Creative Biolabs is the world leading service provider for the discovery of in vitro diagnostics (IVD) antibodies. Based on our years of experience and advanced platform, we are confident in offering the best and most suitable IVD antibody discovery service against various markers for liver cancer.
Highly Up-regulated in Liver Cancer (HULC)
Highly up-regulated in liver cancer (HULC) is a long non-coding RNA, and the gene is located on chromosome 6P.24.3 with the length about 500 nucleotides and contains two exons. However, the transcribed RNA of HULC is short of substantial ORF (open-reading frame), so it has no protein product. The function of HULC is the post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. It can downregulate some microRNAs expression such as miR-372. HULC was first identified in liver cancer with elevated expression. Highly expressed of HULC was found in colorectal carcinomas that have a metastasis to the liver. What's more, a variety of studies have shown that HULC is associated with cell survival, proliferation, invasion, tumor growth and angiogenesis, thus, indicating that HULC is essential for oncogenesis.
Downstream Oncogenic Pathways of HULC
The high levels of HULC in liver cancer indicate that it possesses oncogenic functions to promote cancer progression by many cellular activities. The mechanism of how HULC participates in HCC is involved in a lot of factors, including EEF1E1 (Eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 epsilon 1) and SK1 (sphingosine kinase 1). There is a negative correlation of the expression between HULC and EEF1E1 (known as a tumor suppressor) in liver cancer tissue. Overexpressed HULC can decrease the expression of EEF1E1, while knockdown of HULC increases the expression of EEF1E1. Moreover, inhibition the increased expression of EEF1E1 reverses the suppression of tumor by downregulating HULC. Taken together, these suggest that HULC enhance HCC growth partly by decreasing EEF1E1 expression. HULC has a positive correlation with SK1 in liver cancer cells and knockdown of SK1 reverses HULC promoted angiogenesis.
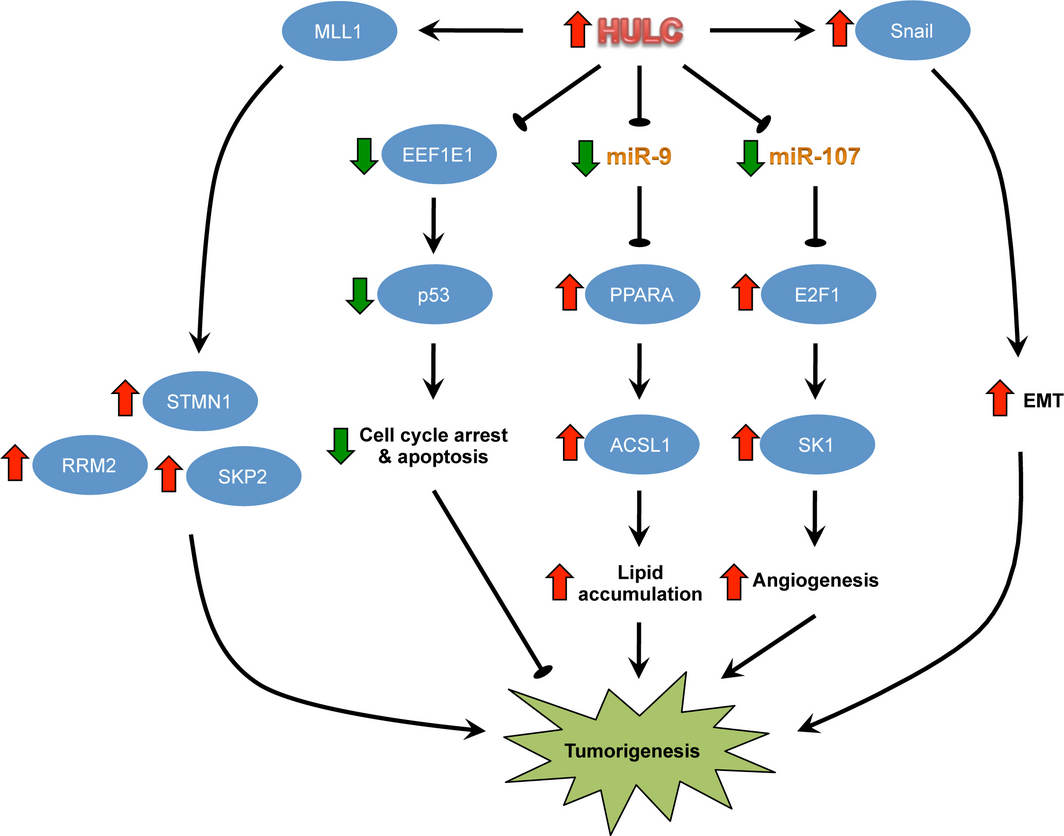 Fig 1. Downstream oncogenic pathways activated by HULC. (Yu, X.,2017)
Fig 1. Downstream oncogenic pathways activated by HULC. (Yu, X.,2017)
HULC as a Vital Biomarker for Liver Cancer
The highly expressed HULC that first identified in HCC was from an HCC-specific gene library. Following studies showed that HULC was significantly increased in plasma as well in liver cancer patients. Furthermore, it also indicted that the HULC expression is correlated with tumor size and tumor capsular. Therefore, HULC may play vital roles in tumor occurrence, growth, and invasion, and higher levels of HULC predicted a higher risk of tumor growth, invasion, and occurrence in liver cancer. Hence, IVD assays for HULC biomarker can help to predict the diagnosis of liver cancer.
With years of research on IVD technology, Creative Biolabs now provides the unique IVD assays to meet our clients' IVD demands precisely. If you are interested in our service, please do not hesitate to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Yu, X. (2017). “Hulc: an oncogenic long non‐coding rna in human cancer.” Journal of Cellular & Molecular Medicine, 21(2), 410-417.
For Research Use Only.