AAV is a kind of single-stranded DNA, nonenveloped virus. It replicates with the help of helper virus only, for example, herpes simplex virus or adenovirus. AAV vectors have broad potential for therapeutic gene delivery. Besides, AAVs also possess the ability to stimulate homologous recombination in cells at high efficiency. The above process was referred to as AAV-mediated gene targeting, resulting in the introduction of a diverse array of genomic modifications both in vivo and in vitro.
Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive B cell engineering services to help you achieve your project target. For more technologies about B cell engineering, please inquire our One-Stop Solution for B Cell Engineering.
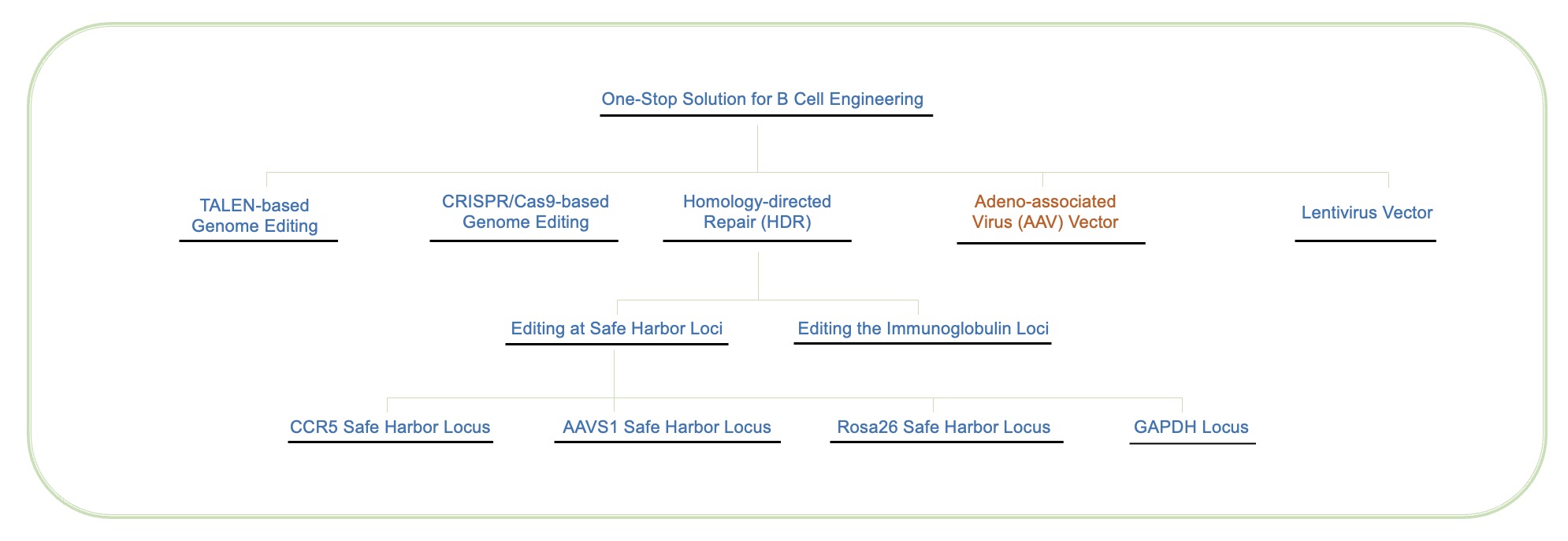 Fig.2 Our one-stop solution for B cell engineering. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.2 Our one-stop solution for B cell engineering. (Creative Biolabs)
Creative Biolabs provides AAV vector method to help you engineer B cells for specific cell therapy needs.
Nonhomologous Integration of AAV into the Cell Genome
AAV-Mediated Gene Targeting
AAV vectors containing DNA sequences homologous to a specific chromosomal site can be recombined with the matching genomic locus. By modifying the DNA sequence between the homology arms, targeted modifications can be introduced into the host genome.
Combining AAV with Targeted Nucleases
Nonhomologous Integration of AAV into the Cell Genome
Paper Title: Engineering AAV vectors to evade innate immune and inflammatory responses
Technology: AAV Vector
Journal: Science Translational Medicine SCI TRANSL MED
IF: 19.319
Published: 2021
Background: AAV vectors are frequently used in gene therapy, but they trigger an immune response through Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9), a receptor that senses foreign DNA. This article incorporated short noncoding DNA sequences into the AAV genome to directly antagonize TLR9 activation and "cloak" the much larger AAV DNA sequence from detection.
Results: In mice and pigs, administration of these modified AAV vectors resulted in reduced innate immune and T cell activation with improved gene expression. In macaques, the modified vector is delayed. However, it did not fully prevent the development of uveitis. The success of AAV-based gene therapies may improve due to the incorporation of these cloaking sequences.
As a highly promising gene delivery vector, AAV has low immunogenicity and ability to mediate persistent gene expression in nondividing cells. Its efficacy has been evidenced in many clinical diseases:
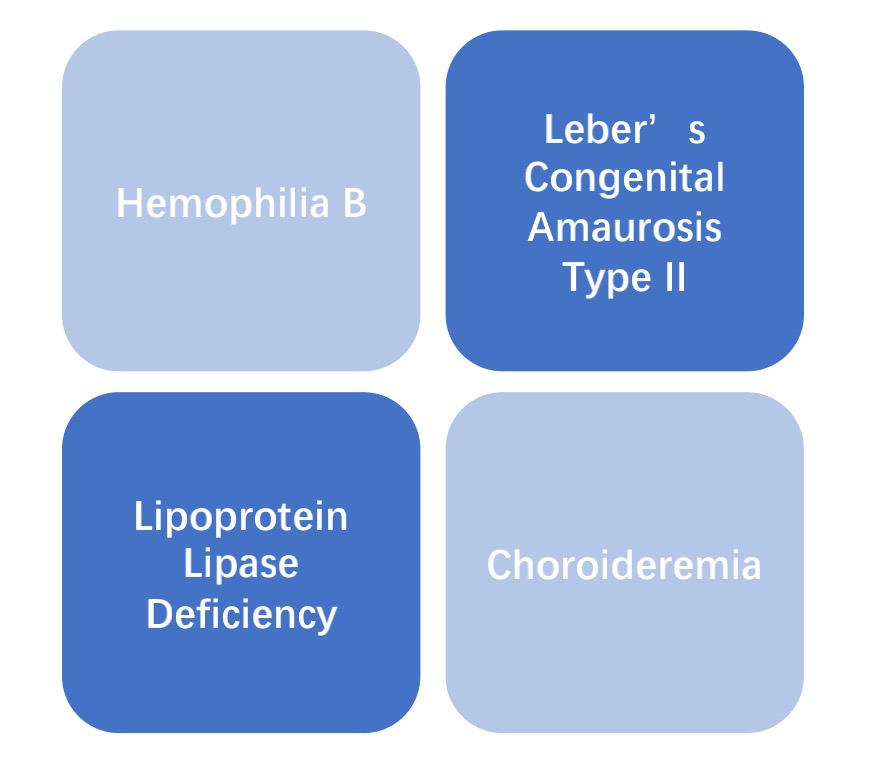 Fig.6 The application of AAV in diseases. (Creative Biolabs)
Fig.6 The application of AAV in diseases. (Creative Biolabs)
We offer professional consultation guidance before, during and after the project, please contact us for your tailored solution.