Protozoon-derived Exosome Research & Applications
Overview Protozoan Exosomes Advantages Testimonials FAQs
At Creative Biolabs, we specialize in research on protozoon-derived exosomes, advancing our understanding of these biological molecules and their roles in various infectious processes. Protozoon-derived exosomes facilitate communication between protozoan cells and host cells, impacting immune responses, parasitic survival, and pathogen resistance. Our research aims to help clients uncover the biological mechanisms of protozoa and their interactions with hosts, supporting innovative applications in therapeutic development, drug resistance studies, and biomarker discovery.
Overview
Protozoon-derived exosomes play a pivotal role in pathogen-host interactions. These vesicles are secreted by protozoan cells and released into the surrounding environment, serving as mediators of signaling between the protozoa and host cells. Exosomes carry a variety of bioactive molecules, such as proteins, lipids, and RNAs, that facilitate communication, modulate immune responses, and aid in the survival and adaptation of protozoa in hostile environments. They contribute to the pathogenesis of various protozoal infections by enhancing drug resistance, immune evasion, and host cell manipulation.
Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive services for the study of protozoon-derived exosomes, offering in-depth isolation, characterization, and functional analysis. We help researchers unlock the potential of these exosomes for a wide range of applications, from vaccine development to studying immune responses.
Contact Creative Biolabs for advanced research services on protozoon-derived exosomes and their applications in your studies.
Exosomes from Multiple Protozoan Sources
Protozoon-derived exosomes are produced by a variety of protozoa and are involved in numerous infectious diseases and immune evasion strategies. Below, we highlight the research on exosomes from several protozoan species and their roles in host-pathogen interactions.
|
Protozoon-derived Exosomes
|
Research
|
|
Leishmania-derived Exosome
|
Leishmania exosomes carry virulence factors, including the metalloproteinase GP63, and play a significant role in cutaneous leishmaniasis. They protect Leishmania RNA virus 1, enhancing their stability and aggressiveness.
|
|
Giardia-derived Exosome
|
Giardia exosomes contain antigenic proteins involved in immune evasion, with their release influenced by pH and cholesterol levels. Proteomic analysis revealed their role in modulating immune responses during infection.
|
|
Trypanosoma brucei-derived Exosome
|
Trypanosoma brucei exosomes mediate immune escape by transferring serum resistance-associated proteins, causing erythrocyte clearance and inducing anemia. They also promote regulatory T-cell differentiation.
|
|
Trypanosoma cruzi-derived Exosome
|
Exosomes from T. cruzi stimulate bone marrow macrophages, increasing prostaglandin E2 expression and lipid droplet formation, which supports parasite replication.
|
|
Naegleria fowleri-derived Exosome
|
Exosomes from Naegleria fowleri contribute to immune modulation, increasing the risk of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis by affecting monocyte surface expression of CD86 and HLA-DR.
|
|
Trichomonas-derived Exosome
|
Trichomonas exosomes contain small RNAs, including fragments of 5′ tRNA, and mediate communication between parasite strains to enhance cytoneme and filopodia formation.
|
|
Entamoeba-derived Exosome
|
Exosomes from Entamoeba regulate immune responses and are involved in the process of parasite encystation. Proteomic profiling revealed the presence of Gal/GalNAc lectins and calreticulin markers.
|
|
Acanthamoeba-derived Exosome
|
Acanthamoeba exosomes from non-pathogenic strains exhibit stronger immune-stimulating protease-dependent functions than those from pathogenic strains.
|
|
Plasmodium-derived Exosome
|
Plasmodium exosomes contain virulence proteins involved in parasite growth and infestation, offering new insights into drug resistance and parasite pathogenesis.
|
|
Neospora-derived Exosome
|
Neospora-derived exosomes carry antigens and regulators of pathogenesis, and play a role in maintaining host infection. They hold potential for use in vaccines.
|
|
Toxoplasma-derived Exosome
|
Exosomes from Toxoplasma gondii have been studied for their potential in immunization to prevent tachyzoite infections, increasing survival rates and neutralizing antibodies.
|
Reach out to Creative Biolabs for more details on our research services involving protozoon-derived exosomes from these species.
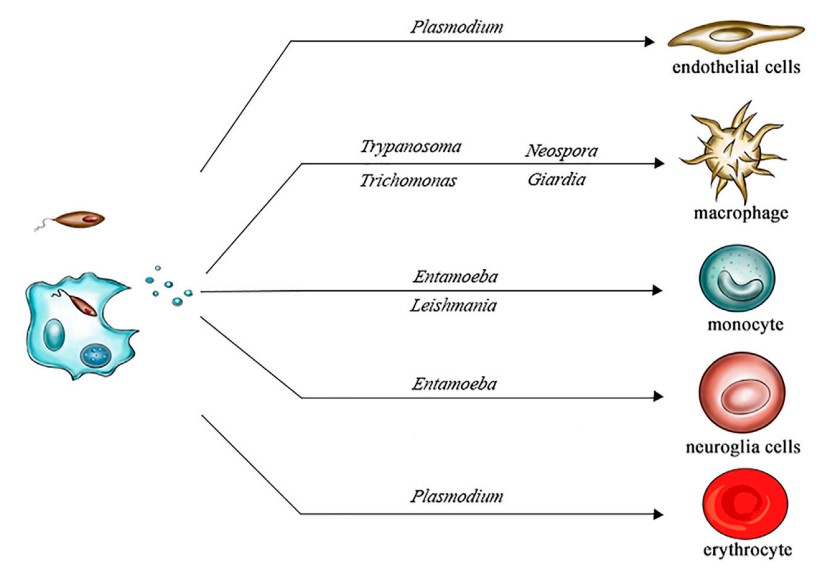 Fig.1 Various protozoa release exosomes that infect various cells.1
Fig.1 Various protozoa release exosomes that infect various cells.1
Benefits of Working with Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs offers several advantages in the study of protozoon-derived exosomes:

Expertise in Protozoon Exosome Research
Our team of scientists specializes in protozoon exosome isolation, characterization, and functional analysis.

Comprehensive Service
We provide end-to-end services, from exosome isolation to advanced functional studies and characterization.

Broad Range of Protozoa
Our services cover exosomes from multiple protozoan species, enabling a comprehensive understanding of their biological roles.

Customizable Research Solutions
Whether you need exosome profiling, functional analysis, or application studies, Creative Biolabs offers flexible services tailored to your research goals.
Contact us to discuss your protozoon-derived exosome research needs and explore how Creative Biolabs can assist in advancing your work.
Customer Testimonials
At Creative Biolabs, we value the feedback from our clients and are proud to support their research in protozoon-derived exosome studies. Here are some of their experiences:
"We have been working with Creative Biolabs for over a year now on our project involving Plasmodium-derived exosomes. Their expertise in isolating and characterizing exosomes has been invaluable to our research."
"The high-quality exosome preparations provided by Creative Biolabs have enabled us to make significant advances in understanding immune modulation in Toxoplasma gondii infections."
"Creative Biolabs' team is highly knowledgeable and responsive, and their services have been crucial in our study of protozoon exosomes and their role in immune evasion."
Contact Creative Biolabs today to get started on your protozoon-derived exosome research and see how our services can support your scientific goals.
Protozoon-derived exosomes are a rapidly evolving research frontier that bridges parasitology, immunology, and molecular biology. At Creative Biolabs, we are dedicated to supporting scientists with reliable, data-driven services that accelerate discovery and deepen understanding of protozoan communication systems. Whether your focus is on exosome isolation, proteomic profiling, or intercellular signaling mechanisms, our experienced team and advanced technical platform can provide the expertise and precision you need. Contact us to discuss your project or request a custom proposal. Our specialists will help design a solution that fits your research objectives and budget.
FAQs
Q: What methods do you use for the isolation of protozoon-derived exosomes, and how do they compare in terms of yield and purity?
A: We employ a variety of techniques for exosome isolation, including ultracentrifugation and size-exclusion chromatography. Each method has its advantages, and the choice often depends on the specific protozoon species and the intended application. Our studies indicate that size-exclusion chromatography often yields higher purity, while ultracentrifugation may provide a better overall yield.
Q: How do you characterize the biological activity of protozoon-derived exosomes?
A: We characterize biological activity through several assays, including in vitro cell uptake studies and functional gene expression analyses in recipient cells. This comprehensive assessment helps us determine the exosomes' roles in intercellular communication and their mechanisms of action.
Q: What are some specific applications of protozoon-derived exosomes in biotechnology or environmental science?
A: Protozoon-derived exosomes have potential applications in environmental monitoring, particularly in biomarker discovery for pollution exposure. They can also be utilized in biotechnology for developing biodegradable materials or bioindicators due to their unique molecular compositions and interactions with surrounding environments.
Q: How do you ensure the integrity of the exosomes throughout the research process?
A: We implement strict protocols for sample handling and processing, including maintaining cold chain conditions and minimizing freeze-thaw cycles. Additionally, we use standardized procedures for isolation and storage to preserve the structural and functional integrity of the exosomes.
Q: Can you provide examples of specific protozoon-derived exosomes that have shown promise in diagnostic applications?
A: Research has shown that exosomes derived from species like Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia lamblia can carry unique surface markers and genetic materials relevant to infections. These characteristics hold promise for developing diagnostic tools that could improve the accuracy and speed of identifying protozoan diseases in clinical settings.
Reference
-
Wang, Xinlei et al. "The state of the art of extracellular vesicle research in protozoan infection." Frontiers in genetics vol. 13 941561. 12 Aug. 2022. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2022.941561.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Various protozoa release exosomes that infect various cells.1
Fig.1 Various protozoa release exosomes that infect various cells.1













