Therapeutic Exosomes for Traumatic Brain Injury
Exosomes have shown promise as cell-free therapies in regenerative medicine for tissue repair and functional restoration. In preclinical studies of traumatic brain injury (TBI) repair strategies, exosomes have been shown to promote neurological recovery and vascular remodeling, modulate neuroinflammatory and peripheral immune responses, and stimulate the positive effects of brain growth factors in the treatment of TBI. Creative Biolabs has a deep understanding and compelling quality of service in exosome therapy for TBI and is able to provide customized research services on the therapeutic potential of exosomes.
Pathogenesis of TBI
TBI is one of the leading causes of acute injury, long-term disability and even death worldwide. TBI is mainly divided into primary physical injuries such as hemorrhage and tissue damage, and secondary injuries such as cytotoxic edema and hypoxic ischemia. Moreover, secondary injuries are accompanied by mitochondrial dysfunction and M1-type polarization of microglia, which induce adverse reactions such as oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, vascular abnormalities and metabolic disorders.
Patients with TBI experience spontaneous neurological recovery, which facilitates compensation for tissue damage, but their functional recovery is very slow, compromising long-term self-sufficiency. Intact neurological function depends on the remodulation of brain circuits such as neurogenesis and axonal remodeling, but disrupted connectivity of the central system after TBI attenuates the spontaneous repair of neurological function. Furthermore, arterial administration of restorative cell phenotypes mediated by secreted factors, especially MSCs, causes cerebral ischemia, and only a minimal number of MSCs reach brain areas by intravenous administration. Therefore, existing interventions are still accompanied by unavoidable side effects and limited efficacy without healing, and there is still a clinical need to identify effective treatments to reduce mortality in TBI.
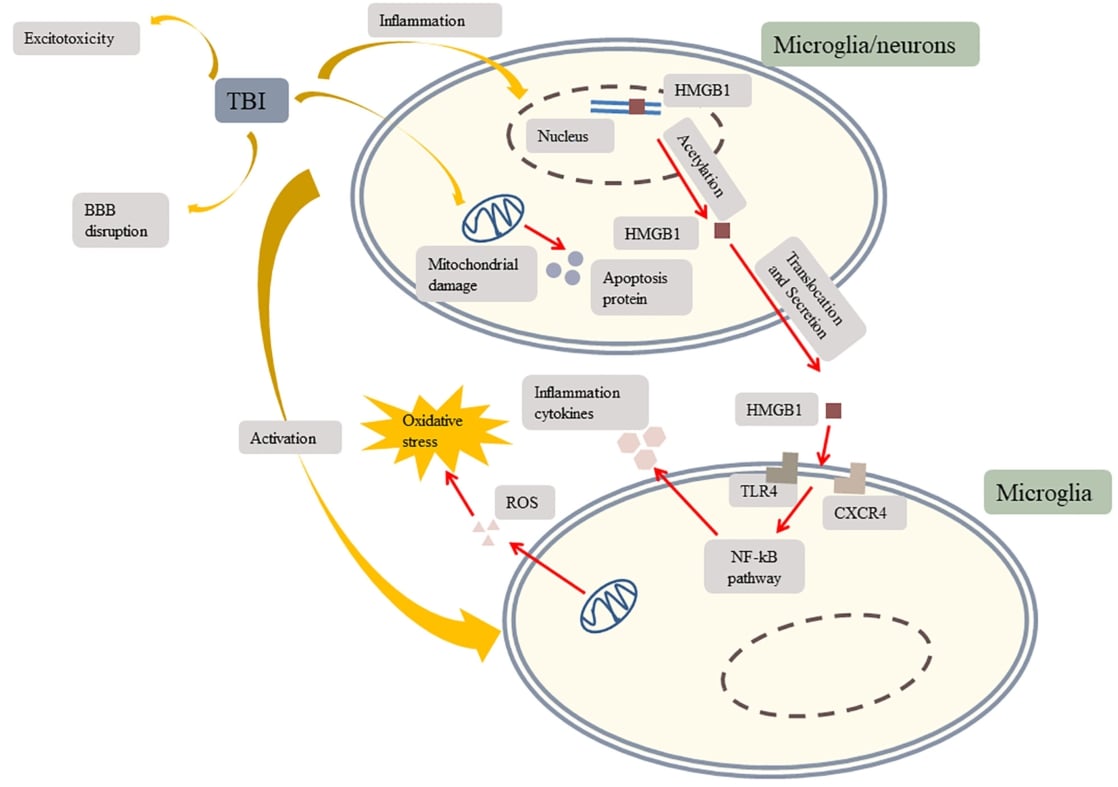 Fig.1 TBI induces inflammation, mitochondrial damage, microglial activation, excitotoxicity, and BBB disruption. (Yang, 2020)
Fig.1 TBI induces inflammation, mitochondrial damage, microglial activation, excitotoxicity, and BBB disruption. (Yang, 2020)
Therapeutic Exosomes for TBI
The main purpose of TBI treatment strategies is to promote brain tissue repair and neuroplasticity, and a cell-free exosome-based therapeutic strategy could provide new ideas for this purpose. The therapeutic effects of exosomes benefit from their contents, including miRNAs and enzymes similar to the parent cell components, but avoiding the replication of parent cells and the induction of microvascular occlusion. In addition, exosomes play a crucial role in short- and long-distance communication between cells, crossing the blood-brain barrier and reducing off-target effects and safety risks of systemic distribution of therapeutic agents in the brain. New preclinical evidence suggests that administration of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)-derived exosomes is sufficient to exert the restorative therapeutic effects of intact MSCs in TBI. MSCs-derived exosomes amplify the intrinsic brain repair process in experimental TBI mice, enhancing neuroplasticity and recovery of central system function. During administration, exosomes carry bioactive factors that reach multiple parenchymal cells, including brain endothelial cells, neural stem/progenitor cells and oligodendrocyte precursor cells through paracrine effects or direct action. The reported exosome-delivered miRNA-124, miRNA-17-92, miRNA-21, and miRNA-138 reduced the expression of axonal inhibitory molecules and increased the secretion levels of growth and plasticity-positive factors, thereby stimulating angiogenesis, neuronal cell migration, axonal sprouting, and oligodendrogenesis. At the same time, the suppression of inflammatory factors promoted the polarization of M2-type microglia. Together, these neuroregenerative events with positive effects promote brain tissue repair and neuroprotective functions.
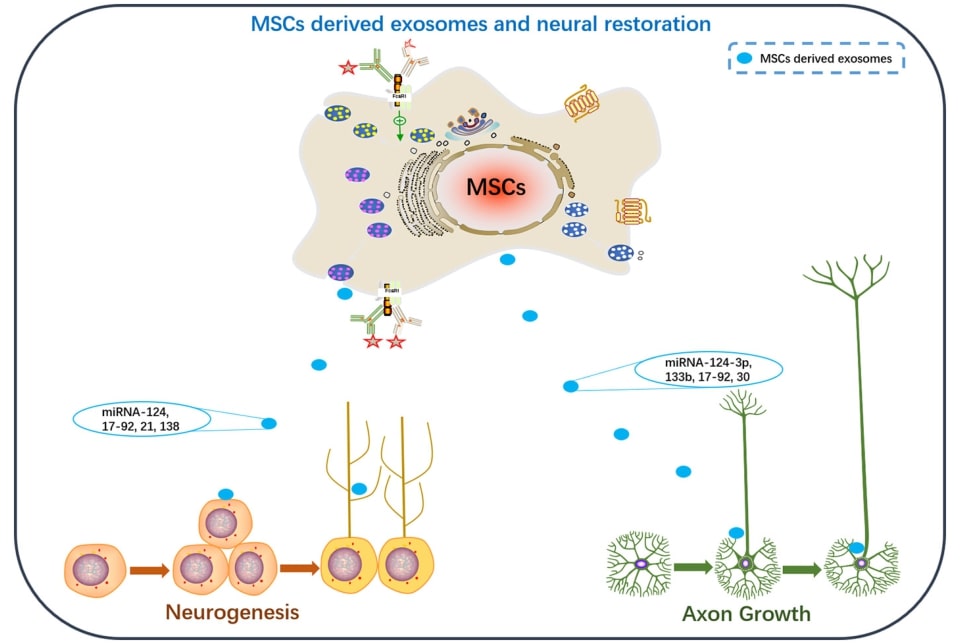 Fig.2 MSCs derived exosomal miRNAs have great potential in neurorestorative therapy. (Yang, 2022)
Fig.2 MSCs derived exosomal miRNAs have great potential in neurorestorative therapy. (Yang, 2022)
Exosome-based interventions have opened up new applications for TBI treatment. As an alternative strategy to whole cell therapy, exosomes stimulate the secretion of high levels of trophic factors from brain parenchymal cells, improving TBI repair and reducing cognitive impairment. Creative Biolabs has a deep understanding and research into the multifaceted applications of exosomes, as well as the ability to provide technical services including extraction, characterization and functional validation. Please contact us to advance your research on exosomes for TBI.
References
-
Yang, Q.; et al. Will sirtuins be promising therapeutic targets for TBI and associated neurodegenerative diseases? Front Neurosci. 2020, 14: 791.
-
Yang, Y.; et al. Exosomal microRNAs have great potential in the neurorestorative therapy for traumatic brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2022, 352: 114026.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 TBI induces inflammation, mitochondrial damage, microglial activation, excitotoxicity, and BBB disruption. (Yang, 2020)
Fig.1 TBI induces inflammation, mitochondrial damage, microglial activation, excitotoxicity, and BBB disruption. (Yang, 2020)
 Fig.2 MSCs derived exosomal miRNAs have great potential in neurorestorative therapy. (Yang, 2022)
Fig.2 MSCs derived exosomal miRNAs have great potential in neurorestorative therapy. (Yang, 2022)









