beneficial microbial populations and suppress pathogenic ones.
Q: What are the potential applications of Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes in biotechnology?
A: The unique properties of these exosomes make them valuable in various biotechnological applications, such as natural preservatives in food products, enhancers of probiotic efficacy, and vehicles for targeted delivery of bioactive compounds. Their ability to interact positively with host cells opens avenues for developing functional foods and dietary supplements.
Q: What are some of the challenges researchers face when studying exosomes from Propionibacterium freudenreichii?
A: Challenges include the complexity of isolating pure exosomal populations from bacterial cultures, the need for standardized characterization protocols, and the difficulties in elucidating the specific functional roles of exosomes within complex biological systems. Additionally, understanding the stability and bioavailability of these exosomes in diverse environments remains a crucial challenge.
Q: How can exosomes from Propionibacterium freudenreichii contribute to the development of new food technologies?
A: The exosomes are being investigated for their potential roles as natural emulsifiers, flavor enhancers, and preservative agents. Their incorporation into food matrices could improve nutritional profiles, enhance safety by inhibiting pathogenic bacteria, and provide interactive benefits that foster a healthy gut microbiome.
Q: Are there any known signaling pathways influenced by Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes in recipient cells?
A: Preliminary studies suggest that these exosomes can modulate signaling pathways related to inflammation, oxidative stress, and cellular proliferation. Further research is needed to delineate specific receptors and pathways involved in the biological responses elicited by these exosomes.
Q: What future research directions are being considered in the study of Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes?
A: Future research is likely to focus on the detailed mechanisms of action of these exosomes, their role in host-microbe interactions, and their stability and efficacy in food applications. Additionally, exploring their potential use in agricultural settings to improve soil health and crop resilience is a promising area of investigation.
Reference
-
Rodovalho, Vinícius de Rezende et al. "Extracellular Vesicles Produced by the Probiotic Propionibacterium freudenreichii CIRM-BIA 129 Mitigate Inflammation by Modulating the NF-κB Pathway." Frontiers in microbiology vol. 11 1544. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01544
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Characterization of the morphology and size for Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes.1
Fig.1 Characterization of the morphology and size for Propionibacterium freudenreichii-derived exosomes.1













