Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are a class of nanoparticles that can be manipulated using magnetic fields. Such particles commonly consist of two components, a magnetic material, often iron, nickel, and cobalt, and a chemical component. MNPs are used as vascular contrast agents (CAs) in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Recently, diagnostic strategies based on MNPs have received considerable attention. New generations of MNPs have been specifically designed and developed for biomedical applications.
 Fig.1 Maghemite silica nanoparticle cluster.Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki,
without modification.
Fig.1 Maghemite silica nanoparticle cluster.Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki,
without modification.
Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs) and In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD)
When cancer is discovered earlier, the cure rate is greatly improved. Therefore, early detection and timely diagnosis of cancer are key to reduce the mortality rate of patients. Tumor imaging technology has an important role in cancer diagnosis and the choice of late clinical treatment options. MNPs are the contrast agents that are most widely researched and used in cancer imaging. In MRI, research has demonstrated that early lesion detection of glioblastoma multiforme may be achieved by sensitive imaging of superparamagnetic nanoparticles (NPs) or aggregates.
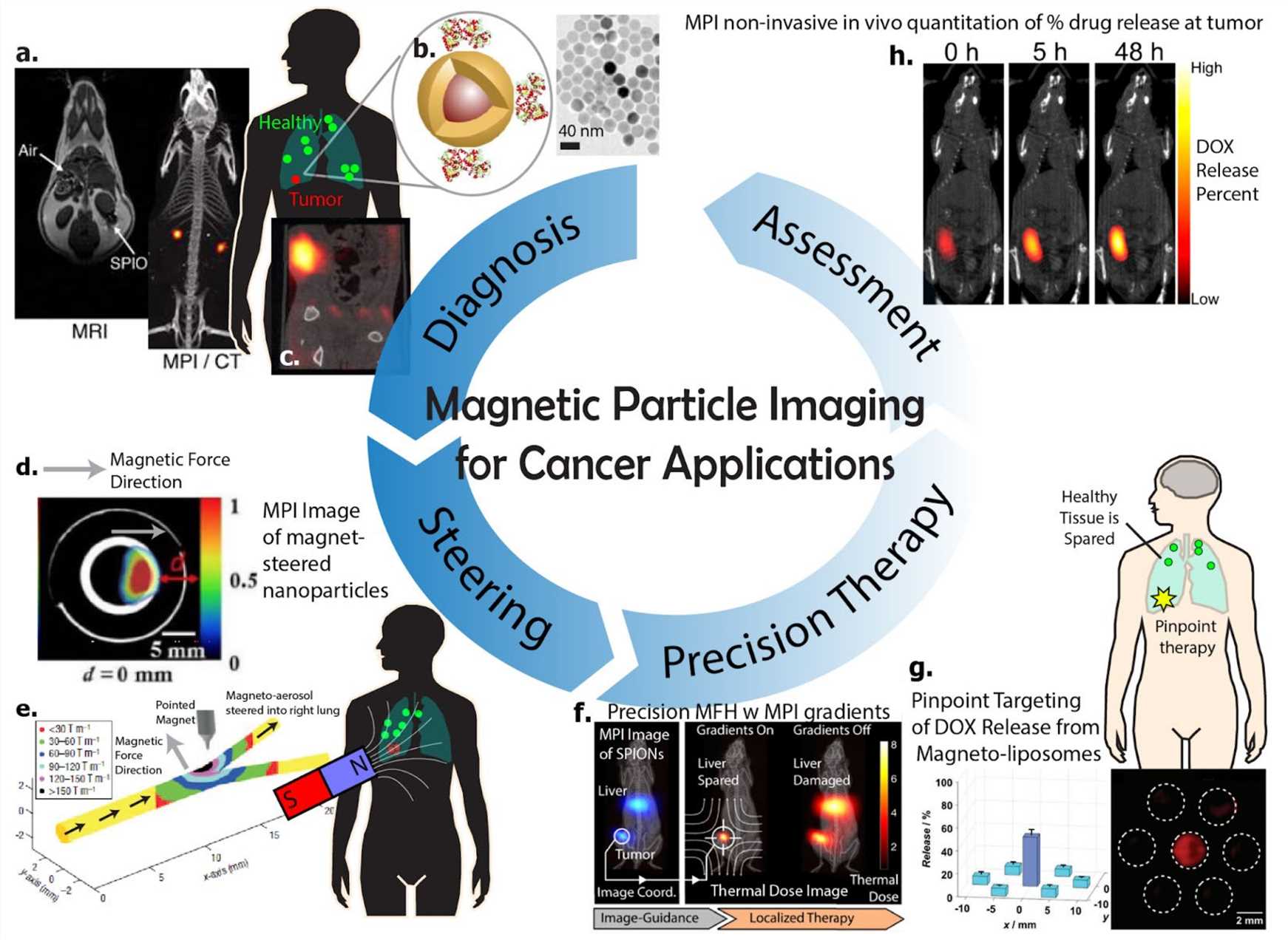 Fig.2 Overview for MNPs imaging’s prospects in cancers.1
Fig.2 Overview for MNPs imaging’s prospects in cancers.1
Application of MNPs
A whole range of theranostic nanoplatforms was designed and most of them have been applied in the field of cancer. In addition, there is also tremendous activity in the field of MNPs labeled stem cells in regenerative medicine. In recent years, MNPs were used, among others, as platforms for drug delivery, gene delivery, phototherapy, controlled drug release systems and more.
- Drug Delivery Using MNPs
- Gene Delivery Using MNPs
Cancer remains one of the most devastating diseases and the treatment shows limited efficacy and severe side effects. Therefore, massive efforts in the field of MNPs theranostics have been directed to visualize, increase drug delivery and monitor their efficacy in cancer.
Scientists developed a human serum albumin (HSA) coated iron oxide nanoparticle (HINP) formula and used multiple imaging modalities to validate its tumor-targeting attributes. They sought to impart an anti-tumor drug onto the HINPs and assess the potential of the conjugates as theranostic agents. 0.5 mg of the drug and 1 mg of iron oxide nanoparticles could be loaded into 10 mg of HSA matrices, resulting in drug-loaded HINPs (DHINPs). In a follow-up therapeutic study on a murine breast cancer xenograft model, D-HINPs showed a striking tumor suppression effect that greatly outperformed the free drug.
Biomolecules, such as therapeutic proteins, cannot diffuse across cell membranes like small drugs and thus require transporters for cell entry. Translocation of genes into cells can, in principle, be achieved by conjugating or non-covalently absorbing them on the MNPs.
Scientists demonstrated that MNPs can be used to deliver and follow small interfering RNA (siRNA) administration to tumors in vivo by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF).
Creative Biolabs is pleased to share our cutting-edge technology and extensive expertise to meet every specific requirement of diagnostics project development. Please feel free to contact us for a detailed quote and further discussion with our scientists.
Reference
- Tay, Zhi Wei, et al. "Magnetic particle imaging: an emerging modality with prospects in diagnosis, targeting and therapy of cancer." Cancers 13.21 (2021): 5285. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.