Entamoeba-derived Exosome Research & Application
Overview Workflow Insights Advantages Testimonials FAQs
Overview
Exosomes derived from Entamoeba histolytica, the causative agent of amoebiasis, have become an increasingly important focus in parasitology research. These exosomes are key mediators of inter-parasite communication and regulation of host immune responses. Recent studies suggest that Entamoeba-derived exosomes can influence the immune system by modulating host immune cells, such as neutrophils, while also facilitating parasite-to-parasite communication. The cargo within these exosomes, including small RNA molecules and proteins like Gal/GalNAc lectin and calreticulin, is critical in facilitating these interactions and enhancing the immune-modulating abilities of the exosomes. Understanding the mechanisms by which Entamoeba exosomes regulate immune responses and parasite behavior offers valuable insights into the parasite's pathogenesis and suggests novel strategies for parasite management.
Creative Biolabs provides specialized isolation and profiling services for Entamoeba-derived exosomes, enabling researchers to delve deeper into these complex biological processes. Our team can assist in dissecting how these exosomes contribute to immune modulation and inter-parasitic communication, paving the way for further investigations in parasitology.
Isolation Workflow for Entamoeba-Derived Exosomes
At Creative Biolabs, we follow a meticulous process for isolating Entamoeba exosomes while offering additional optional services for detailed characterization. Our standard protocol ensures high-purity exosomes, which are essential for downstream analyses such as proteomic profiling and functional assays.
Standard Exosome Isolation Workflow:
-
Culture Preparation:
-
Axenically culture Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites under standard conditions to ensure optimal parasite growth.
-
Once in mid-log phase, transfer trophozoites into encystation media to stimulate cyst formation.
-
Medium Collection:
-
After culturing, collect Entamoeba culture media and centrifuge at low speed to remove larger cellular debris.
-
Filter the supernatant to clear any remaining contaminants.
-
Exosome Enrichment:
-
Sediment exosomes from the supernatant using specific chemical reagents and centrifuge again to concentrate exosome particles.
-
The final exosome precipitate is collected for subsequent analysis.
-
Purification and Concentration:
-
Purify the exosome fraction using high-speed ultracentrifugation.
-
Further refinement may include sucrose gradient centrifugation to ensure high-quality exosome preparation.
Optional Additional Services:
-
Characterization (optional):
-
Advanced techniques, such as electron microscopy (EM), nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), and Western blotting, for size distribution and marker identification.
-
Molecular Profiling (optional):
-
Small RNA sequencing, proteomic profiling, and lipidomic analysis to deeply explore the composition of Entamoeba-derived exosomes.
-
Functional Studies (optional):
-
Immune modulation assays, such as ROS production or NETosis quantification, to assess the functional impact of exosome cargo on host immune cells.
Get in touch with Creative Biolabs to customize your Entamoeba exosome isolation workflow according to your research needs.
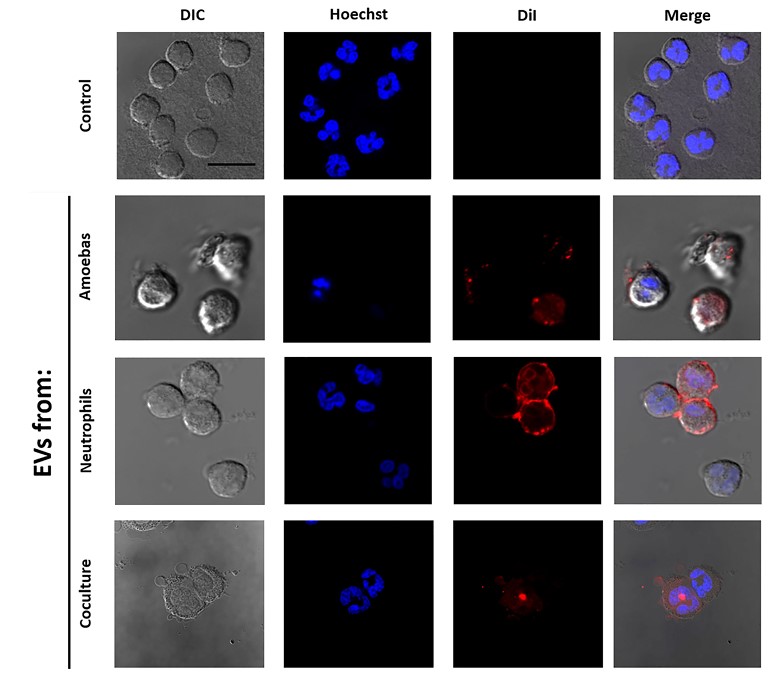 Fig.1 Interaction of EVs from E.histolytica trophozoites, neutrophils or coculture with human neutrophils.1
Fig.1 Interaction of EVs from E.histolytica trophozoites, neutrophils or coculture with human neutrophils.1
Insights into Entamoeba-Derived Exosomes and Their Features
Below is a summary of recent research findings on Entamoeba-derived exosomes, which highlight their complex cargo and potential roles in parasitic communication and immune modulation.
|
Research Focus
|
Findings and Insights
|
|
Protein Cargo
|
Proteomic analysis showed that Entamoeba-derived exosomes are enriched in Gal/GalNAc lectin proteins while being depleted of cytoskeletal proteins, confirming selective protein loading.
|
|
Proteomic Profiling
|
Mass spectrometry revealed that Entamoeba exosomes contain proteins involved in vesicle formation, molecular binding, and intracellular signaling, with little association with plasma membrane or other endosomal compartments.
|
|
Small RNA Profiling
|
PAGE assays identified 27-nt small RNAs, predominantly tRNA fragments, in exosomes. These small RNAs were resistant to RNase A digestion, suggesting they play a role in RNA interference (RNAi).
|
|
Exosome Function in Encystation
|
Functional assays demonstrated that exosomes from encysting Entamoeba promoted the encystation of other parasites, while exosomes from trophozoites hindered encystation, highlighting inter-parasite communication.
|
|
ROS Regulation in Neutrophils
|
Co-culture exosomes from Entamoeba trophozoites and neutrophils induced higher ROS production, suggesting an immune-modulating role.
|
|
Impact on NETosis
|
Exosomes from Entamoeba trophozoites suppressed neutrophil respiratory burst and NETosis, demonstrating an immune evasion strategy employed by the parasite.
|
For a deeper understanding of how Entamoeba-derived exosomes impact immune functions, reach out to Creative Biolabs' team for detailed analysis and consultation.
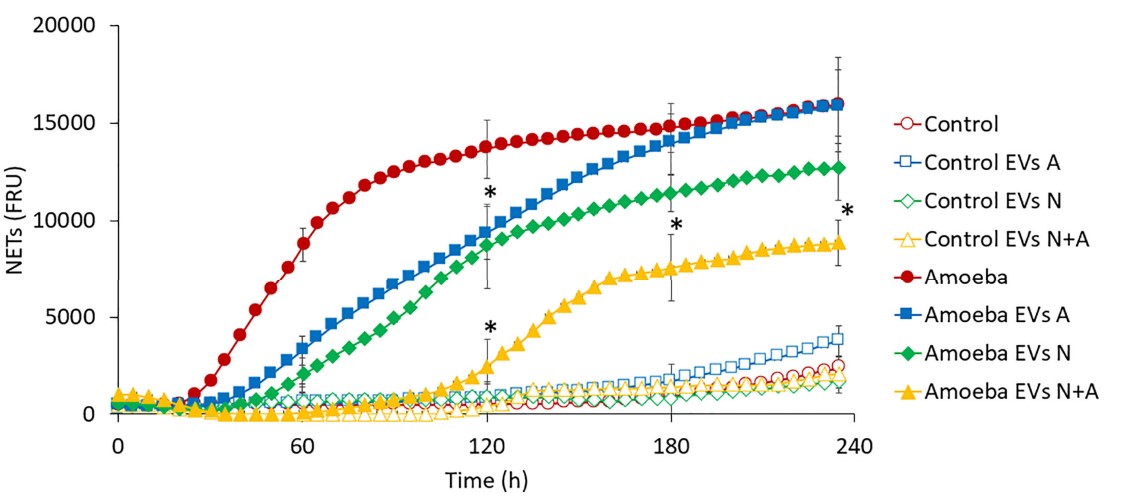 Fig.2 Exosomes derived from Entamoeba regulated NETosis in Entamoeba histolytica-stimulated neutrophils.2
Fig.2 Exosomes derived from Entamoeba regulated NETosis in Entamoeba histolytica-stimulated neutrophils.2
Key Advantages of Working with Creative Biolabs
 Comprehensive Exosome Isolation:
Comprehensive Exosome Isolation:
Creative Biolabs provides a robust, reproducible protocol for isolating exosomes with high purity, tailored to your specific experimental requirements.
 Customization and Flexibility:
Customization and Flexibility:
We offer optional services for in-depth characterization and profiling, allowing you to investigate various biological aspects of Entamoeba-derived exosomes, such as protein cargo, RNA composition, and functional effects.
 State-of-the-Art Technology:
State-of-the-Art Technology:
Creative Biolabs utilizes cutting-edge technologies like mass spectrometry, NTA, and EM to provide reliable, high-resolution data that supports your research goals.
 Expert Scientific Support:
Expert Scientific Support:
Our team of experts in parasitology and exosome biology provides invaluable insights into the complexities of Entamoeba exosomes, ensuring your project progresses smoothly and efficiently.
Contact Creative Biolabs today for a consultation on how we can support your Entamoeba-derived exosome research and provide reliable results.
Customer Reviews
-
"We are extremely pleased with the results from Creative Biolabs' exosome isolation service. The exosome samples were of high quality, and the functional assays provided meaningful insights into Entamoeba interactions."
-
"The team at Creative Biolabs was highly knowledgeable and guided us through the entire process—from exosome isolation to RNA sequencing. Their customized approach helped us gain a better understanding of Entamoeba-host interactions."
-
"Creative Biolabs' commitment to quality and their flexibility in offering optional profiling services made our research much easier and more productive. We highly recommend their exosome research services."
Join other research teams who trust Creative Biolabs for expert guidance in Entamoeba-derived exosome studies. Contact us to get started with your project.
The research on Entamoeba-derived exosomes opens new pathways to understand parasite behavior and host-pathogen interactions. Creative Biolabs provides high-quality services in exosome isolation, profiling, and functional studies, enabling deeper exploration into the molecular mechanisms driving parasitic diseases. Our customized solutions will meet the unique needs of your research. Reach out to Creative Biolabs for a personalized consultation and discover how we can support your exosome research goals.
FAQs
Q: What are the key molecular components found in exosomes derived from Entamoeba?
A: Entamoeba-derived exosomes typically contain a unique composition. Specific proteins associated with cell signaling, immune responses, and metabolic processes have been identified as key components, which can provide insights into the biological functions and potential roles of these exosomes in Entamoeba biology.
Q: How do the characteristics of Entamoeba-derived exosomes differ from those of exosomes from other eukaryotic sources?
A: Entamoeba-derived exosomes exhibit distinct physicochemical properties, such as size, lipid composition, and protein profiles, that can differ significantly from exosomes derived from mammalian cells. The unique adaptation of Entamoeba to its environment may influence the biogenesis and cargo packaging of its exosomes, leading to specialized functional roles.
Q: What role do Entamoeba-derived exosomes play in intercellular communication?
A: Entamoeba-derived exosomes may facilitate intercellular communication by transferring bioactive molecules that can modulate the behavior of host cells or neighboring microorganisms. This process could influence immune responses, cell signaling pathways, and even the behavior of other protists in the microbial ecosystem.
Q: Are there any known receptors or mechanisms through which host cells uptake Entamoeba-derived exosomes?
A: While the exact mechanisms are still under investigation, studies suggest that host cells can recognize and internalize Entamoeba-derived exosomes through specific receptor-mediated endocytosis pathways. Identifying these receptors can provide valuable insights into how Entamoeba communicates with its host and the potential implications for pathogenicity.
Q: What potential applications do Entamoeba-derived exosomes have in biotechnology or environmental science?
A: Entamoeba-derived exosomes may have several applications in biotechnology, such as serving as delivery vehicles for biomolecules in synthetic biology or as tools for environmental monitoring of amoebic infections in ecological studies. Their unique properties may also lend themselves to novel approaches in biosensing or bioimaging technologies.
Q: How do environmental factors influence the biogenesis and functionality of Entamoeba-derived exosomes?
A: Environmental factors such as nutrient availability, temperature, and cellular stress can significantly impact the biogenesis of Entamoeba-derived exosomes. These conditions can alter the exosome's cargo and influence its bioactivity, potentially affecting how Entamoeba interacts with its environment and host organisms.
Q: What challenges exist in studying Entamoeba-derived exosomes compared to those from other organisms?
A: Studying Entamoeba-derived exosomes presents unique challenges, including the difficulty in culturing Entamoeba in laboratory settings, the complex nature of exosome isolation, and the need for specific methods to analyze their content accurately. Additionally, understanding the functional roles of these exosomes within the context of Entamoeba's life cycle and host interactions remains an ongoing area of research.
References
-
Díaz-Godínez, César, et al. "Immunomodulatory effect of extracellular vesicles from Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites: Regulation of NETs and respiratory burst during confrontation with human neutrophils." Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 12 (2022): 1018314. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.1018314.
-
Díaz-Godínez, César, et al. "Immunomodulatory effect of extracellular vesicles from Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites: Regulation of NETs and respiratory burst during confrontation with human neutrophils." Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 12 (2022): 1018314. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only Part C of the original image and revising the title. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2022.1018314.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Interaction of EVs from E.histolytica trophozoites, neutrophils or coculture with human neutrophils.1
Fig.1 Interaction of EVs from E.histolytica trophozoites, neutrophils or coculture with human neutrophils.1
 Fig.2 Exosomes derived from Entamoeba regulated NETosis in Entamoeba histolytica-stimulated neutrophils.2
Fig.2 Exosomes derived from Entamoeba regulated NETosis in Entamoeba histolytica-stimulated neutrophils.2









