Therapeutic Exosomes for Inflammatory Diseases
In recent years, there have been more and more reports on exosomes for the treatment of inflammatory diseases, indicating that exosomes have great therapeutic potential. Creative Biolabs is the world's leading supplier of exosome services and products, and has been focusing on the discovery and clinical research of exosome drugs. Creative Biolabs has now established a mature exosome research platform and is committed to exploring the unlimited potential of exosomes with global customers.
Occurrence and Causes of Inflammation
Inflammation is a protective behavior of the body against infection and trauma. Inflammation can remove harmful factors and damaged tissue, thereby repairing the tissue and returning the body to normal. Inflammation usually manifests as redness, swelling, heat, pain, and dysfunction. However, some inflammations also cause damage to the body itself, such as attacks on the body's own tissues, inflammation in transparent tissues, and so on. Factors that cause inflammation include microorganisms, body metabolites, harmful chemicals, abnormal immune responses, dead tissue, and more. The most common causes of inflammation are viral or bacterial infections. Viruses can invade the cells of body and kill them, causing inflammation. Bacteria trigger an inflammatory response by releasing substances called endotoxins.
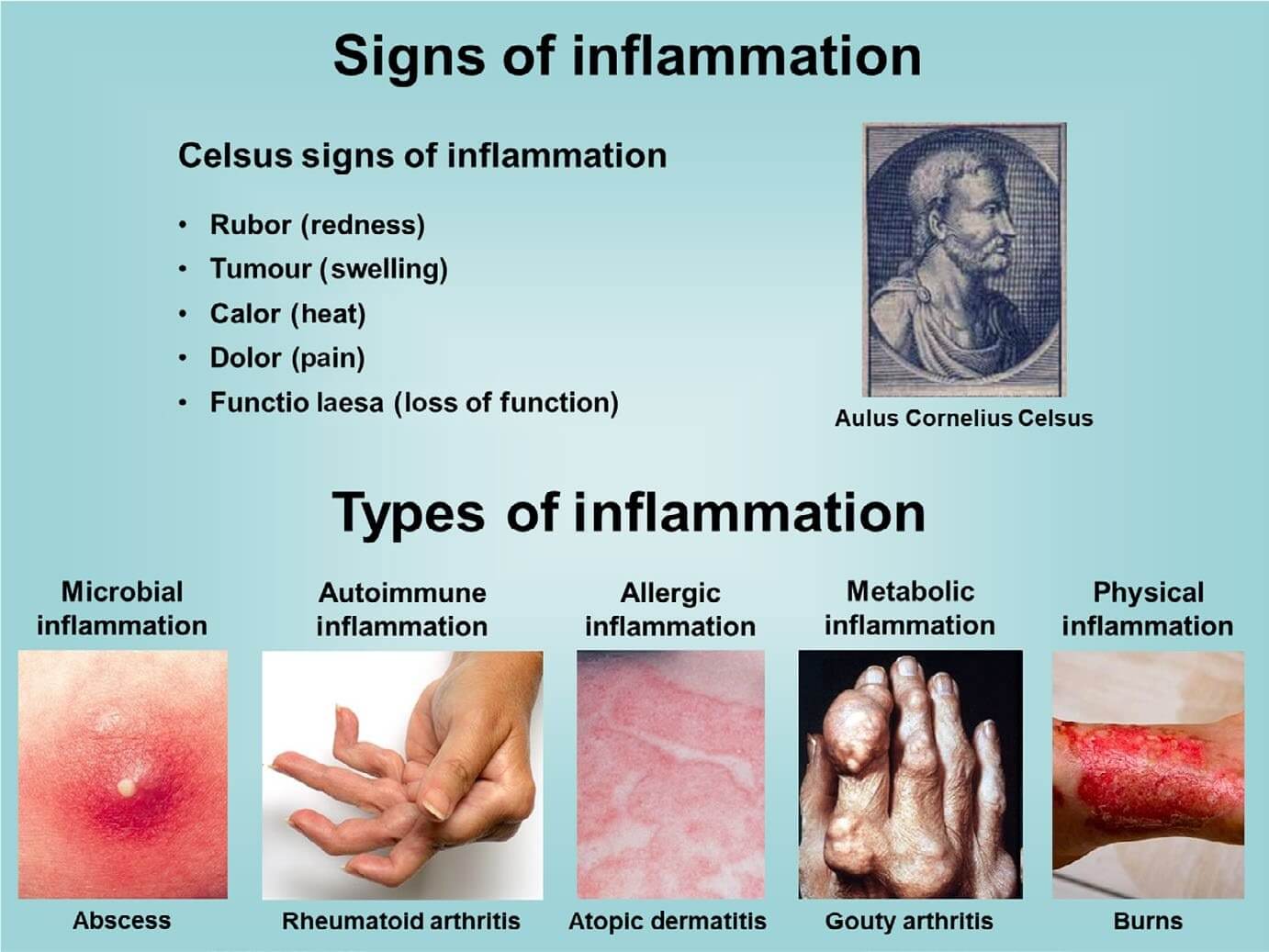 Fig.1 Signs and types of inflammation.1
Fig.1 Signs and types of inflammation.1
Inflammation is divided into acute and chronic inflammation according to its intensity or duration. Acute inflammation is the initial response to irritation, and local symptoms usually develop within minutes. Acute inflammation typically lasts for days or weeks. However, chronic inflammation is associated with untreated acute inflammation, poor diet, poor lifestyle, chronic stress, exposure to environmental toxins and other factors. Chronic inflammation may persist for months, years, or life. Chronic inflammation is considered to be the cause of all diseases. During the development of chronic inflammation, inflammatory cells can infiltrate fat and other tissues and accumulate. Moreover, pro-inflammatory mediators (such as cytokines) secreted by inflammatory cells in excess for a long time can lead to various organ degeneration and dysfunction, such as cardiovascular, diabetes, psychiatric diseases, cancer, chronic liver disease, etc.
Therapeutic Exosomes for Inflammatory Diseases
The number of trials of exosomes for the treatment of inflammatory diseases is increasing. Mesenchymal stem cells can perform multiple functions, including immune regulation, homing, and differentiation, enabling damaged tissues to form a balanced inflammatory and regenerative microenvironment under severe inflammatory conditions. However, more studies have shown that mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes (MSC-Exo) have a good anti-inflammatory effect. Adipose-derived stem cell-derived exosomes (ADSCs-Exo) have been found to reduce neutrophil apoptosis and increase their phagocytic capacity, promote macrophage polarization to an anti-inflammatory phenotype, inhibit osteoclast activation, and reduce bone resorption to treat periodontitis. ADSCs-Exo for the treatment of periodontitis has been approved for Phase I clinical trials.
Exosomes from different stem cell sources can treat osteoarthritis (OA) by promoting cartilage repair, inhibiting synovitis, and mediating subchondral bone remodeling. Intra-articular injection of synovial mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes can promote the migration and proliferation of chondrocytes and reduce the degree of cartilage damage in a mouse model of OA. In addition, infrapatellar fat pad stem cell-derived exosomes can inhibit the expression of inflammatory factors and have a strong ability to repair cartilage, thereby delaying the degeneration of articular cartilage and improving the abnormal gait of OA mice.
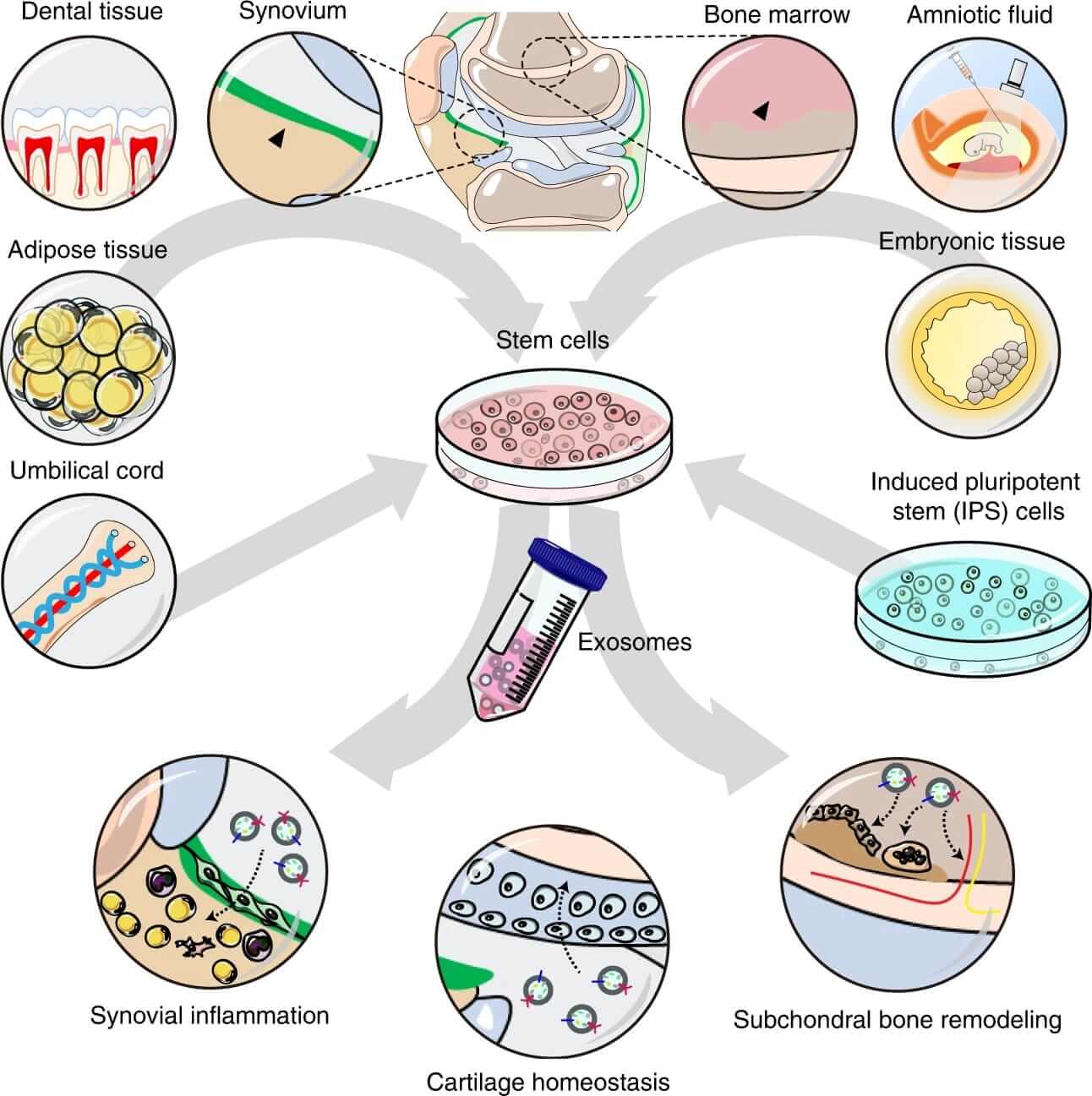 Fig.2 The therapeutic effects of stem cells-derived exosomes on OA.2,3
Fig.2 The therapeutic effects of stem cells-derived exosomes on OA.2,3
With years of experience and mature technology, as well as a high-level scientific research team, Creative Biolabs has been committed to working with customers to explore exosome drugs that can treat various inflammatory diseases. We can provide one-stop services from exosome extraction and modification to efficacy validation in vivo and in vitro. Please feel free to contact us with ideas for your needs and we will be happy to serve you.
References
-
Hawiger, J.; Zienkiewicz, J. Decoding inflammation, its causes, genomic responses, and emerging countermeasures. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology. 2019, 90(6):e12812.
-
Ni, Z.; et al. Exosomes: roles and therapeutic potential in osteoarthritis. Bone Research. 2020, 8:25.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Signs and types of inflammation.1
Fig.1 Signs and types of inflammation.1
 Fig.2 The therapeutic effects of stem cells-derived exosomes on OA.2,3
Fig.2 The therapeutic effects of stem cells-derived exosomes on OA.2,3









