Exosome and COVID-19
With excellent drug carrier properties and efficacy similar to its source, exosomes are able to exhibit relevant diagnostic features not only in the pathological setting of COVID-19, but also as a preventive and therapeutic tool to maintain the activity they carry. Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive range of exosome analysis and research services for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19, advancing the health care of COVID-19.
COVID-19 Mechanism
The global pandemic of COVID-19 has caused multiple physical and economic losses to humans, and has severely changed the way people live during the epidemic. COVID-19 is the third large-scale virus-induced infectious disease to emerge in the 21st century since SARS and MERS. Being inhaled from the respiratory tract, COVID-19 causes an acute cytokine storm in the lungs by binding to the same receptor as SARS, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). Subsequent maturation of the virus and further transmission to distant sites leads to damage to the alveoli and infected tissues, causing respiratory dysfunction and complications occurring in other systems. Meanwhile, the unpredictable high frequency of mutations in COVID-19 viruses urges scientific and medical researchers worldwide to continuously explore and refine preventive, diagnostic and therapeutic strategies against COVID-19.
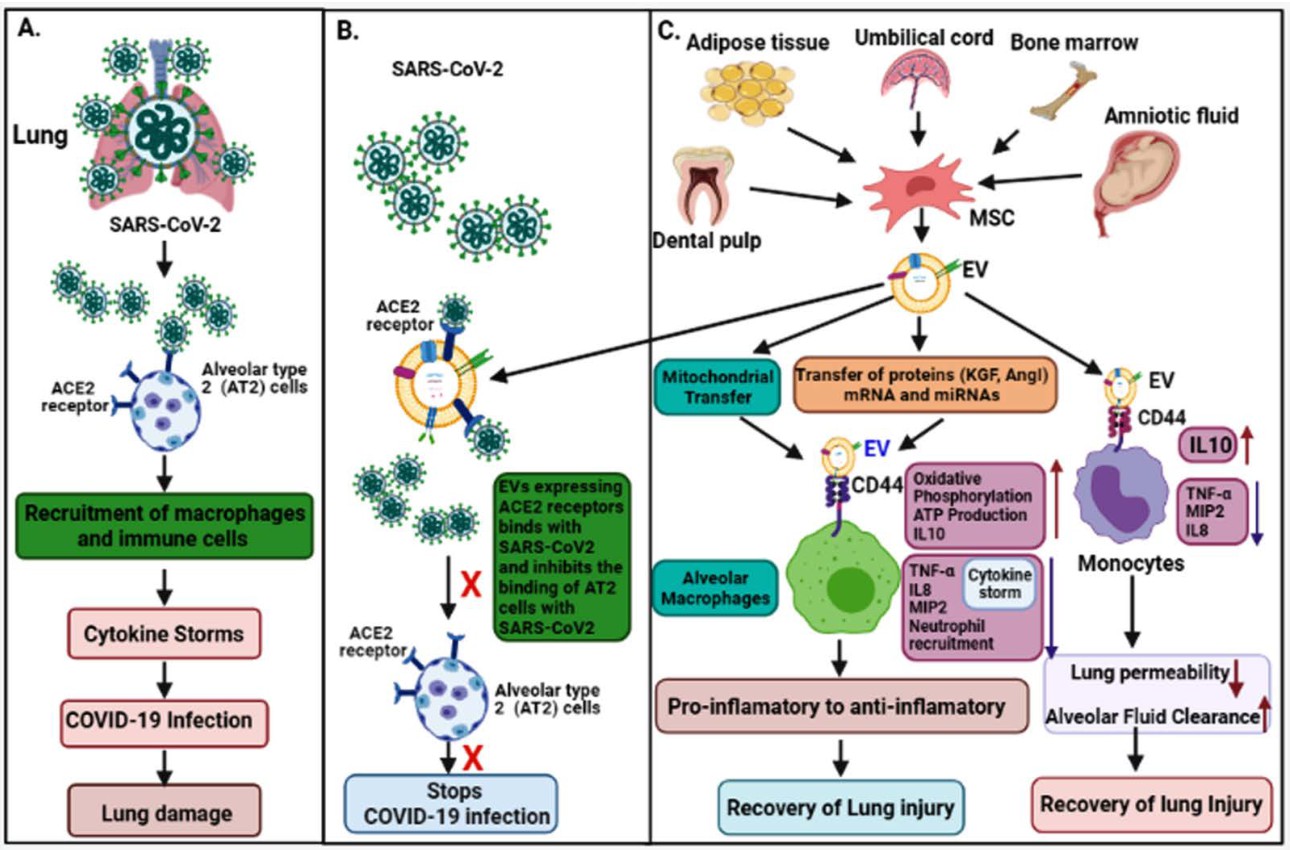 Fig.1 The pathogenesis of COVID-19 and its EV-mediated therapeutic recovery. (Karn, 2021)
Fig.1 The pathogenesis of COVID-19 and its EV-mediated therapeutic recovery. (Karn, 2021)
Exosome-based Strategy for Studying COVID-19
Immune escape of the virus and lesions of infected cells are the main factors leading to the progression of COVID-19, causing a cytokine storm whose intensity is closely related to the severity of the disease. Starting with infected cells, the virus completes a new wave of cellular infection through exosome secretion and propagation to the extracellular compartment. Multiple abnormally high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interferon-γ, IL-1β, IL-2/4/6/8/10/17 and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, were detected in patient sera, which were induced by activation of the NF-κB pathway by Tenascin-C (TNC) and fibrinogen-β (FGB). Thus, exosomes present in biological fluids such as serum, deliver these pathological signals to mediate immune disorders that have occurred in T lymphocytes and can be used as a diagnostic marker for COVID-19. To calm the immune and inflammatory storm to normal levels, MSCs-derived exosomes (MSCs-EXO) are used to inherit the immunomodulatory role of their parent cells, delivering IL-10 and TGF-β to suppress the abnormal immune activation of COVID-19. Meanwhile, miR-145 contained by MSCs-EXO also facilitates the repair of damaged areas of lung tissue by promoting lung epithelial cells and alleviating adverse lung pathology. Vaccination has become an effective means of preventing COVID-19 and reducing its incidence. Vaccines developed using the structural protein of COVID-19 and its mRNA as antigens, especially the Spike protein or its subunits chimerized into exosomes, have been shown to induce high titer specific antibody production. More importantly, exosomes are able to effectively protect the conformation of antigenic peptides, meeting the criteria for vaccine potency.
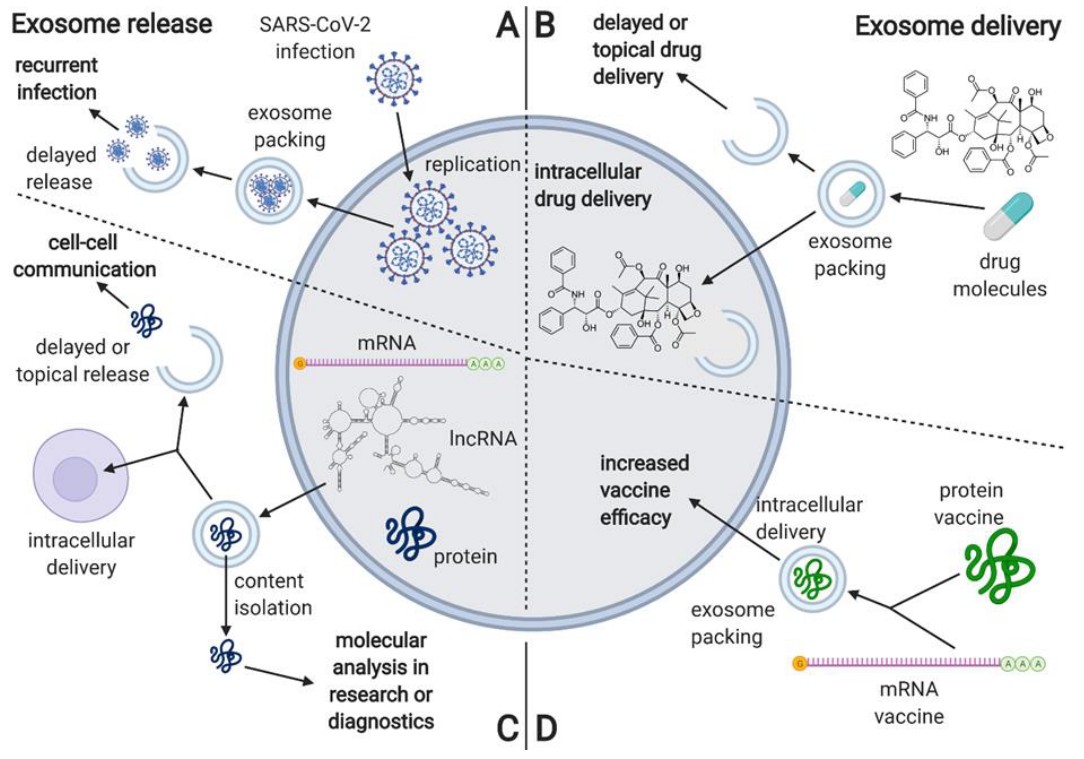 Fig.2 Description of COVID-19 related to exosomes. (Borowiec, 2021)
Fig.2 Description of COVID-19 related to exosomes. (Borowiec, 2021)
Based on the special advantages in immunomodulatory, immunogenicity, drug delivery, and so on, exosomes have shown great potential to play important roles in different aspects to help deal with the globalized epidemic of COVID-19:
Exosome-related Solutions for COVID-19 at Creative Biolabs
At Creative Biolabs, we have extensive experience in conducting research projects on COVID-19 with the help of exosomes, covering every stage of COVID-19, including prevention, diagnosis and treatment. To ensure that you get the results you want, we guarantee the highest level of quality and efficiency throughout the process. Please contact us to advance your research.
References
-
Karn, V.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-based therapy for COVID-19: Promises, challenges and future prospects. Biomedicines. 2021, 9(10): 1373.
-
Borowiec, B.M.; et al., Small extracellular vesicles and COVID19-using the "trojan horse" to tackle the giant. Cells. 2021, 10(12): 3383.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 The pathogenesis of COVID-19 and its EV-mediated therapeutic recovery. (Karn, 2021)
Fig.1 The pathogenesis of COVID-19 and its EV-mediated therapeutic recovery. (Karn, 2021)
 Fig.2 Description of COVID-19 related to exosomes. (Borowiec, 2021)
Fig.2 Description of COVID-19 related to exosomes. (Borowiec, 2021)









