During drug development, biochemical assay kits are used to study the pharmacokinetics of drugs, which involves measuring the drug's absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion in the body. By measuring drug levels in different biological samples such as blood, urine, and tissues, researchers can determine the drug's half-life, clearance rate, and bioavailability, which are crucial parameters for optimizing drug dosing and formulation.
Biochemical Assay Kits
In the ever-evolving landscape of biological and medical research, biochemical assay kits have emerged as indispensable assets. These meticulously crafted kits empower scientists to probe the molecular intricacies of life with unparalleled accuracy and efficiency. Whether your quest is to unravel metabolic pathways or identify potential drug candidates, biochemical assay kits deliver the reliable data necessary for informed decision-making and the advancement of scientific knowledge.
Core Principles
Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions
Many kits harness the power of enzymes. Enzymes can accelerate specific chemical reactions, converting substrates into products at a rapid pace. For example, in a glucose assay kit, the enzyme glucose oxidase reacts with glucose in the sample, producing hydrogen peroxide. This hydrogen peroxide then reacts with another reagent in the kit, generating a measurable color change. The intensity of the color is directly proportional to the amount of glucose present, allowing for accurate quantification.
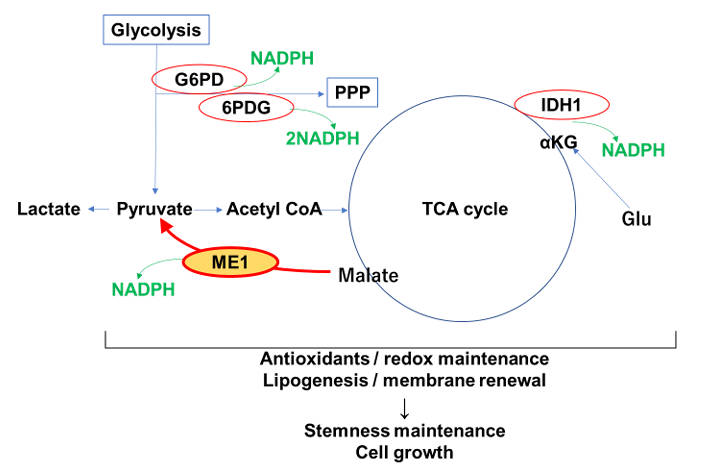 Fig.1 Role of ME1 in production of NADPH.1
Fig.1 Role of ME1 in production of NADPH.1
Antibody - Antigen Interactions
Immunological-based assay kits rely on the highly specific binding between antibodies and antigens. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system to recognize and neutralize foreign substances. In these kits, antibodies are labeled with a detectable marker, such as a fluorescent dye or an enzyme. When the labeled antibody binds to its specific antigen in the sample, the marker can be detected, enabling the quantification of the antigen. This principle is widely used in assays for detecting proteins, hormones, and infectious agents.
Applications
Pharmacokinetic Studies
Cellular Signaling Pathways
Biochemical assay kits are essential tools for studying cellular signaling pathways. For example, kits can be used to measure the activity of kinases, enzymes that play a key role in transmitting signals within cells. By measuring kinase activity under different experimental conditions, researchers can gain insights into how cells respond to various stimuli, such as growth factors or hormones, and how these signaling pathways are involved in diseases like cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
Protein-Protein Interactions
Understanding protein-protein interactions is fundamental to understanding cellular function. Biochemical assay kits can be used to detect and quantify these interactions. For instance, immunoprecipitation kits can be used to isolate protein complexes from cell lysates, followed by western blotting or mass spectrometry to identify the interacting proteins. This helps in mapping protein-protein interaction networks and discovering new therapeutic targets.
Metabolomics Research
Metabolomics is the study of all the small molecules in a biological system. Biochemical assay kits are used to measure the levels of various metabolites in biological samples such as blood, urine, and tissues. By analyzing changes in metabolite levels under different physiological or pathological conditions, researchers can gain insights into metabolic pathways and identify potential biomarkers for diseases.
Unrivaled Advantages
Precision and Accuracy
Biochemical assay kits are designed and manufactured to the highest standards, ensuring precise and accurate results. The use of standardized reagents and protocols minimizes variability, allowing for reliable comparisons between samples and experiments.
Time–Efficiency
With their simplified workflow and pre-packaged reagents, biochemical assay kits can significantly reduce the time required for sample analysis. This is especially important in high-throughput settings, where a large number of samples need to be processed quickly.
Cost–Effectiveness
Compared to traditional biochemical assays that require extensive reagent preparation and specialized equipment, biochemical assay kits offer a cost-effective solution. They eliminate the need for expensive reagents and reduce the risk of wasted samples due to errors, saving you money in the long run.
User–Friendly
Biochemical assay kits are designed with the user in mind. They come with clear and detailed instructions, making them easy to use even for researchers with limited experience in biochemical assays.
FAQs
-
Can I use biochemical assay kits with samples from different species?
Some biochemical assay kits are species-specific, while others can be used with samples from multiple species. It's important to check the kit's instructions or consult with the manufacturer to determine if the kit is suitable for your sample type. In some cases, minor modifications to the protocol may be required when using samples from different species.
-
What should I do if I get unexpected results with a biochemical assay kit?
If you encounter unexpected results, first double-check that you followed the kit's instructions correctly. Ensure that the sample was prepared properly and that the reagents were added in the correct order and amounts.
Biochemical assay kits are the cornerstone of modern molecular analysis. With their precise principles, streamlined workflow, diverse applications, and unbeatable advantages, these kits are empowering researchers and clinicians around the world to make groundbreaking discoveries and improve human health. Choose biochemical assay kits and unlock the full potential of your research and diagnostic endeavors.
Reference
- Fujiwara-Tani, Rina, et al. "Significance of Malic Enzyme 1 in Cancer: A Review." Current Issues in Molecular Biology 47.2 (2025): 83. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb47020083
Product list
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Sphingomyelin Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL1)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: Assay Kit
- Analyte: Sphingomyelin
- Target Source: Serum, plasma, other biological samples
- Species Reactivity: All
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Sphingomyelin Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL1)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL2)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: Assay Kit
- Analyte: AMPK Phosphorylation
- Target Source: Cells
- Species Reactivity: Human, mouse, rat
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL2)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Custom Cell-Based ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL3)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: ELISA Kit
- Analyte: Custom Cell-Based
- Target Source: Cells
- Species Reactivity: human, mouse, rat and more
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Custom Cell-Based ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL3)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
ERK Phosphorylation Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL4)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: Assay Kit
- Analyte: ERK Phosphorylation
- Target Source: Cells
- Species Reactivity: Human, mouse, rat
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
ERK Phosphorylation Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL4)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human SHP2 (Y542) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL5)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: ELISA Kit
- Analyte: Human SHP2 (Y542) Phosphorylation
- Target Source: Cells
- Species Reactivity: human
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human SHP2 (Y542) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL5)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse 4EBP1(S65) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL6)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: ELISA Kit
- Analyte: Human/Mouse 4EBP1(S65) Phosphorylation
- Target Source: Cells
- Species Reactivity: human
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse 4EBP1(S65) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL6)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse AKT1(S473) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL7)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: ELISA Kit
- Analyte: Human/Mouse AKT1(S473) Phosphorylation
- Target Source: Cells
- Species Reactivity: human, rat, mouse
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse AKT1(S473) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL7)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse GSK3A(S21) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL8)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: ELISA Kit
- Analyte: Human/Mouse GSK3A(S21) Phosphorylation
- Target Source: Cells
- Species Reactivity: human, rat, mouse, canine
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse GSK3A(S21) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL8)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse GSK3B(S9) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL9)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: ELISA Kit
- Analyte: Human/Mouse GSK3B(S9) Phosphorylation
- Target Source: Cells
- Species Reactivity: human, rat, mouse
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse GSK3B(S9) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL9)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse LKB1(S431) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL10)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: ELISA Kit
- Analyte: Human/Mouse LKB1(S431) Phosphorylation
- Target Source: Cells
- Species Reactivity: human, mouse, rat
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse LKB1(S431) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL10)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse RB(T821/826) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL11)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: ELISA Kit
- Analyte: Human/Mouse RB(T821/826) Phosphorylation
- Target Source: Cells
- Species Reactivity: human, rat, mouse
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse RB(T821/826) Phosphorylation ELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL11)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse RPS6(S235/236) PhosphorylationELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL12)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: ELISA Kit
- Analyte: Human/Mouse RPS6(S235/236) Phosphorylation
- Target Source: Cells
- Species Reactivity: human, rat, mouse
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Human/Mouse RPS6(S235/236) PhosphorylationELISA Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL12)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
NFKB Phosphorylation Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL13)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: Assay Kit
- Analyte: NFKB Phosphorylation
- Target Source: Cells
- Species Reactivity: Human, mouse
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
NFKB Phosphorylation Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL13)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Glycolysis Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL14)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: Assay Kit
- Analyte: Glycolysis
- Species Reactivity: All
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Glycolysis Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL14)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Screening Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL15)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: Screening Kit
- Analyte: Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor
- Species Reactivity: All
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Screening Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL15)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor Screening Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL16)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: Screening Kit
- Analyte: Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor
- Species Reactivity: All
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor Screening Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL16)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Farnesyltransferase Inhibitor Screening Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL17)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: Screening Kit
- Analyte: Farnesyltransferase Inhibitor
- Species Reactivity: All
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Farnesyltransferase Inhibitor Screening Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL17)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
MMP-1 Inhibitor Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL18)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: Assay Kit
- Analyte: MMP-1 Inhibitor
- Species Reactivity: Human
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
MMP-1 Inhibitor Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL18)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
MMP-9 Inhibitor Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL19)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: Assay Kit
- Analyte: MMP-9 Inhibitor
- Species Reactivity: Human
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
MMP-9 Inhibitor Assay Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL19)
-
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor Screening Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL20)
- Tag: Biochemical Assay Kit
- Subcategory: Screening Kit
- Analyte: Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor
- Species Reactivity: All
-
Biochemical Assay Kit
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor Screening Kit (CAT#: Z01MM2-JL20)
For Research Use Only.