Exosome-Based Vaccines
The development of novel cell-free vaccines using exosomes is a milestone in the prevention and treatment of diseases. Currently, trials using exosome-based vaccines have mainly involved tumors, viral infections, and non-viral infections.
Creative Biolabs has years of experience in disease research and treatment projects using exosomes and offers the most comprehensive exosome-based vaccine research services.
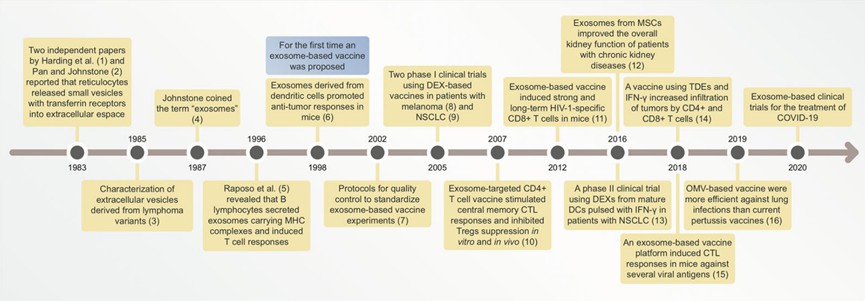 Fig.1 Timeline illustrating main discoveries related to exosome-based vaccines. (Santos & Almeida, 2021)
Fig.1 Timeline illustrating main discoveries related to exosome-based vaccines. (Santos & Almeida, 2021)
Vaccine strategies against tumors focus on restoring immune system sensitivity and reactivating a robust and sustained immune response. For example, tumor-derived exosomes have been shown to serve as biomarkers for vaccine studies where immunotherapy is the primary strategy. The specific antigens (p53 and RAS, etc.) or related antigens (HER2, etc.) carried on their surface cross-initiate CTL effects and retain long-term T memory cells, which may also be related to their miRNAs cargo. Exosomes from dendritic cells are enriched with more MHC class I and II molecules than their parent cells, allowing not only less time and space depletion but also higher activity stability. Exosomes secreted by B lymphocytes are antitumor vaccines capable of inducing MHC class II T cells. More beneficially, exosomes acting as vaccine adjuvants are more likely to penetrate the tumor microenvironment to overcome immunosuppression.
Both against infectious viruses such as COVID-19 and non-infectious viruses such as HBV, exosome-based vaccines have shown potential in clinical studies to prevent infection and reduce morbidity. Exosome-based vaccines, which use engineering techniques to prepare mock viral structural proteins or mRNA to serve as antigens, are able to excite antibodies with higher titers and potency than conventional vaccines, which are primarily based on prophylactic effects.
The process of bacterial infection induces pathogenesis by releasing drug-resistant factors into the host. However, exosomes of bacterial origin (OMV) are ideal immune activators. After being engineered to attenuate or detoxify, OMV can be rapidly internalized by the host and promote the secretion of cytokines such as INF. Furthermore, non-viral pathogens are not limited to this. Cell-free vaccine platforms against parasites contain multiple life-cycle proteins and miRNAs that interact with the host, and their potential applicability in public health efforts against non-viral infectious diseases is very promising.
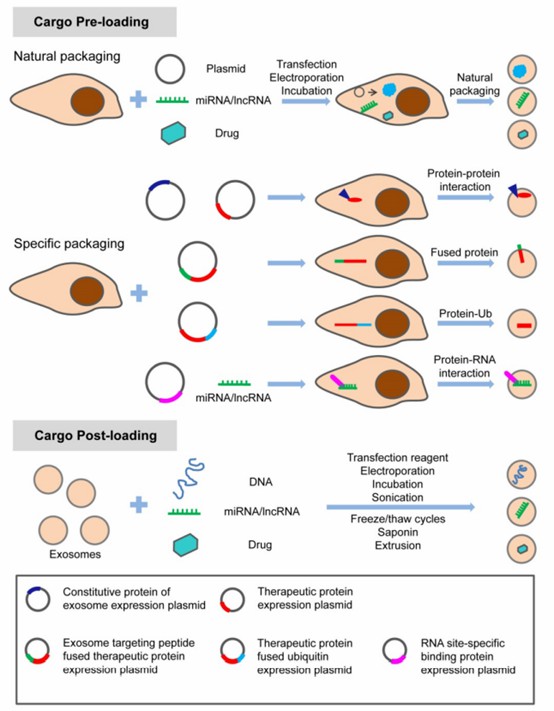 Fig.2 Methods of loading specific proteins, nucleic acids and small molecular drugs into engineered exosomes. (Liu & Su, 2019)
Fig.2 Methods of loading specific proteins, nucleic acids and small molecular drugs into engineered exosomes. (Liu & Su, 2019)
Exosome-based Vaccine Development Services at Creative Biolabs
Current results from exosome-based vaccine studies for many types of diseases are exciting, with powerful vaccine effects against tumors and protection against viral and non-viral infections. Meanwhile, the development of more sophisticated engineering modification techniques has also facilitated the study of exosomes for applications such as drug carriers and antigen presentation. Creative Biolabs has a deep understanding of exosome-based vaccines for multiple diseases, and our top-notch team provides you with high-quality research services. Please contact us to advance your project.
References
-
Santos, P.; Almeida, F. Exosome-based vaccines: History, current state, and clinical trials. Front Immunol. 2021, 12: 711565.
-
Liu, C.; Su, C. Design strategies and application progress of therapeutic exosomes. Theranostics. 2019, 9(4): 1015-1028.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Timeline illustrating main discoveries related to exosome-based vaccines. (Santos & Almeida, 2021)
Fig.1 Timeline illustrating main discoveries related to exosome-based vaccines. (Santos & Almeida, 2021)
 Fig.2 Methods of loading specific proteins, nucleic acids and small molecular drugs into engineered exosomes. (Liu & Su, 2019)
Fig.2 Methods of loading specific proteins, nucleic acids and small molecular drugs into engineered exosomes. (Liu & Su, 2019)









