Tumor Model Construction Service for Exosome Functional Research
Overview Services Features FAQs
Overview
Exosomes: An Emerging Research Objective in Cancer Therapy
As small extracellular vesicles containing a variety of biologically active substances, exosomes are almost involved in the entire process of tumor development and are closely related to tumor progression. However, exogenous exosomes can be used as carriers of tumor therapeutic drugs to target anti-tumor components such as loaded nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, and small molecular compounds to tumor cells to achieve tumor cell killing.
A large number of studies have shown that natural exosomes or engineered exosomes can treat tumors by inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and metastasis, regulating tumor microenvironment, inhibiting tumor angiogenesis, regulating tumor drug resistance, and activating immune cells. Therefore, exosome therapy is expected to become a new and efficient way of tumor treatment. Experimental animal models have long been used as an important tool for studying human diseases and developing new drugs.
Animal models currently available for tumor research mainly include induced tumor animal models, transplanted tumor animal models, and genetically engineered mouse models. These models can be used for screening and efficacy studies of new exosome drugs. Creative Biolabs can provide various tumor animal model construction services and in vivo efficacy evaluation services to help customers study the efficacy and safety of therapeutic exosomes.
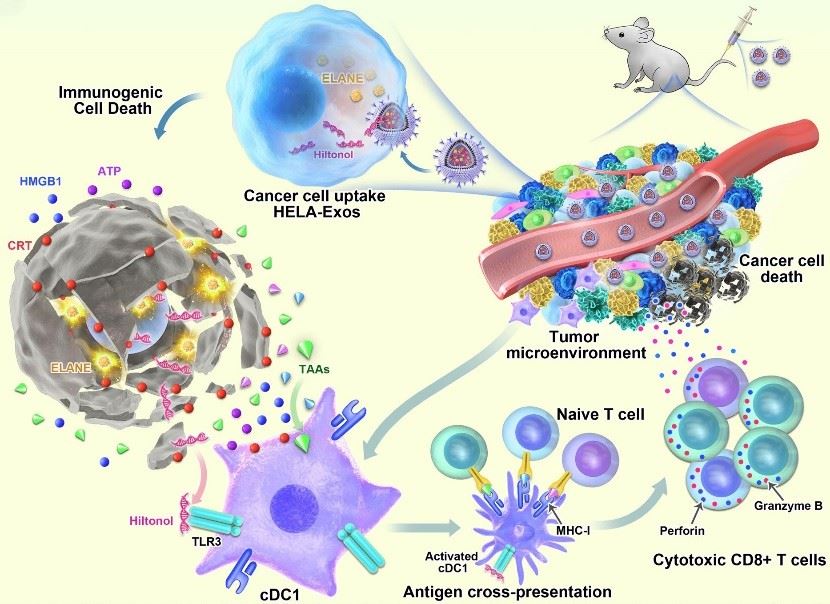 Fig.1 Mechanism by which HELA-Exos activate DCs in situ in a mouse xenograft model of TNBC.1,2
Fig.1 Mechanism by which HELA-Exos activate DCs in situ in a mouse xenograft model of TNBC.1,2
Services
Creative Biolabs Tumor Disease Model Library for Exosome Functional Research
We can provide including but not limited to the following tumor disease animal models for exosome functional research.
Features
-
A diverse range of tumor animal models
-
Flexible and customized experimental designs and research plans
-
Advanced laboratory facilities and technology platforms
-
A professional exosome research team
Creative Biolabs can provide tumor and cancer-targeted exosome modification services, exosome loading services, and corresponding tumor animal model construction services according to your needs. At the same time, we can also provide you with other exosome research services, including exosome extraction, exosome identification, exosome engineering, exosome labeling, and in vivo and in vitro verification of exosomes, which can meet your various needs for exosome drug development. If you want to develop exosome drugs for tumor treatment, please contact us without hesitation. Our professional team will respond to your inquiry as soon as possible and formulate the most cost-effective overall experimental plan for you.
FAQs
How do I choose the appropriate tumor animal model for exosome research?
A: The choice of an appropriate model depends on your research objectives, tumor type, and experimental design. Our scientific team will work with you to understand your specific needs and, based on the tumor's pathological characteristics, research goals, and budget, recommend the most suitable model.
Q: What is the potential application of exosomes in cancer treatment?
A: Exosomes have shown great potential in cancer treatment because they can carry various bioactive molecules, such as proteins, mRNA, and miRNA, to specifically target tumor cells. They can also exert anti-tumor effects by modulating immune responses, promoting apoptosis, or inhibiting tumor angiogenesis. Currently, the role of exosomes in cancer therapy is receiving increasing attention and research interest.
Q: How is the efficacy of exosomes evaluated in tumor animal models?
A: We use a variety of methods to evaluate the efficacy of exosomes in tumor animal models, including monitoring tumor growth curves, conducting histopathological analysis, detecting biomarkers, and utilizing imaging technologies (such as CT and MRI). Our team designs an appropriate evaluation plan based on the specific needs and goals of the research.
Q: Can your company assist with exosome-related drug development research?
A: Yes, we can assist clients with exosome-related drug development research. We provide comprehensive support services, including drug screening, efficacy evaluation, safety testing, and pharmacokinetic studies.
References
-
Huang, L.; et al. Engineered exosomes as an in situ DC-primed vaccine to boost antitumor immunity in breast cancer. Molecular Cancer. 2022, 21(1):45.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Mechanism by which HELA-Exos activate DCs in situ in a mouse xenograft model of TNBC.1,2
Fig.1 Mechanism by which HELA-Exos activate DCs in situ in a mouse xenograft model of TNBC.1,2









