A typical quantum dot (QD) has a diameter ranging from 2 to 10 nm and contains about 200 to 10,000 atoms. Compared with fluorescent proteins and organic dyes, QDs have unique optical and electronic properties such as size- and composition-tunable light emission, improved signal brightness, resistance to photobleaching, and simultaneous excitation of multiple fluorescence colors. In addition, different colors of QDs can be simultaneously excited with a single light source, which provides significant advantages for multiplexed detection of target molecules.
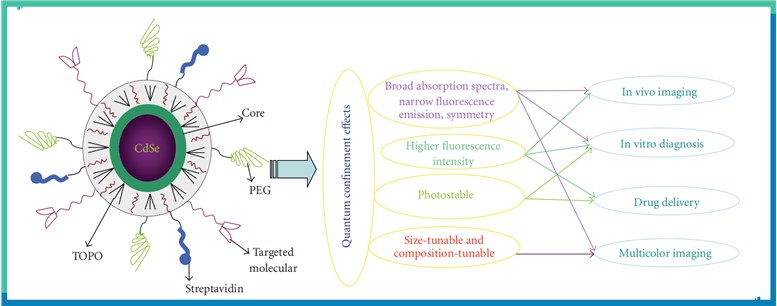 Fig.1 Properties of QDs. (Peng, 2010)
Fig.1 Properties of QDs. (Peng, 2010)
Quantum Dots (QDs) for In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD)
Unique properties of QDs provide significant advantages toward the primary requirements (sensitivity, selectivity, and multiplexing) of in vitro diagnostics (IVD).
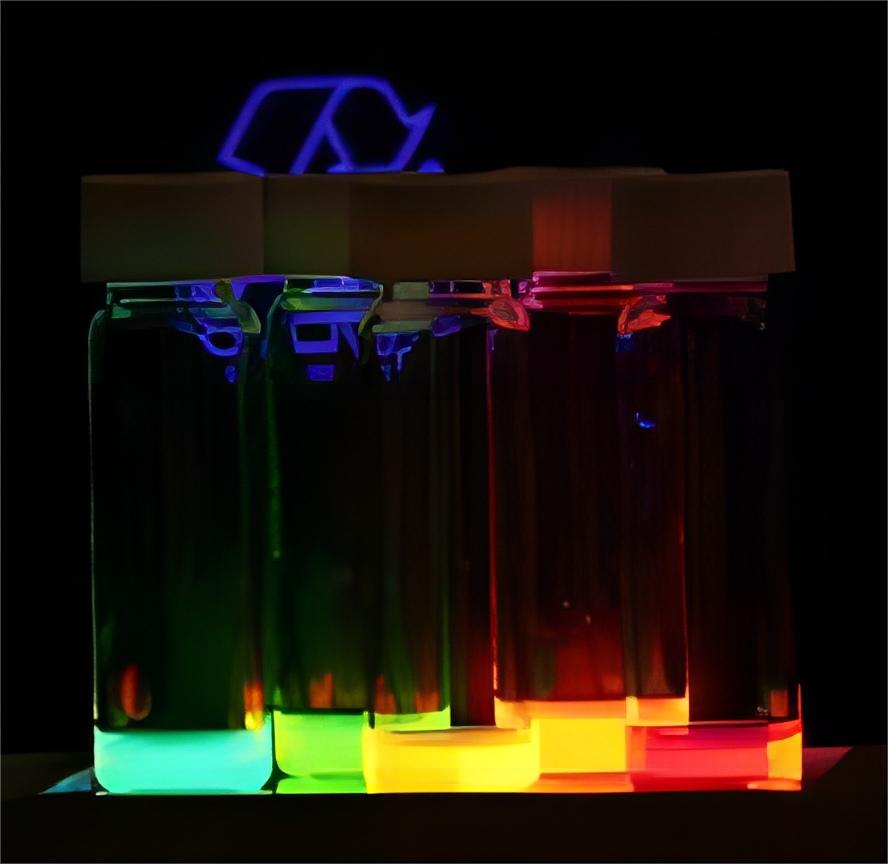 Fig.2 Quantum Dots.2
Fig.2 Quantum Dots.2
- Ovarian Cancer
- Breast Cancer
Ovarian cancer is the second most common malignancy of the female genital tract and the leading cause of death from gynecological malignancies. Carbohydrate antigen 125 (CA 125) is an epithelial antigen and a useful tumor marker in the detection and therapy of ovarian cancer. Scientists have successfully used QDs to detect CA 125 in ovarian cancer specimens with high specificity and sensitivity. Comparison between QDs and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) showed that QDs labeling signals were brighter, more specific, and stable than those of FITC.
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is overexpressed in approximately 25-30% of invasive breast cancer and plays an important role in breast cancer prognosis and treatment selection. In a study, scientists used QDs conjugated with antibodies for assessment of HER2 status in breast cancer. The study showed that compared with conventional IHC, QDs-immunohistochemistry (QDs-IHC) analysis system is more sensitive, accurate, and economic.
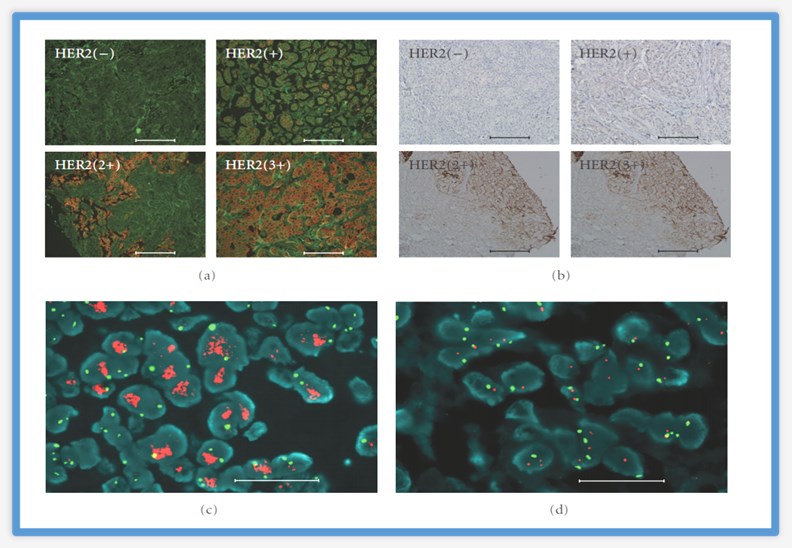 Fig.3 Accurate HER2 testing by QDs-IHC. (Peng, 2010)
Fig.3 Accurate HER2 testing by QDs-IHC. (Peng, 2010)
QDs for Tissue and Cellular Imaging
One promising application for QDs in the IVD field is immune-histofluorescence (IHF), in which QD-antibody conjugates are used for tissue staining. Tissues are usually preserved as formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) or frozen and then cut into thin tissue sections (5-10 mm) for clinical imaging-based diagnostics. FFPE sections are well suited for high-quality histological staining. Multiple-fluorophore-based staining allows higher-order multiplexing for maximum information retrieval from patient tissue biopsy to uncover the underlying genetic and phenotypic characteristics, which are important for establishing personalized medicine approaches.
Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive IVD development services from gene level to tissue level by many diagnostic platforms. If you want to know more information, please directly contact us.
References
- Peng, Chun-Wei, and Yan Li. "Application of quantum dots-based biotechnology in cancer diagnosis: current status and future perspectives." Journal of Nanomaterials 2010 (2010): 1-6.
- From Wikipedia: By Walkman16 - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:QD_S.jpg
For Research Use Only.