Pancreatic Cancer Tissue Exosome Research and Application
Overview Services Biological Functions Advantages Application Areas Client Feedback FAQ
Scientific Context: Exosomes as Drivers of Pancreatic Tumor Biology
Pancreatic cancer, especially pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), is characterized by aggressive progression, early metastasis, and poor prognosis. One emerging hallmark of PDAC is the active role of extracellular vesicles, especially exosomes, in intercellular communication. These nanoscale vesicles carry a diverse cargo of proteins, lipids, mRNAs, and non-coding RNAs that reprogram recipient cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME) and distant organs.
Pancreatic tumor-derived exosomes have been found to:
-
Stimulate pancreatic stellate cell activation and fibrotic stroma formation
-
Promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)
-
Enable immune evasion and immune cell reprogramming
-
Establish pre-metastatic niches in organs like the liver and lungs
-
Mediate resistance to chemotherapeutic agents
Understanding how tissue-derived exosomes regulate these pathways can unlock new targets for early detection and treatment of pancreatic cancer. At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to empowering academic and translational researchers with cutting-edge tools and services for studying pancreatic cancer tissue-derived exosomes. Leveraging years of scientific experience in exosome biology, molecular profiling, and tumor microenvironment modeling, our platform offers customized support for projects exploring the biological and pathological functions of exosomes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC).
What We Offer: Comprehensive Pancreatic Exosome Research Services
We provide end-to-end experimental support tailored for academic, biotech, and pharmaceutical research teams. Our flexible service modules can be combined into integrated projects or accessed individually.
-
High-Yield Exosome Isolation from Pancreatic Tissues
-
Mechanical dissociation or enzymatic digestion of tumor tissues
-
Differential ultracentrifugation and/or size exclusion chromatography (SEC)
-
Validation via nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), TEM, and western blot
-
Molecular and Functional Profiling
-
Proteomic profiling via LC-MS/MS
-
miRNA/mRNA sequencing to uncover functional cargo
-
Surface marker identification (e.g., CD63, CD9, EpCAM, TSPAN8)
-
Mechanism-Based Functional Assays
-
Co-culture experiments with stromal, immune, or endothelial cells
-
Migration/invasion assays and proliferation assays
-
Induction of stellate cell activation or immune cell modulation
-
EMT quantification (Snail, Twist, ZEB1 expression)
-
Custom Study Design & Data Interpretation
-
Experimental strategy consulting for grant proposals or ongoing research
-
Bioinformatic data integration and comparative analysis
-
Customized timelines, reporting, and documentation
Biological Focus Areas of Pancreatic Cancer Exosomes
-
Exosome-Stellate Cell Interactions
A key hallmark of pancreatic cancer is the desmoplastic response—driven by pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs). Exosomes from tumor cells stimulate PSCs, promoting secretion of collagen, fibronectin, and α-SMA, contributing to a stiff and hypoxic microenvironment that supports cancer growth and invasion.
We help researchers study this dynamic interaction and identify exosomal signals that mediate pro-fibrotic reprogramming.
-
Exosomes in Liver Pre-metastatic Niche Formation
Studies show that pancreatic cancer-derived exosomes selectively target hepatic Kupffer cells and induce TGF-β and fibronectin production, thereby recruiting bone marrow-derived macrophages and neutrophils to establish a metastatic niche.
Our platform allows mechanistic investigation into miRNA-mediated pathways (e.g., miR-21, miR-301a) that orchestrate this process.
-
Exosome-Mediated Drug Resistance
We support research into how pancreatic exosomes reduce drug efficacy through:
-
Delivery of miRNA-155 to inhibit dCK and reduce drug metabolism
-
Promotion of EMT through fibroblast-derived exosomes
-
Enrichment of anti-apoptotic proteins that protect tumor cells
These studies aid in identifying new targets to reverse resistance mechanisms.
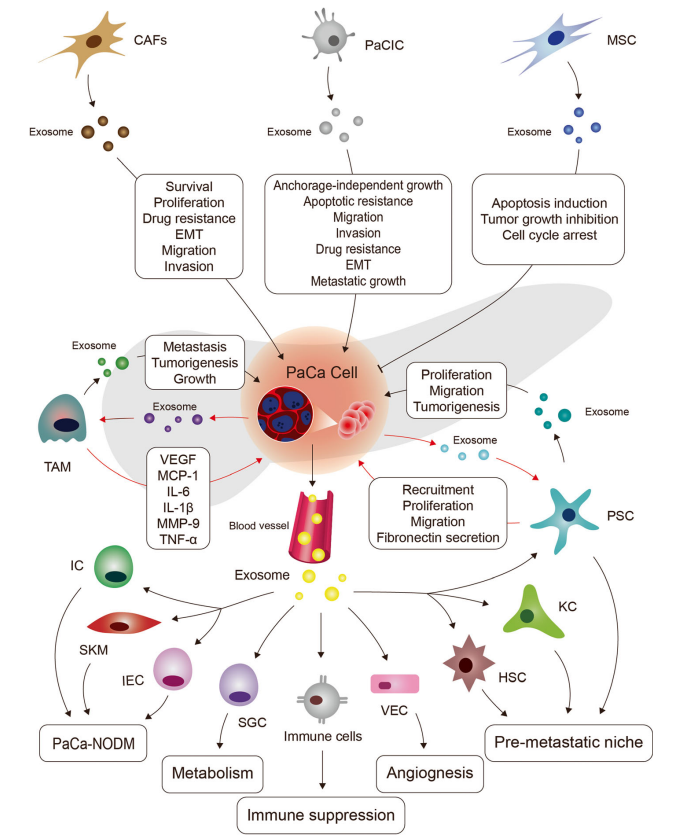 Fig.1 Intercellular crosstalk in pancreatic cancer.1
Fig.1 Intercellular crosstalk in pancreatic cancer.1
Advantages of Partnering with Creative Biolabs
Our lab stands out for the following strengths:
-
Extensive Exosome Expertise: Specialized knowledge in tissue-derived vesicle processing, which is more complex than cell line or fluid-derived samples.
-
Multi-Omics Integration: Combine transcriptomic, proteomic, and bioinformatics approaches to derive actionable insights.
-
Flexible, Research-Focused Approach: We collaborate closely with academic researchers and adapt protocols to suit novel scientific questions.
-
Transparent Communication: We provide clear documentation, timeline updates, and co-publication opportunities when needed.
Research Applications We Support
Whether you're pursuing a hypothesis-driven study or conducting exploratory profiling, our services support diverse goals:
-
Biomarker discovery from early-stage or resected pancreatic tumor tissue
-
Studying tumor-stroma communication using co-culture models
-
Investigating exosome immune modulatory effects
-
Assessing therapeutic efficacy or resistance mechanisms
-
Screening for candidate targets in engineered exosome research
What Our Clients Say
"Creative Biolabs' support in isolating and characterizing pancreatic tumor-derived exosomes significantly accelerated our biomarker discovery project. Their flexibility and scientific input made a real difference."
— Dr. KiXXXX, USA
"The team went above and beyond to help us analyze the impact of miRNA-enriched exosomes on stellate cell behavior. Their technical expertise in vesicle isolation from dense tumor tissue was impressive."
— Dr. RaXXXX, Spain
If you are investigating the mechanisms of pancreatic tumor progression, treatment resistance, or metastatic spread, exosomes offer a promising research avenue. With Creative Biolabs, you gain not just a service provider—but a research partner. Contact us today to discuss your project and receive a free consultation.
Common Questions
Q: How do you ensure the integrity of exosome samples during isolation?
A: We employ stringent protocols that minimize shear stress and avoid contamination, utilizing ultracentrifugation and size-exclusion chromatography under controlled conditions to maintain the integrity and purity of exosome samples.
Q: What types of analyses can you perform on exosome content?
A: We provide a range of analytical services, including surface marker profiling via western blot, RNA sequencing for transcriptomic analysis, and mass spectrometry for proteomic assessment, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of exosomal molecular signatures.
Q: Can you provide support for downstream applications using exosome samples?
A: Yes, we offer guidance and technical support for various downstream applications such as functional assays, co-culture systems to study tumor-stroma interactions, and potential biomarker validation studies, helping to streamline your research process.
Q: Is co-culture model setup included in your services?
A: We offer optional co-culture assays using pancreatic stellate cells, macrophages, or other TME-relevant cell types, depending on your research goal.
Q: Can you help us identify novel exosomal miRNA biomarkers?
A: Yes, we provide full miRNA-seq services, from RNA extraction to library prep, sequencing, and differential expression analysis.
Q: How can exosome research enhance our understanding of pancreatic cancer biology?
A: Exosome research can reveal critical insights into tumor progression, immune modulation, and cancer metastasis, shedding light on the molecular mechanisms driving pancreatic cancer and identifying novel biomarkers for early detection and monitoring.
Q: Is it possible to collaborate on multidisciplinary projects involving exosome research?
A: Absolutely! We encourage collaborations that integrate multiple disciplines, combining expertise in molecular biology, bioinformatics, and systems biology to advance the field of pancreatic cancer research through innovative exosome studies.
Reference
-
Sun, Wei, et al. "The potential roles of exosomes in pancreatic cancer initiation and metastasis." Molecular cancer 19 (2020): 1-18. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Intercellular crosstalk in pancreatic cancer.1
Fig.1 Intercellular crosstalk in pancreatic cancer.1









