Transporters belong to membrane proteins, which also include GPCRs, kinases, and ion channels. These proteins play significant roles in both the physiological and pathological processes of organisms. Transport proteins facilitate the exchange of chemicals inside and outside biological membranes, as well as signals. Due to their functions, transporter proteins have been identified as important players in targeted drug development and drug transport. However, the study of transporter proteins is challenging. Creative Biolabs provides a high-quality membrane protein platform that can support the study of different membrane proteins.
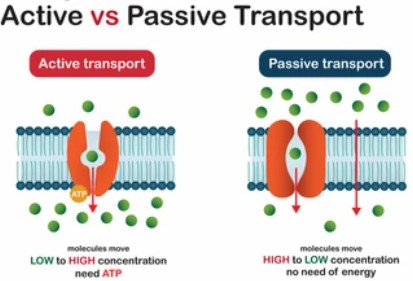
The main function of transport proteins is to regulate the exchange of substances within and outside of cells. Transporter proteins typically have multiple transmembrane topologies, specific recognition of transported substrates, and can actively transport molecules against a concentration gradient using energy dissipation. Transporters rely on conformational transitions to transport substrate molecules down or up the concentration gradient, while simultaneously transporting sodium ions down the concentration gradient to provide the energy needed for protein conformational transitions. Depending on the direction of substrate transport, transporters can be categorized as uptake or efflux transporters.
Drug-related transporters in the human body can be divided into two major groups according to their function. One group is the soluble carrier (SLC) superfamily, which facilitates drug uptake into cells and is present in all tissues and organs of the body. These transporters use the ion concentration gradient on both sides of the cell membrane to transport substrates across the membrane. Most SLC transporters consist of 7-14 transmembrane helices and have an intracellular or extracellular flexible structural domain that assists the transmembrane helices to form transmembrane channels. More than 400 SLC transporters have been identified and characterized into 65 subfamilies, with oligopeptide transporters (PEPTs), organic anion transporters (OATs), organic anion peptide transporters (OATP), and organic cation transporters (OCTs) being the main SLC transporters involved in drug transport. Another group of transporters is the ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABC) superfamily, which uses the energy derived from ATP hydrolysis to transport drugs out of the cell. The human genome encodes 49 genes for ABC transporters, which are classified into 7 subfamilies (A to G) based on evolutionary differences.
Combined with the characteristics of drug transporters, common strategies for drug design targeting drug transporters include pre-drug modification to improve bioavailability, introducing acidic groups to improve hepatic selectivity, and increasing compound polarity to reduce the efflux ratio. Small molecule inhibitors targeting the transporters are the main research direction at present, as they can effectively enhance drug activity. Therapeutic antibody drugs have higher specificity and targeting, making them more advantageous in some diseases. However, complex membrane proteins such as transporters can be less accessible to suitable antigens, making it challenging to develop therapeutic antibodies against them. Developing therapeutic antibodies against transporters requires more time and effort to obtain suitable transporter immunogens. Both types of drugs have advantages and disadvantages, and the choice needs to be made on a case-by-case basis to determine the best research approach.
Creative Biolabs has accumulated a wealth of relevant knowledge and experience in transporter research and is well-positioned to help with any research challenges related to transporters. We would be pleased to discuss any research needs you may have.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.