The first multiplex immunoassay systems have already been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. This advance implies that miniaturized and parallelized array techniques for protein detection have finally been recognized as powerful tools for predictive early diagnosis of disease. Committed to the development of disease diagnostics strategies over years, Creative Biolabs has established our technology platform and we are confident in offering high-quality protein array development for disease diagnostics services.
Introduction of Protein Array
Protein-detecting microarrays employ a wide variety of capture agents (antibodies, fusion proteins, DNA RNA aptamers, synthetic peptides, carbohydrates, and small molecules) immobilized at high spatial density on a solid surface to selectively extract target proteins from complex mixtures, including serum and cell lysate samples. Extracted proteins may then be rapidly detected and quantified. This approach enables large-scale analyses of protein interactions across the entire proteome (comprehensive proteome analysis) as well as experiments focusing on a limited number of protein interactions (focused proteome analysis) in a high-throughput fashion with less consumption of the sample than occurs with other methods. The protein-detecting microarray is no longer a vision, but rather an indispensable tool for comprehensive proteomic studies that is especially applicable to prediction/early diagnosis of disease.
Examples of Protein Array Application for Disease Diagnostics
- Prostate cancer
The elucidation of blood protein markers that allow more accurate or earlier diagnosis of prostate cancer should have a positive impact on prostate cancer treatment and management. In this context, serum samples from control subjects and patients with benign or malignant prostatic disease were analyzed with antibody arrays targeting multiple candidate prostate cancer markers. Several potential disease-associated protein alterations were discovered, and significant elevation of thrombospondin-1 was observed in patients with benign prostatic cancer disease, with repression in patients with prostate cancer being the most significant.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Specific antimicrobial antibodies present in the sera of patients with IBD are valuable serological biomarkers for the diagnosis prognosis of IBD. The whole E. coli proteome microarray analysis identified 169 proteins as highly immunogenic in healthy controls, 186 proteins as highly immunogenic in Crohn's disease (CD) patients, and only 19 proteins as highly immunogenic in ulcerative colitis (UC) patients. Novel biomarkers for specifically distinguishing CD patients from healthy controls (accuracy: 86.4%) and CD from UC patients (accuracy: 80.2%) were found using a supervised learning algorithm.
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
An independent study using synovial proteome microarrays containing 225 peptides and proteins that represented candidate and control antigens identified that distinct serum antibody profiles in patients with RA. Autoreactive B-cell responses were identified that targeted citrullinated epitopes in distinct subsets of patients who had early RA with a significant predictive predisposition to severe RA. These studies suggested the potential of proteomic analysis for both diagnosis and severity based sub-classification of patients with RA, primarily based on their cytokine and autoantibody profiles.
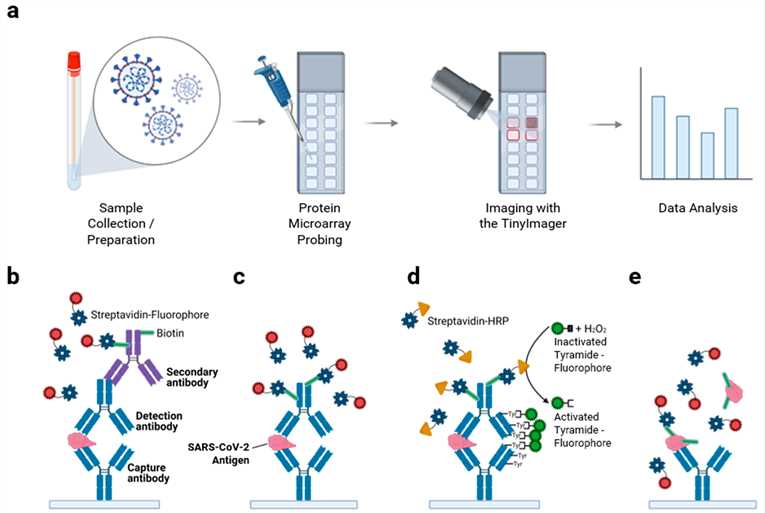 Fig.1 Workflow and antigen detection scheme in protein microarray technology.1, 2
Fig.1 Workflow and antigen detection scheme in protein microarray technology.1, 2
Services at Creative Biolabs
Focusing on the in vitro diagnostics (IVD) development services for years, Creative Biolabs has equipped advanced technologies, the latest facilities, professional expertise, and excellent scientific staff. With all the progress we made step-by-step in practice, we are capable of providing high-quality protein array development services to global customers.
- Professional and experienced
- Top-rated customer experience
- Flexible service form with preferential price
As a global-leading biotechnology company, Creative Biolabs has never stopped making progress. Every effort we made is to provide better service to our customers. If you are interested in protein array development for disease diagnostics services or any other IVD development services, please don't hesitate to contact us for more information.
Published Data
1. Development of a Protein Array for Detecting Antibodies Against Borrelia miyamotoi
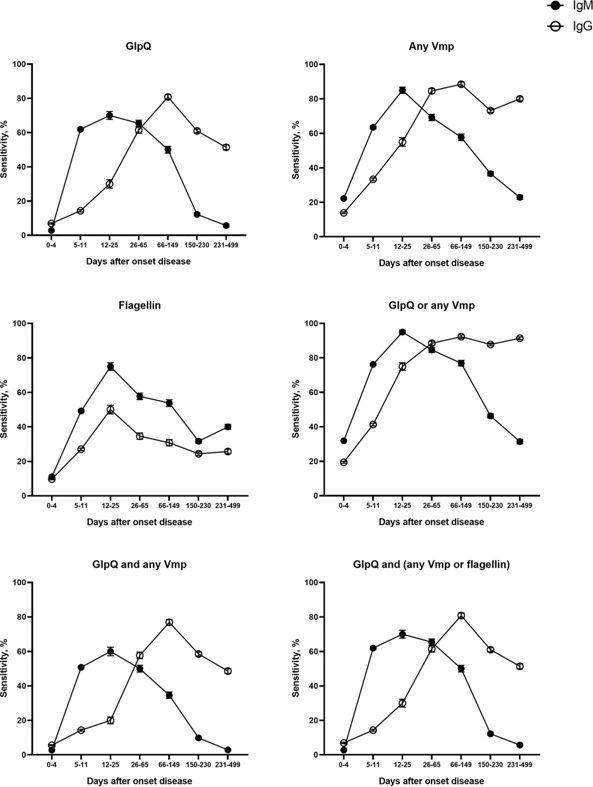 Fig.2 Diagnostic accuracy of individual and combination of antigens in the protein array.3,2
Fig.2 Diagnostic accuracy of individual and combination of antigens in the protein array.3,2
This study developed a protein array to simultaneously detect IgM and IgG responses to various recombinant B. miyamotoi antigens, such as glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase (GlpQ), flagellin, and variable major proteins (Vmps). Sera from PCR-confirmed Borrelia miyamotoi disease (BMD) cases, cross-reactive controls, and healthy individuals from Ixodes-endemic and non-endemic regions were analyzed. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis set the reactivity cutoff at 5 μg/mL for both IgM and IgG. While individual antigens showed high sensitivity, they had relatively low specificity. GlpQ performed best, with 88% sensitivity and 94.2% specificity for IgM/IgG. Using a previously published diagnostic algorithm improved specificity to 98.5% but reduced sensitivity to 79.5%. Researchers proposed seroreactivity be defined as reactivity against GlpQ and any Vmp or flagellin, achieving 84.3% sensitivity and 97.9% specificity. This novel serological tool provides an effective method for diagnosing BMD in clinical and epidemiological settings.
2. Miniaturized Protein Microarray for Serological Screening of IgG Antibodies Against Zoonotic and Production-Related Pathogens in Pigs
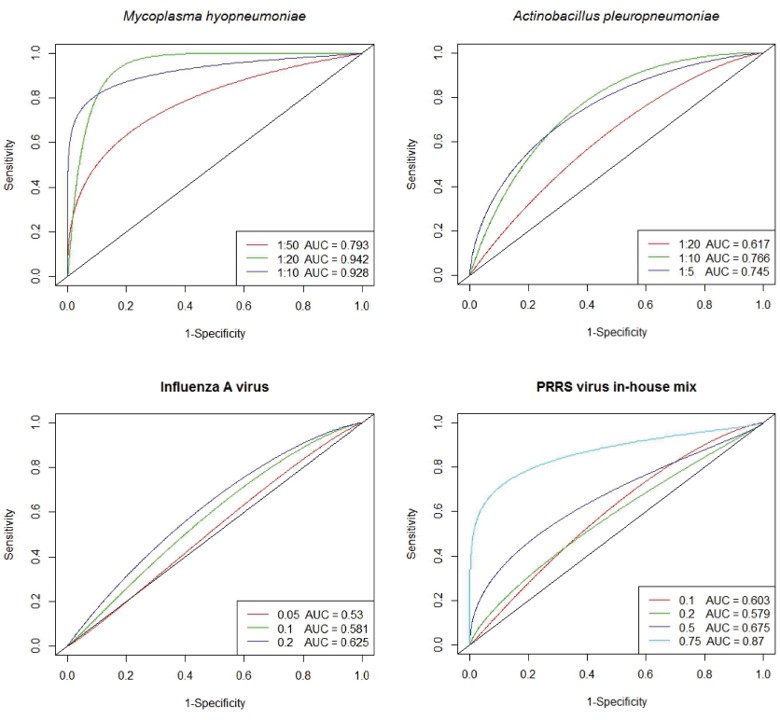 Fig.3 ROC curves for the respiratory diseases.4,2
Fig.3 ROC curves for the respiratory diseases.4,2
This work developed a protein microarray-based assay to detect IgG antibodies against various zoonotic agents and pathogens responsible for production diseases in pigs. Antigens from ten significant swine pathogens were immobilized as ‘antigen-spots’ on microarray chips to test pig serum for antibodies. Serum samples were collected from pigs at three German abattoirs, and ELISA tests were conducted to create a reference panel for microarray analysis. ROC curve analysis, using ELISA results as a reference, demonstrated high area under curve values for antigens from two zoonotic agents, Toxoplasma gondii (0.91) and Yersinia enterocolitica (0.97), as well as three production diseases, Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (0.94), Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae (0.77), and the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (0.87). This new microarray assay enables efficient screening of antibodies against multiple pathogens in a single test, improving herd health monitoring.
References
- Beck, Sungjun, et al. "A protein microarray-based respiratory viral antigen testing platform for COVID-19 surveillance." Biomedicines 10.9 (2022): 2238.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Hoornstra, Dieuwertje, et al. "Development and validation of a protein array for detection of antibodies against the tick-borne pathogen Borrelia miyamotoi." Microbiology spectrum 10.6 (2022): e02036-22.
- Loreck, Katharina, et al. "Development of a miniaturized protein microarray as a new serological IgG screening test for zoonotic agents and production diseases in pigs." PLoS One 14.5 (2019): e0217290.
For Research Use Only.