Rabbits have played an important role in immunology. Today, rabbits are still a major source for a wide variety of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). Rabbits belong to the order Lagomorpha, which is distinct from the Rodentia. Rabbit antibodies are able to recognize epitopes on human antigens and increase the total number of targetable epitopes. mAbs contain a defined antigen-binding site that typically binds with high affinity and specificity to only one epitope. mAbs are currently widely used to treat human diseases, such as cancer and autoimmune diseases and 11 rabbit mAbs are FDA-approved in vitro diagnostic tools in the clinic. Ten of these mAbs are being used to detect the expression of tumor-associated antigens. One mAb is used to detect helicobacter pylori infections.
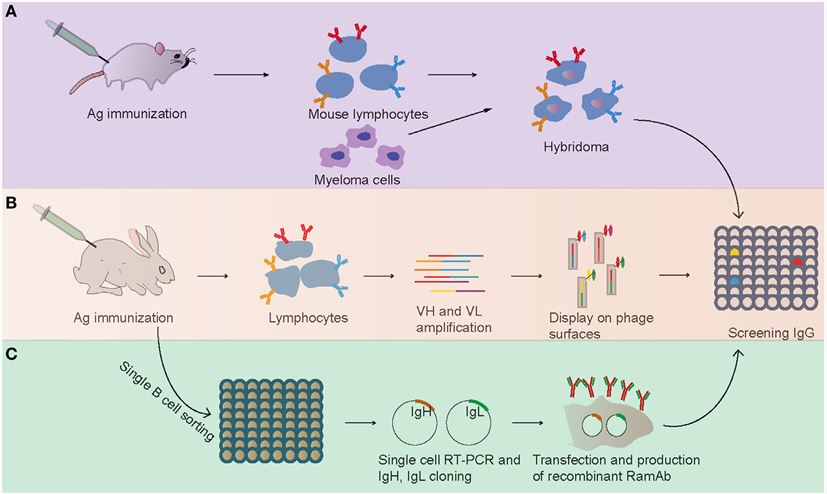 Fig.1 Schematic of rabbit mAb generation.1
Fig.1 Schematic of rabbit mAb generation.1
Generation of Rabbit mAbs
- Hybridoma technology
Hybridoma technology is a method to generate stable cell lines that constantly secret a defined mAb. B cells are fused with a myeloma cell line in polyethylene glycol. The hybridomas are cloned by limiting dilution, screened for favorable mAb and then expanded in culture.There are two hybridoma types: homo-hybridomas where both host B cells and fusion cell line emerged from the same species; hetero-hybridomas derived from two different species. Currently, scientists successfully generated stable rabbit–mouse hetero-hybridoma.
- Phage display technology
Bacteriophage are viruses that infect and replicate within bacteria. The first phage antibody libraries based on pIII fusion proteins were published using either scFv or Fab fragments. The first rabbit antibody library selected by phage display was used a scFv format. Due to the higher expression levels of human compared to rabbit constant domains in bacteria, a chimeric rabbit/human Fab format consisting of rabbit variable domains VL and VH recombinantly fused to human constant domains CL and CH1, respectively, proved particularly successful for the selection of rabbit mAbs by phage display.
- Alternative methods
Alternative methods include the clonal expansion of B cells. Single B-cell selection based on antigen capture by fluorescence-activated cell sorting, magnetic beads, solid-phase panning or hemolytic plaques followed by light- and heavy-chain cloning has also been applied to the generation of rabbit mAbs from peripheral B cells.
Rabbit MAb in Vitro Diagnostics
Aside from therapeutic applications, rabbit mAbs have become highly valuable reagents for diagnostic applications and for laboratory research. For example, rabbit mAbs can detect activating mutations in lung cancer tissues. Rabbit mAbs are also suitable to detect post-translational modifications. mAbs are being used to detect the expression of tumor-associated antigens, including HER2, estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors and PD-L1. Recently, a rabbit mAb to human androgen receptor splice variant7 has emerged as a promising tool for the detection of circulating tumor cells in prostate cancer.
Advantages of Rabbit MAbs in IVD Area
- Exhibit higher affinity for the antigen
- Give superior sensitivity
- Allow for epitope recognition that may not be feasible with other systems
- Natural diversity
- High affinity and specificity
- Novel epitope recognition
- Cross-reactivity to human and mouse targets
- Ease of humanization
Reference
- Zhang, Zaibao, et al. "Advances in the isolation of specific monoclonal rabbit antibodies." Frontiers in Immunology 8 (2017): 494. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.