Methylation is a common form of protein post-translational modification (PTM) and frequently occurs on histones. The methylation of histones affects chromosome structure and the binding of other proteins, playing a critical role in the regulation of physiological and pathological processes. As research progresses, the role of methylation modifications in epigenetic regulation is gradually being revealed. Based on our excellent hybridoma technique and phage display technique, Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive services to support the development of methylation-specific antibodies.
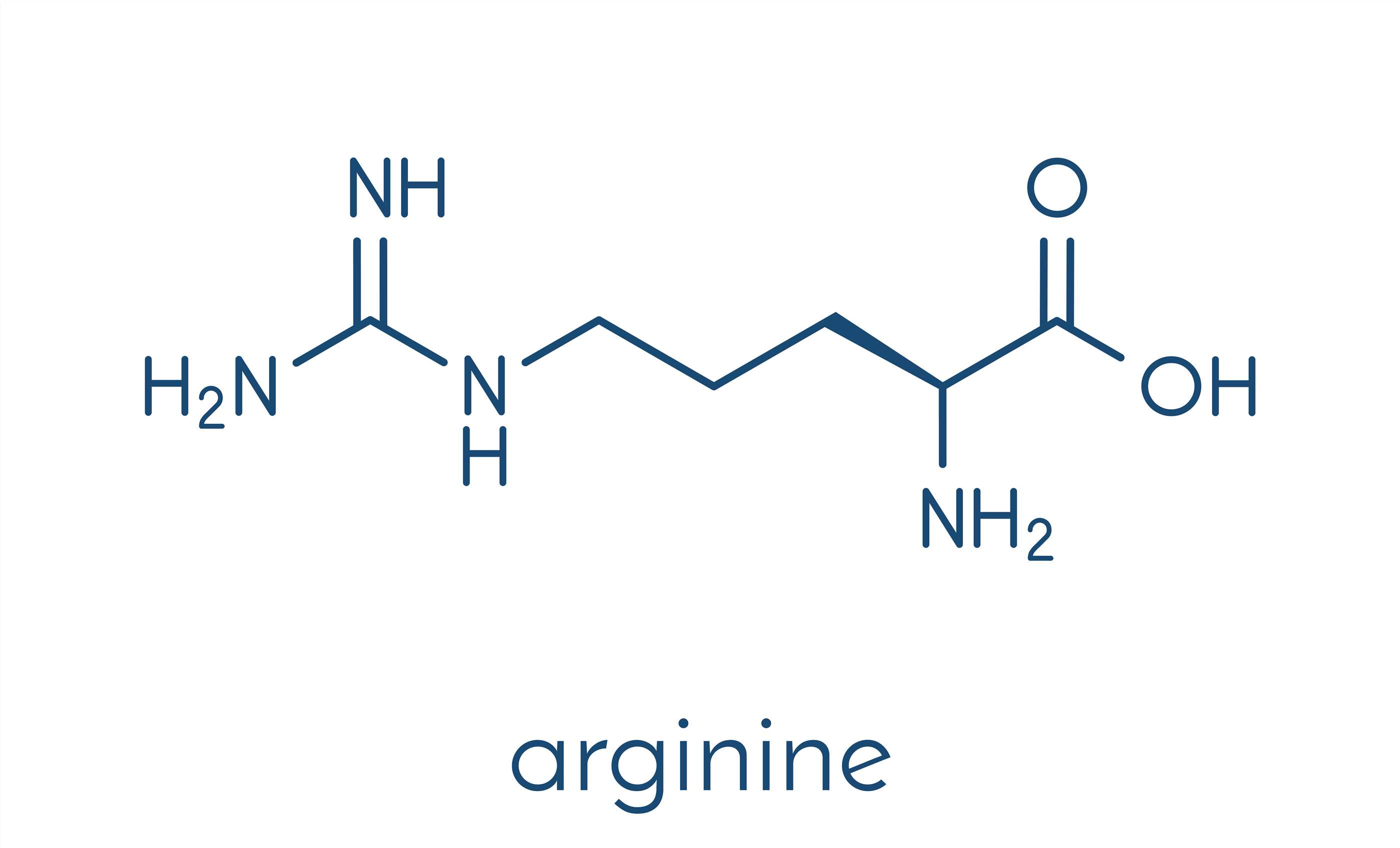
Protein methylation is the enzymatic transfer of a methyl group to a residue in a protein, usually lysine or arginine but also histidine, cysteine, and asparagine. Methylation of proteins is a common modification. Studies on rats have shown that about 2% of total protein extracts from rat hepatocyte nuclei were dimethylated with arginine residues.
Current studies have found that protein methylation regulates interactions within or between target protein molecules and affects their affinity with RNA, thereby, influencing various cellular processes such as cellular localization, transcriptional regulation, ribosome assembly, and RNA processing. Protein methylation is closely related to many diseases, including cancer, aging, and Alzheimer's disease, making it an important focus in epigenetics research.
Among the methylation of various proteins, histone methylation has been most intensively studied. Histone methylation refers to methylation that occurs at the N-terminal arginine and lysine residues of H3 and H4 histones, mediated and catalyzed by histone methyltransferases. There are two modes of arginine methylation: mono- and bi-methylation, while bi-methylation can be divided into asymmetric methylation and symmetric methylation. There are three modes of lysine methylation: mono-, di-, or trimethylation. The functions of histone methylation mainly include heterochromatin formation, gene imprinting, X chromosome inactivation, and transcriptional regulation. The majority of histones undergo reversible covalent modifications and can be demethylated in the presence of histone demethylases.
Commonly used methods to study methylation include chromatin immunoprecipitation, western blotting, protein microarrays and other techniques, all of which require the use of methylation-specific antibodies. However, similar to PTM specific antibodies, the development of methylation-specific antibodies is not an easy task. Several factors can affect the development of methylation-specific antibodies, and failure to address all aspects of the process can easily lead to experimental failure. The collection of methylated peptides or proteins is also a crucial step in the development of methylation-specific antibodies. Generally, peptides or proteins containing methylated components in protease digested samples can be enriched using methylated arginine or methylated lysine antibodies to identify methylated arginine and methylated lysine residues, respectively. Once the methylation-specific antibody is obtained, it needs to be specifically tested to ensure that it recognizes the intended target and can be successfully used in subsequent experiments. The specificity and sensitivity of the antibodies can generally be confirmed using peptide containment assays, peptide arrays, and other methods.
Creative Biolabs has a wealth of knowledge about PTM-specific antibody discovery. We would be happy to discuss our knowledge and experience in methylation-specific antibody development with you.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.