Eye Disease Model Construction Service for Exosome Functional Research
Overview Services Features FAQs
Overview
Development Prospects of Exosomes in the Treatment of Eye Diseases
Exosomes are a special type of extracellular vesicles that can be derived from mesenchymal stem cells, endothelial cells, hematopoietic cells, and tumor cells. Exosomes can promote the repair and regeneration of damaged tissues or cells. Through communication with cells, exosomes can promote cell migration and proliferation, reduce oxidative stress, and transfer specific biologically active substances to target cells or damage sites.
With the aging population and changes in lifestyle, the incidence of eye diseases is gradually increasing, and its treatment has become a research hotspot. Due to the advantages of low immunogenicity and maintaining biochemical activity during storage, the mechanism of action of exosomes in the treatment of eye diseases has become a research hotspot. Therefore, exosomes have broad prospects for development as a cell-free substitute for stem cell therapy. The ability of exosomes to repair and regenerate has been validated in eye disease models.
Creative Biolabs is actively concerned about human eye health and the research progress of exosomes in the treatment of eye diseases. We have established the most professional one-stop platform for exosome research, which can provide global customers with standardized eye disease animal model construction services for in vivo function research of exosomes.
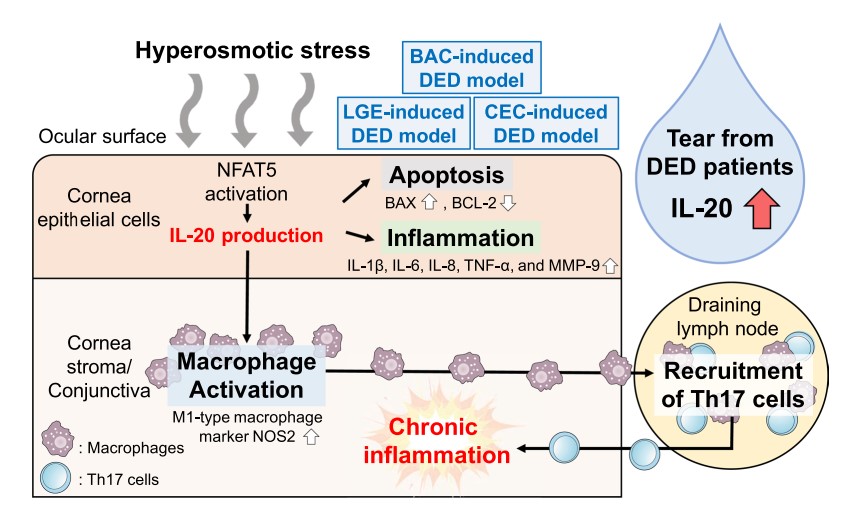 Fig.1 Interleukin-20 is involved in dry eye disease and is a potential therapeutic target.1,2
Fig.1 Interleukin-20 is involved in dry eye disease and is a potential therapeutic target.1,2
Services
Creative Biolabs Eye Disease Model Library for Exosome Functional Research
We can provide including but not limited to the following eye disease animal models for exosome functional research.
|
Eye Disease Animal Models
|
Inducer
|
Induction Mechanism
|
Applicable Animals
|
Model Features
|
|
Dry eye disease (DED) animal models
|
Benzalkonium chloride (BAC) induction
|
BAC is a commonly used preservative in clinical eye drops, and it is also a common factor that causes DED clinically. The toxic effect of BAC can cause punctate peeling of the corneal epithelium and decrease the stability of the tear film.
|
Mouse, Rat
|
This method can cause tear film stability impairment, ocular surface inflammation, corneal epithelial cell apoptosis and goblet cell loss, squamous metaplasia, etc. These pathological changes are similar to human DED.
|
|
Combined induction of scopolamine and evaporative hyperactivity
|
Scopolamine is a peripheral anticholinergic drug that competitively inhibits lacrimal gland M receptors by inhibiting parasympathetic nerve excitation and significantly reduces tear secretion. The dry environment simulated by compound fans can further lead to DED.
|
Mouse
|
This method can cause signs of DED such as a significant decrease in tear secretion, a decrease in the number of conjunctival goblet cells, and an increase in corneal fluorescence staining.
|
|
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) animal models
|
Streptozotocin (STZ) induction
|
STZ has a selective destruction effect on islet β cells. STZ-induced chronic progressive diabetes can lead to retinal microvascular leakage and occlusion, resulting in DR.
|
Rat
|
The modeling method is simple and economical, with good repeatability and a high modeling rate, and the induced retinal pathological changes are close to human DR.
|
|
Macular degeneration animal models
|
Sodium iodate induction
|
Sodium iodate is an antimetabolite that specifically induces degeneration of the retinal pigment epithelium, leading to macular degeneration.
|
Mouse, Rat
|
This modeling method can well simulate the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration.
|
Features
-
Highly relevant animal models for eye diseases
-
Comprehensive support from experimental design to data analysis
-
Tailored solutions based on your research objectives
-
Advanced exosome research technologies
At present, the development of therapeutic drugs for eye diseases is in full swing. Creative Biolabs has an integrated platform for eye disease model construction and detection. We can provide a full range of services on exosome research, including exosome extraction, exosome identification, exosome engineering, exosome labeling, and in vivo and in vitro verification of exosomes, to evaluate the in vivo efficacy of candidate exosome drugs for customers. If you are urgently looking for the best eye disease animal model to validate your innovative exosomes, please contact us. Our professional team will tailor the most suitable in vivo experiment program for you.
FAQs
Q: How do I choose the right animal model for exosome research on eye diseases?
A: The selection of an appropriate animal model depends on your specific research goals and the type of eye disease you are studying. Our scientific team will collaborate with you to understand your research needs and, based on the disease's pathological characteristics, experimental objectives, and budget, recommend the most suitable animal model.
Q: What are the sample requirements for exosome research services?
A: We encourage clients to discuss their sample needs with our team before submission to ensure that the samples' quality and quantity meet our experimental standards. In general, samples should be efficiently extracted and purified and must remain stable during transportation and storage. We can provide specific guidelines on handling and storage to help ensure optimal experimental results.
Q: What is the future potential of exosomes in treating eye diseases?
A: Exosomes hold great promise for treating eye diseases due to their low immunogenicity, ability to transport various bioactive molecules, and capacity to promote cell regeneration. As research advances, exosomes are expected to become a new and effective extracellular therapy for a wide range of eye conditions.
References
-
Wang, HH.; et al. Interleukin-20 is involved in dry eye disease and is a potential therapeutic target. Journal of Biomedical Science. 2022, 29(1):36.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Interleukin-20 is involved in dry eye disease and is a potential therapeutic target.1,2
Fig.1 Interleukin-20 is involved in dry eye disease and is a potential therapeutic target.1,2









