Creative Biolabs provides high-quality service in phage display antibody library construction and screening. In order to select antibodies with high affinity and specificity, we have developed a series of selection strategies. The strategy here is based on valency, and it allows us to select antibody fragments capable of modulating cell surface receptor functions when in a divalent format.
Antibodies (Abs) displaying an agonist or antagonist activity are useful tools to stimulate or block physiological functions in the cell. A number of Abs have been applied in diagnosis and therapy requiring multivalent reagents, either because the biological activity of Abs depends on the polymeric nature of Ag, or because it requires an effect on the formation of homodimeric species. Under normal conditions, dimerization is necessary for the activation of numbers of surface receptors by their natural ligands. Therefore, divalent Abs are especially required for stimulating or blocking the activity of such ligands.
The antibodies generated by the traditional methods are often monomeric fragments (such as scFvs and Fabs). Strategies for engineering multivalent fragments are laborious and inappropriate for massive screening. Creative Biolabs has developed this strategy allows the selection of Ab fragments from phage display libraries based on valency. This approach utilizes the advantage of high-throughput screening by phage display technology of monovalent Ab fragments.
There are two steps available as our standard protocol. Firstly, standard protocols will be used to select the monovalent Ab fragments from phage display libraries. Then tag the selected monovalent Ab fragment with an epitope (such as Myc tag) which could be recognized by a specific anti-tag Ab in the next step. Secondly, the tagged Ab fragments are dimerized using the anti-tag Ab as a dimerization domain to generate a divalent binding site for the Ag of interest. Then, cells will be challenged with the anti-tag-Ab fragment complexes, and inhibition or enhancement of specific cellular functions can be evaluated.
Featured Advantages
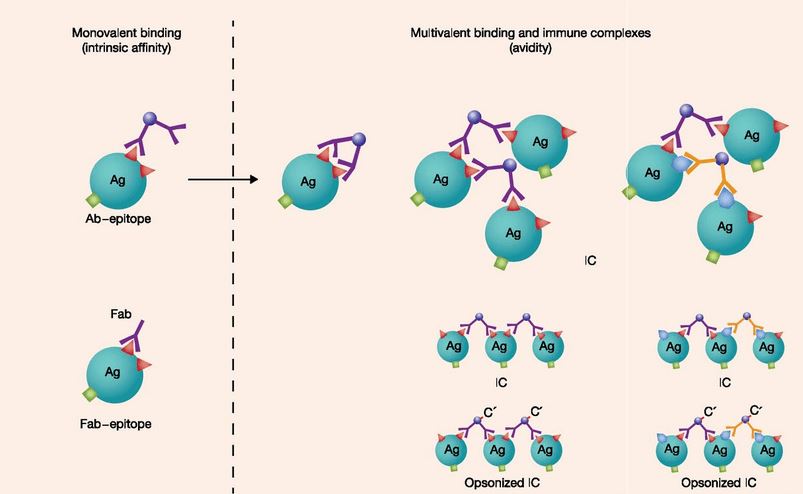 Fig.1 Diagrammatic representation of various antibody-epitope bonds (Eisen 2014). Left, monovalent binding of an epitope by an intact bivalent antibody or an antibody fragment (Fab). Right, various multivalent antibody-epitope bonds: concatenated linkages (…Ag-Ab-Ag-Ab…) form immune complexes (IC) involving the same or diverse epitopes.
Fig.1 Diagrammatic representation of various antibody-epitope bonds (Eisen 2014). Left, monovalent binding of an epitope by an intact bivalent antibody or an antibody fragment (Fab). Right, various multivalent antibody-epitope bonds: concatenated linkages (…Ag-Ab-Ag-Ab…) form immune complexes (IC) involving the same or diverse epitopes.
Creative Biolabs’ scientists have extensive experience in phage display library screening based on valency to obtain dimeric Abs. This strategy allows for conditional selection of monomeric or dimeric Abs and can be readily suited to mass screening for activity. Furthermore, Abs those prove to be active as dimers can be further engineered for multivalency.
For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us or directly sent us an inquiry.
References
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.