The nano-immuno assay (NIA) technology has been demonstrated to be ideal for comprehensive and quantitative protein characterization and profiling of signaling events. It holds great promise as a molecular diagnostic tool to facilitate precision medicine.
Signaling Pathway Analysis
When there are charge variations among post-translationally-modified isoforms of the target protein, the iso-electric focusing (IEF) separation is able to separate and discriminate the different forms and detect them without using antibodies specific to the modifications. This useful feature of the charge-capillary NIA (CNIA) has been exploited to discover novel post-translational modifications (PTMs) in a number of signaling pathways and their association with important biological processes. For instance, scientists used this method to provide novel insights about VEGF induced c-Src phosphorylation changes at pY418 and pY527. The high resolution of the charge-CNIA technique can even allow species-specific protein isoforms to be resolved in some cases.
Biomarker Assessment
The CNIA technology shows promise in the development of biomarkers that predict response to therapy. In a study of the dynamic phosphorylation status of signaling molecules in NSCLC cells treated with EGFR tyrosine kinase and MEK inhibitors, a specific on-target MEK response pattern to a MEK inhibitor was identified, which was not detectable by conventional WB.
Quality Assessment
The CNIA platforms have been reported to be the choice for product quality control analysis based on it being a high-throughput and automated analysis system, and its proven assay precision, accuracy and sensitivity. The charge-CNIA offers specificity, speed and sensitivity advantages over an imaged capillary isoelectric focusing platform when used to analyze charge heterogeneity of monoclonal antibody (mAb) products in early stage process development.
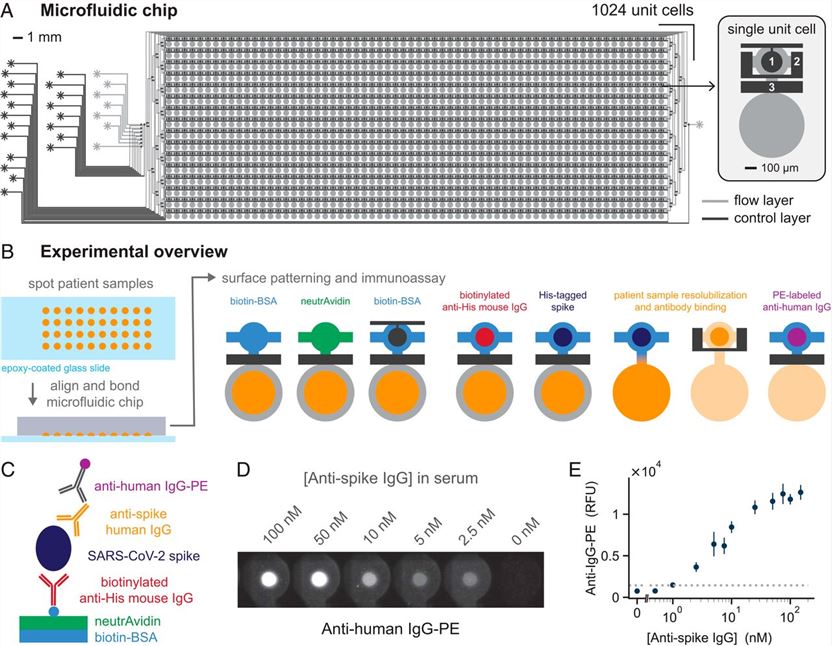 Fig.1 High-efficiency microfluidic NIA for detecting antibodies against SARS-CoV-2.1
Fig.1 High-efficiency microfluidic NIA for detecting antibodies against SARS-CoV-2.1
Biomarker Detection
NIA utilizing surface-enhanced raman scattering (SERS) effect is an analytical technique with high sensitivity that holds a great promise for early cancer detection. SERS has emerged as a strong platform for the development of a sensitive NIA that are capable of detecting low levels of analytes from limited sample. High sensitivity and the wealth of chemical information in the readout signal provide a great potential of SERS in detecting low amounts of biomarkers that may be present at the asymptomatic early stages of disease. A wide range of assays using SERS for detection of nucleic acids, proteins, and other analytes have been realized in recent years.
Reference
- Swank, Zoe, et al. "A high-throughput microfluidic nanoimmunoassay for detecting anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in serum or ultralow-volume blood samples." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 118.18 (2021): e2025289118. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.