Nervous System Disease Model Construction Service for Exosome Functional Research
Overview Services Features FAQs
Overview
Nervous System Disease and Exosome Research
Exosome research is a rapidly emerging field that is gaining increasing attention. In recent studies, exosomes have demonstrated significant potential in targeting, immunogenicity, and the delivery of biologically active molecules, making them a promising avenue for treating nervous system diseases (NSDs). These findings suggest that exploring exosomes could lead to new therapeutic approaches for NSDs.
When developing exosome-based therapies, selecting appropriate animal models is crucial for creating effective therapeutic drugs. Creative Biolabs offers a range of stable and high-quality NSD animal models to support customers in achieving their research goals.
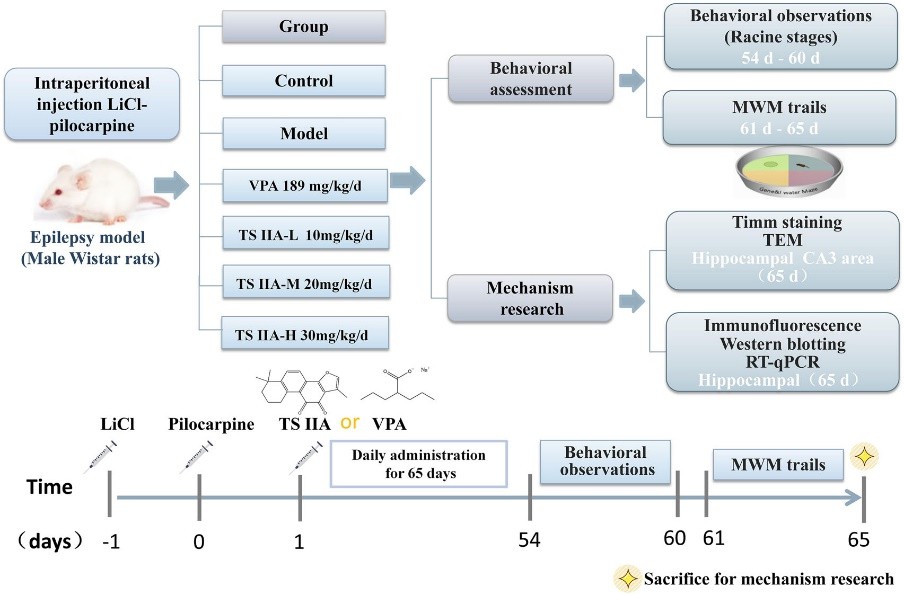 Fig.1 Research diagram of the mechanism of tanshinone IIA to improve cognitive function via synaptic plasticity in epileptic rats.1,2
Fig.1 Research diagram of the mechanism of tanshinone IIA to improve cognitive function via synaptic plasticity in epileptic rats.1,2
Services
Creative Biolabs Nervous System Disease Model Library for Exosome Functional Research
We provide a wide variety of NSD animal models for exosome functional research, including but not limited to the following:
|
NSD Animal Models
|
Inducer
|
Induction Mechanism
|
Applicable Animals
|
Model Features
|
|
Parkinson's disease (PD) animal models
|
6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) induction
|
6-OHDA exhibits strong neurotoxicity, causing acute degeneration of sympathetic adrenergic nerve endings and ultimately leading to irreversible neuronal damage.
|
Rat
|
This model is well-suited for studying the pathogenesis, treatment, and long-term progression of PD, particularly for investigating the pathophysiological changes in the mid-to-late stages of human PD.
|
|
Rotenone induction
|
Rotenone is lipophilic and can cross the blood-brain barrier. It strongly and broadly inhibits the activity of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I in brain tissue.
|
Rat
|
This model effectively mimics the pathological, biochemical, and behavioral characteristics related to PD, making it valuable for studying the disease's pathogenic mechanisms.
|
|
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) induction
|
MPTP is a highly lipophilic natural insecticide that easily crosses the blood-brain barrier. Once in the brain, it inhibits mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I activity, causing degeneration and death of dopaminergic neurons.
|
Mouse
|
This model has a short production cycle, exhibits significant neuronal loss, and presents abnormal behavioral test results. It is one of the most commonly used models for PD research.
|
|
Alzheimer's disease (AD) animal models
|
APP/PS1 mice
|
APP/PS1 double transgenic mice express a fusion protein consisting of mutated presenilin (DeltaE9) and amyloid precursor protein (APPswe). β-amyloid deposits begin to form in the brains of mice aged 6-7 months.
|
Mouse
|
This is the most classic model for studying AD, widely used in research.
|
|
3XTG mice
|
3XTG mice carry three AD-related genes: Psen1, APPswe, and tauP301L. At 12-15 months, these mice exhibit excessive tau phosphorylation in the hippocampus.
|
Mouse
|
This model displays plaque and tangle pathologies associated with synaptic dysfunction, closely resembling the clinical pathology of AD.
|
|
Epilepsy animal models
|
Combined induction of lithium chloride and pilocarpine
|
Pilocarpine activates acetylcholine receptors in the brain, causing persistent generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Lithium chloride increases sensitivity to pilocarpine, reducing its required dosage and significantly lowering mortality caused by its toxicity.
|
Rat
|
This model closely replicates the development of human temporal lobe epilepsy, making it an ideal model for studying this form of epilepsy.
|
Features
-
Six types of animal models for nervous system disease are available.
-
Other nervous system disease models can be consulted based on feasibility
-
Offering customized research plans and professional technical support.
-
Comprehensive services from exosome extraction and labeling to in vivo injection and subsequent functional analysis.
-
Reliable research results.
Creative Biolabs is a professional exosome research technology supplier, which can provide one-stop services including exosome extraction, exosome identification, exosome engineering, exosome labeling, and in vivo and in vitro verification of exosomes. With the support of a strong high-level team and the support of senior biotechnology experts, we can provide high-quality NSD animal models and supporting experimental services for global customers. Please contact us to put forward your needs to customize a rigorous experimental plan for you.
FAQs
Q: How can I obtain a quote for exosome in vivo functional research services?
A: You can describe your project or requirements through the "Online Inquiry" section on the right side of this page. Please provide detailed information so that we can better understand and expedite the progress of your project. Based on your requirements, we will provide a detailed quotation, including the choice of animal models, experimental design, time frame, and cost breakdown.
Q: Can I provide my own exosome samples for research?
A: Absolutely. We accept exosome samples provided by customers for in vivo functional research. We recommend communicating with our team before providing the samples to ensure their quality and quantity meet the experimental requirements. Additionally, we can provide advice on the transportation and storage of your samples.
Q: Upon completion of the experiment, could you provide a detailed report with conclusions and analysis?
A: Yes, upon completion of the project, we will provide a comprehensive experimental report, including the experimental design, methods, results analysis, and graphs. Our team will also offer further explanation and analysis of the results as needed to help customers better understand the experimental outcomes.
Q: What is the typical time frame for research using neurological disease animal models?
A: The research time frame depends on the selected animal model and the complexity of the experimental design. Generally, establishing the model may take several weeks to a few months, and the entire research process, including data collection and analysis, may require several months. Before you finalize the experimental plan and place the order, we will provide you with a timeline to help you plan your schedule effectively.
References
-
Jia, C.; et al. Investigation of the mechanism of tanshinone IIA to improve cognitive function via synaptic plasticity in epileptic rats. Pharmaceutical Biology. 2023, 61(1):100-110.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Research diagram of the mechanism of tanshinone IIA to improve cognitive function via synaptic plasticity in epileptic rats.1,2
Fig.1 Research diagram of the mechanism of tanshinone IIA to improve cognitive function via synaptic plasticity in epileptic rats.1,2









