Recent years, electrochemical approaches have received particular attention due to their rapid detection and great sensitivity for the evaluation of DNA-hazard compounds interaction mechanisms. Creative Biolabs has developed different types of bioanalytical method using nucleic acids probes to detect DNA damage. With rich experience and advanced platform, Creative Biolabs firmly grasps the current directions and strategies in the development and applications of electrochemical DNA sensors for the detection of DNA damage. We provide customized electrochemical DNA biosensors development services for DNA damage detection.
Overview
DNA is a very important biomolecule that has an essential role in the determination of hereditary characteristics. Many compounds bind and interact with DNA causing changes to the structure of DNA and the base sequences, leading to perturbations in DNA replication or cancer. Therefore, it is very important to illustrate the factors that determine affinity and selectivity in binding molecules to DNA, identify these chemical species and ascertain their potency so that human exposure to them can be minimized.
DNA Damage
Oxidative DNA damage caused by oxygen-free radicals leads to various modifications in DNA, such as base-free sites and oxidized bases. The major product of DNA oxidative damage is 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (8-oxoGua). 8-oxoGua, the deoxynucleoside form of 8-oxodGuo, has been the subject of intensive investigation and has become widely accepted as a biomarker of oxidative DNA damage and cellular oxidative stress. At present, HPLC with electrochemical detection (HPLC-ECD) and HPLC with tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) are the most commonly used technique to assess urinary 8-oxodGuo.
The oxidation of the other DNA bases is much more difficult due to their high oxidation potentials. Oxidative damage to DNA by free radicals and exposure to ionizing radiation generates several products within the double helix besides 8-oxoGua, such as 2,8-dihydroxyadenine, 5-formyluracil, and 5-hydroxycytosine.
Electrochemical Biosensors for DNA Damage Detection
The development of electrochemical DNA-biosensors has opened a wide perspective using particularly sensitive and selective methods for the detection of specific interactions. Compared with other transducers, electrochemical ones received particular interest due to a rapid detection and great sensitivity. Combining the characteristics of DNA probes with the capacity of direct and label-free electrochemical detection represents an attractive solution in the detection of DNA base damage.
Among various electrochemical transducers, carbon electrodes exhibit some unique properties and the wide electrochemical potential window in the positive direction allows sensitive electrochemical detection of oxidative damage caused to DNA by monitoring the appearance of oxidation peaks of DNA bases. To design efficient DNA-electrochemical biosensors, Creative Biolabs is fully armed with knowledge concerning the structure and the electrochemical characteristics of DNA molecules. We are able to provide customized DNA damage detection services according to your project needs.
- Detection of DNA damage caused by reduced adriamycin
- Detection of DNA damage caused by reduced thiophene-S-oxide
- Detection of DNA damage caused by hydroxyl radicals
- Detection of DNA damage caused by organic xenobiotics
- Detection of DNA damage caused by hydroquinone and catechol
- Drug/DNA interaction and mechanism research
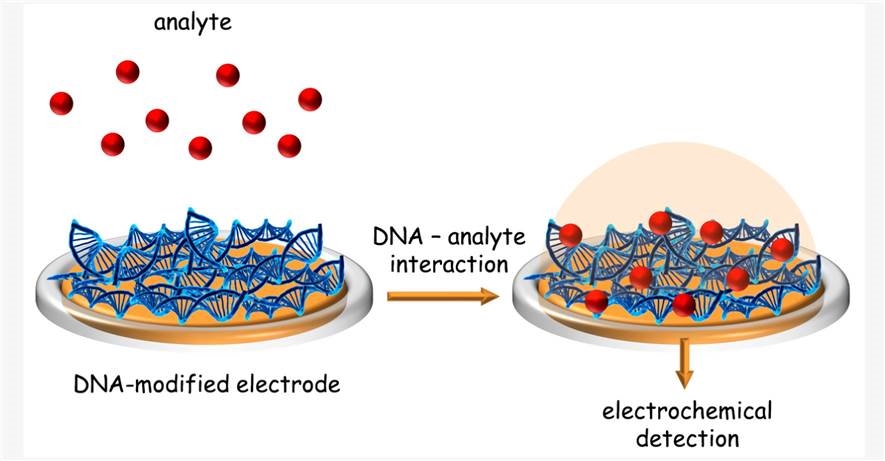 Fig.1 Schematic representation of DNA electrochemical biosensor design and operation.1, 2
Fig.1 Schematic representation of DNA electrochemical biosensor design and operation.1, 2
Electrochemical DNA-biosensors have proved to be excellent tools for investigating the effect of various endogenous and exogenous sources of hazard to genomic material, allowing quick and low cost determination of DNA damage. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us for more information.
Published Data
1. Electrochemical DNA Sensor Based on Poly(proflavine) for DNA Damage Detection and Antioxidant Assessment
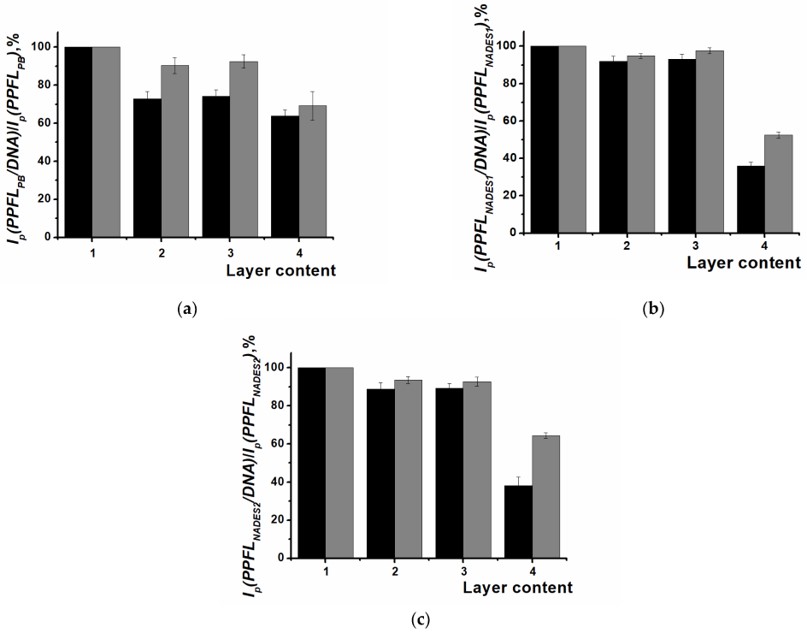 Fig.2 Voltammetric detection of oxidative DNA damage through DNA sensor developed from poly(proflavine).3,2
Fig.2 Voltammetric detection of oxidative DNA damage through DNA sensor developed from poly(proflavine).3,2
In this study, researchers developed electrochemical DNA sensors using electroactive polymer poly(proflavine) (PPFL) for detecting DNA damage. The polymer was synthesized on screen-printed carbon electrodes (SPCEs) using phosphate buffer (PB) and two natural deep eutectic solvents (NADESs) containing malonic or citric acids, D-glucose, and water. Poly(proflavine) coatings were electrochemically polymerized to distinguish thermal and oxidative DNA damage. Cyclic voltammetry, scanning electron microscopy, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy were employed to analyze the electrochemical properties and morphology of the coatings. The voltammetric approach differentiated native and oxidized DNA, while the impedimetric approach identified native, thermally denatured, and oxidized DNA by observing changes in charge transfer resistance. The impact of antioxidants and pharmaceuticals on oxidative DNA damage was also explored.
2. A Novel Label-Free Paper-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Oxidative Stress Biomarker 8-OHdG Detection
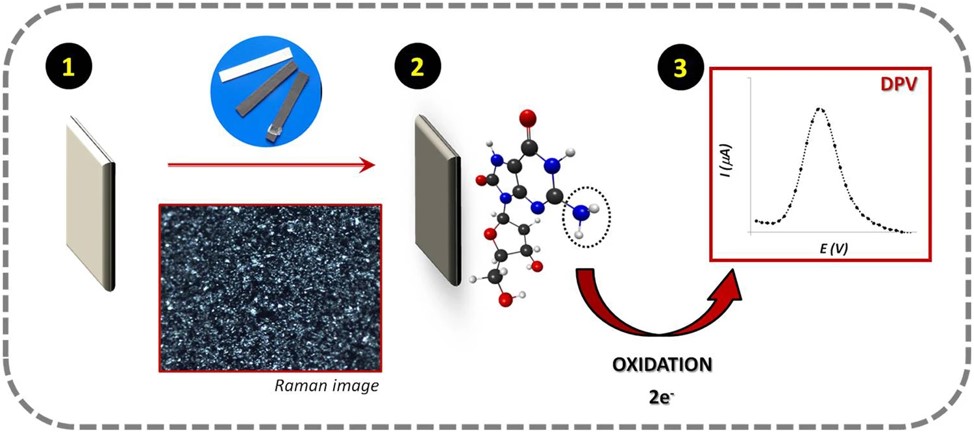 Fig.3 Schematic illustration of the oxidation process of the 8-OHdG molecule observed on a conductive carbon paper substrate.4,2
Fig.3 Schematic illustration of the oxidation process of the 8-OHdG molecule observed on a conductive carbon paper substrate.4,2
This study introduced an affordable, label-free point-of-care (POC) biosensor for sensitive detection of 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG), a key oxidative DNA damage marker linked to cancer. The device employed a carbon-ink 3-electrode setup on a paper substrate, combined with Differential Pulse Voltammetry for direct 8-OHdG detection. The sensor's performance was enhanced by incorporating nanostructured carbon materials and the conducting polymer PEDOT, improving electrocatalytic properties. The oxidative stress biomarker undergoes oxidation, allowing the sensor to function without chemical probes or long incubation times. The paper-based sensor exhibited excellent electrochemical performance, offering a wide linear range (50–1000 ng/ml) and a low detection limit of 14.4 ng/ml. The sensor demonstrated good reproducibility, stability, sensitivity, and selectivity. This carbon-based electrochemical sensor holds promise for miniaturization, enabling in-situ 8-OHdG detection in real biological samples.
References
- Chiorcea-Paquim, Ana-Maria, and Ana Maria Oliveira-Brett. "DNA electrochemical biosensors for in situ probing of pharmaceutical drug oxidative DNA damage." Sensors 21.4 (2021): 1125.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Porfireva, Anna, et al. "Electrochemical DNA Sensor Based on Poly (proflavine) Deposited from Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents for DNA Damage Detection and Antioxidant Influence Assessment." Chemosensors 12.10 (2024): 215.
- Martins, Gabriela V., et al. "based sensing device for electrochemical detection of oxidative stress biomarker 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) in point-of-care." Scientific reports 7.1 (2017): 14558.
For Research Use Only.