Aptamers have been used in a wide range of applications, including disease diagnosis, targeted delivery agents, and therapeutic uses. Creative Biolabs makes full use of our specialized libraries, selection strategies, and aptamer maturation techniques to optimize aptamer stability and performance. Specialized techniques are used to select aptamers for specific downstream applications. With advanced technologies and experienced staff, Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive set of aptamer-related services for global clients to support their research use.
Aptamer Introduction
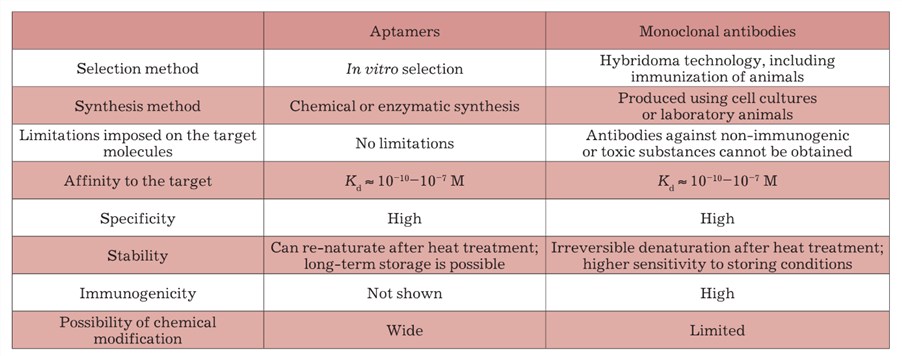
Aptamers are short single-stranded nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) that selectively bind to specific targets including peptides, proteins, and small molecules. Aptamers recognize and bind targets by a 3-dimensional (3D) structure. Since they are chemically synthesized, the process can simply be scaled-up, there are low batch-to-batch variation and high stability. Besides, the production of the aptamer is fast and cost-effective. Aptamers are highly safe biomaterials with no reported in vivo immunogenicity. The specific differences between aptamer and monoclonal antibody (mAb) are shown in the following table.
Table 1 Differences between aptamers and mAb. (Davydova, 2011)
Aptamer Discovery Technology
Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX) is a combinatorial chemistry technique for producing aptamers that specifically bind to a target ligand. The technology was first introduced in 1990 and various aptamers have been developed through this method. The aptamers are selected through an iterative process consisting of binding the target with a highly diverse oligonucleotides library, washing unbound aptamer, and amplification of survived oligonucleotides. Multiple rounds of SELEX enhance the enrichment of the oligonucleotides with high specificity for their targets. The best aptamer clones will be selected after sequencing analysis and affinity assay with enriched oligonucleotides.
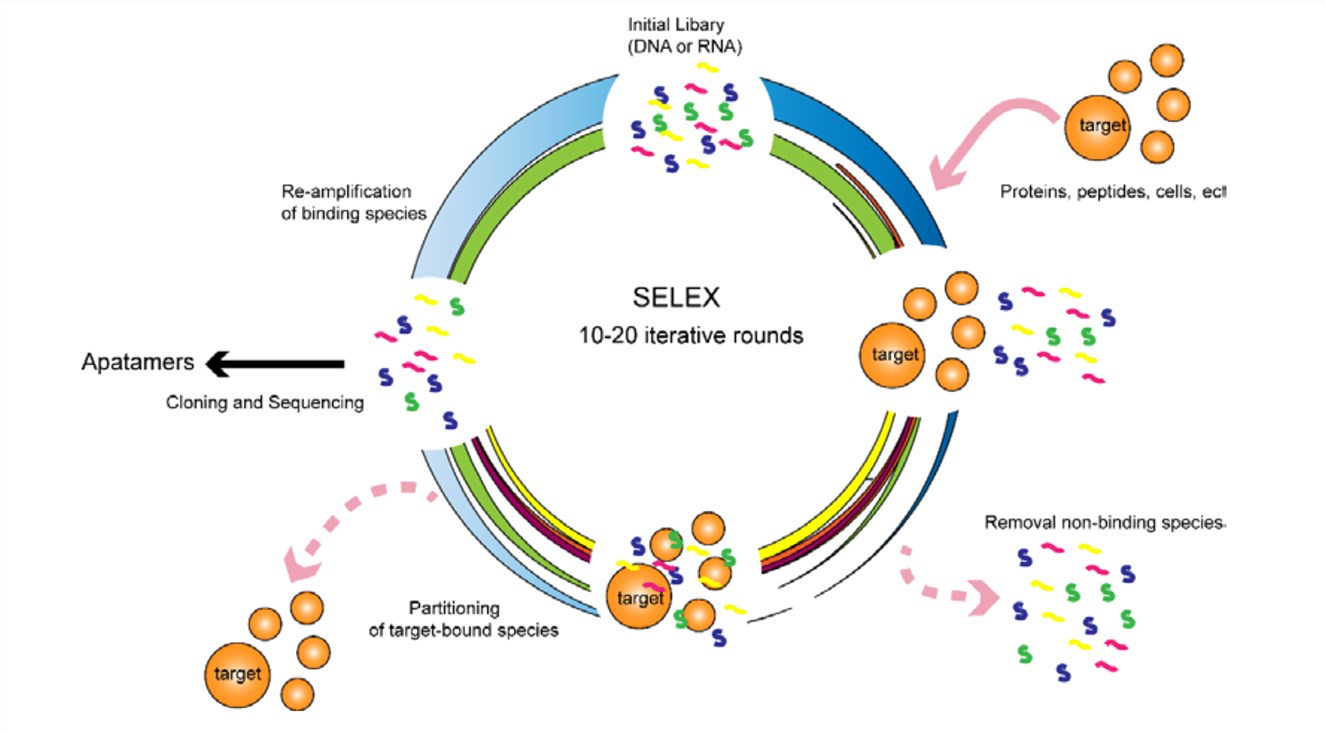 Fig.1 Schematic illustration of the SELEX process.2, 3
Fig.1 Schematic illustration of the SELEX process.2, 3
What Do You Get?
After the best binding aptamer has been identified, we will send the sequence to the customer. Upon request, we can also ship any remaining aptamer to the customer. This allows unlimited future ordering of additional aptamer from any supplier, with any desired modifications, to be used in any application. With an extensive line of services to support your projects, Creative Biolabs is the best choice for high-quality,  cost-effective outsourcing/collaborating options for your research programs. We can meet customer’s unmet needs with many kinds of our aptamer services suitable for various aptamer-based assays.
cost-effective outsourcing/collaborating options for your research programs. We can meet customer’s unmet needs with many kinds of our aptamer services suitable for various aptamer-based assays.
- Aptamers in the Diagnostic Pipeline
- Aptamers as Therapeutic Agents
- Aptamers for Targeted Drug Delivery
- Aptamers for Biomarker Discovery
- Aptamer-guided Combination Solution
- Aptamers as Imaging Tools
Together Creative Biolabs provides high-value aptamer-related services which include the selection and production of custom optimized RNA and DNA aptamers for analytical, diagnostic, and therapeutic applications. Each aptamer can be provided in various quantities and delivered either unmodified or modified. Creative Biolabs understands that each customer has different requirements for their project and we are happy to work with you to design a selection process to best fit your needs. Any questions about selection service or assay development? Please contact us for more information.
Published Data
1. DNA Aptamer Targeting MLL-AF9 Positive Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells via Whole-Cell SELEX
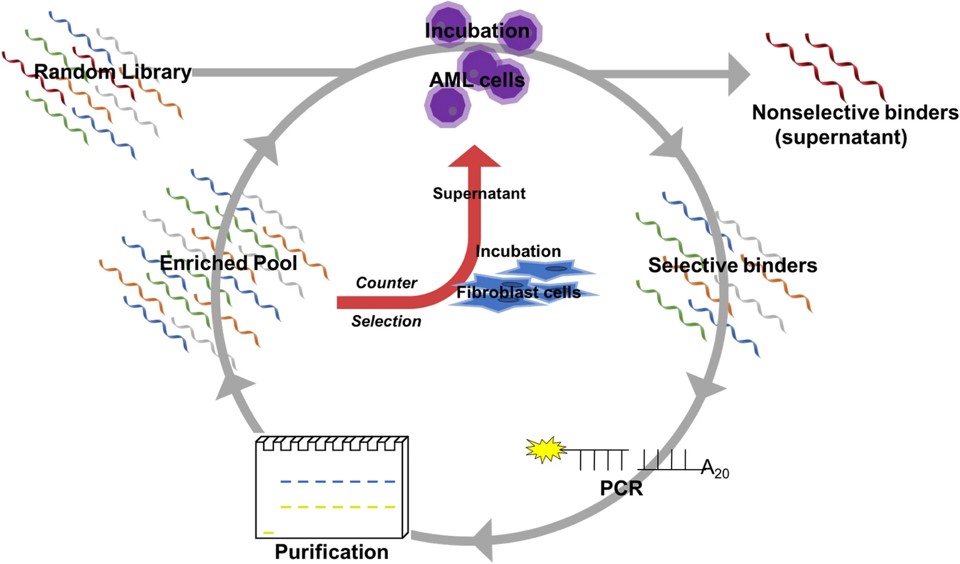 Fig.2 Schematic diagram of SELEX method for selection of MLL-AF9 RAS-specific DNA aptamers.4,3
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of SELEX method for selection of MLL-AF9 RAS-specific DNA aptamers.4,3
In this study, aptamers targeting acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells expressing the MLL-AF9 oncogene were selected using whole cell-SELEX, which included twelve rounds and two counter selections involving fibroblast cells. Sequencing of the aptamer pools revealed three potential sequences, each with two 23-base primer regions surrounding a 30-base central domain. Binding analysis utilizing flow cytometry showed that the lead sequence was specifically bound to AML cells with a dissociation constant of 37.5 ± 2.5 nM, but did not bind fibroblast or umbilical cord blood cells at 200 nM. A truncation study indicated the 5′ primer was not essential for binding. Testing against seven AML patient cultures revealed binding in five. This study developed and characterized a specific DNA aptamer for AML cells, paving the way for future drug-aptamer conjugates.
2. Development of B7H3 DNA Aptamers as Antibody Alternatives for Immunoassays
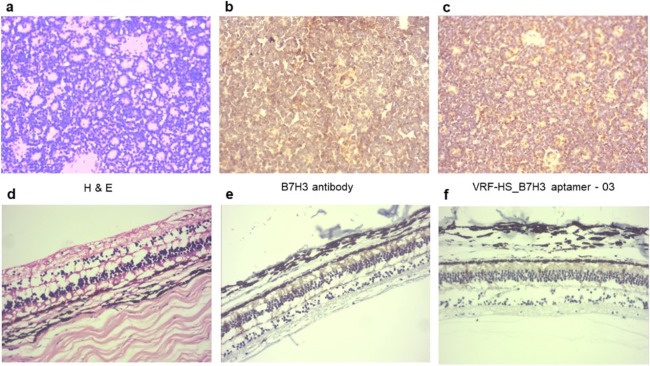 Fig.3 Immunohistochemistry with B7H3 antibody and biotin-labeled B7H3 aptamer to RB tumor sections and retina.5,3
Fig.3 Immunohistochemistry with B7H3 antibody and biotin-labeled B7H3 aptamer to RB tumor sections and retina.5,3
B7H3, an immunoregulatory protein in the B7 family, presents a promising target due to its elevated expression in tumor tissues and its restricted presence in normal tissues. In this study, hybrid-SELEX combined with next-generation sequencing was employed to select ssDNA aptamers that selectively bind to B7H3, offering an alternative to antibodies for a range of assays. These aptamers demonstrated versatility in multiple assays, recognizing B7H3 specifically in flow cytometry, dot-blot, and immunohistochemistry. Their effective performance in sandwich dot-blot and western blot assays highlighted their potential for diagnostic applications, while also highlighting its flexibility and cost-efficiency across a range of protein detection methods. This study suggests that the aptamers developed here could serve as a cost-effective and efficient alternative to traditional B7H3 antibody-based assays.
References
- Davydova, A. S., M. A. Vorobjeva, and A. G. Venyaminova. "Escort aptamers: new tools for the targeteddelivery of therapeutics into cells." Acta Naturae (англоязычная версия) 3.4 (11) (2011): 12-29.
- Zhuo, Zhenjian, et al. "Recent advances in SELEX technology and aptamer applications in biomedicine." International journal of molecular sciences 18.10 (2017): 2142.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Earnest, Kaylin G., et al. "Development and characterization of a DNA aptamer for MLL-AF9 expressing acute myeloid leukemia cells using whole cell-SELEX." Scientific Reports 11.1 (2021): 19174.
- Maradani, Bhavani Shankar, Sowmya Parameswaran, and Krishnakumar Subramanian. "Development of DNA aptamers targeting B7H3 by hybrid-SELEX: an alternative to antibodies for immuno-assays." Scientific Reports 14.1 (2024): 13552.
For Research Use Only.