Ultra-sensitive Targeted Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service
Overview Services Features FAQs
Creative Biolabs provides a highly sensitive exosomal proteomic detection service that combines the precision of immunoassays with the high throughput of nucleic acid technologies, enabling the identification of thousands of proteins from minimal exosomal samples.
Overview of Advanced Exosomal Proteomic Detection
-
Traditional Proteomics Methods
Common proteomics techniques such as bidirectional gel electrophoresis, protein/antibody microarrays, and mass spectrometry have their limitations, including detection speed, throughput, multiplex detection capability, and sensitivity. These factors often restrict the effectiveness of obtaining comprehensive information on complex and large proteomes.
-
Challenges with Traditional Exosome Proteomics
To detect and measure known and unknown proteins in exosomes, mass spectrometry is commonly employed. However, it faces challenges in detecting low-abundance exosomal proteins. Additionally, protein profiling using mass spectrometry is time-consuming and relies heavily on expert data analysis, which can slow down progress in exosome proteomics.
-
Introduction to Advanced Detection Technology
We offer an advanced exosomal proteomic detection service using cutting-edge technology that combines high specificity and sensitivity with high-throughput capabilities.
Ultra-sensitive Targeted Exosomal Proteomic Detection Service
Our service offers rapid, high-throughput, and precise detection of targeted exosomal proteins. We provide a dedicated inflammation panel and other specialized panels for various applications, including immuno-oncology markers such as PD-L1, CD27, and Gal-9. This enhances the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of cytokine research and helps explore the relationship between exosomes, inflammation, and immunity.
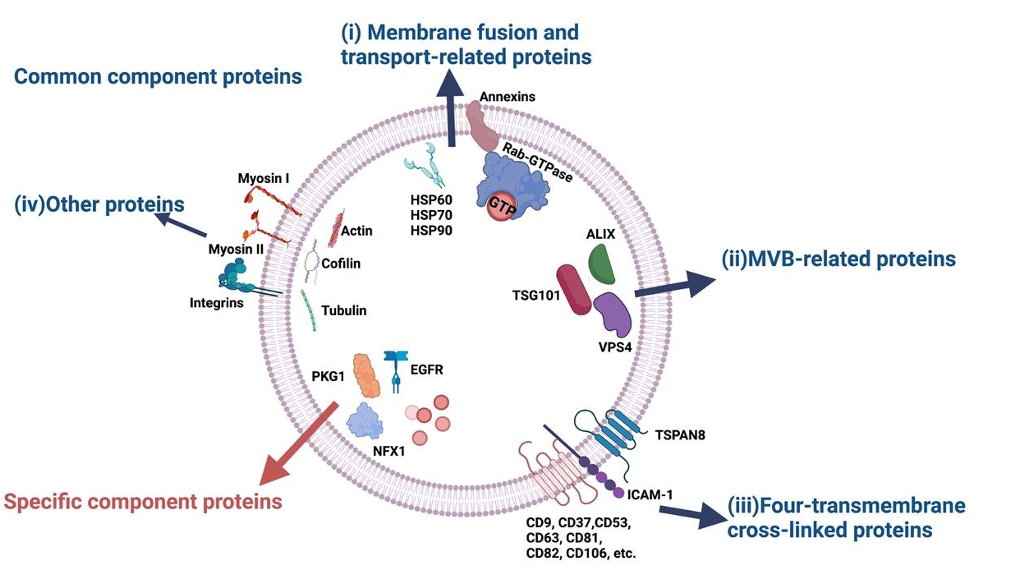 Fig.1 Common component proteins and specific component proteins.1
Fig.1 Common component proteins and specific component proteins.1
Features
-
Targeted detection and quantification of specific proteins within exosomes
-
High specificity and sensitivity for protein detection
-
Multiple protein targets found in a single sample
-
Minimal sample volume required
-
Reliable and precise results for enhanced research outcomes
FAQs
Q: What is the typical turnaround time for results?
A: Results are generally available within 8-12 weeks, depending on the complexity of the analysis and the specific requirements of the proteomic panel. For more expedited services, please contact us to discuss potential options.
Q: Can the protein panel be customized?
A: Yes, we offer customizable options to target specific proteins based on your research needs. Please provide a list of the proteins or biomarkers you are interested in, and our team will work with you to develop a tailored panel that meets your requirements.
Q: What is the minimum sample volume required for the analysis?
A: Our advanced detection technology requires a minimal sample volume of 1-10 µL. This allows for highly sensitive detection while conserving precious sample resources.
Q: How can you guarantee the outcomes' dependability and accuracy?
A: To guarantee the precision and dependability of our findings, we employ cutting edge technology together with strict quality control procedures. Each sample undergoes multiple validation steps, and we adhere to industry standards for proteomic analysis.
Q: Can you detect both known and unknown proteins in exosomes?
A: Our technology is designed to detect both known and unknown proteins with high sensitivity. For known proteins, we provide targeted detection, while for unknown proteins, we use advanced analytical methods to explore novel proteomic profiles.
Q: Are there any sample preparation requirements?
A: Yes, samples should be prepared according to our guidelines to ensure optimal results. We provide detailed sample preparation instructions upon request, or you can contact our technical support team for assistance.
Creative Biolabs offers precise detection of thousands of proteins using just 1-10 µL of sample, covering all major signaling pathways for highly sensitive exosomal protein analysis. Please contact us to learn more.
Reference
-
Li, Xin-Xin, et al. "The roles of exosomal proteins: classification, function, and applications." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24.4 (2023): 3061. Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Common component proteins and specific component proteins.1
Fig.1 Common component proteins and specific component proteins.1









