Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) is based on gamma-rays and single domain antibodies (sdAbs) are normally linked to radionuclides such as 99mTc, 177Lu, 123I and 111In. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) is based on positron-emitting radioisotopes and sdAbs are normally linked to 68Ga, 124I or 89Zr. Prior to radiolabeling, sdAbs are conjugated with bifunctional chelating agents which possess a metal binding moiety for sequestration of the metallic radionuclide and are generally DOTA (macrocyclic), DPTA (acyclic)-, or NOTA-based. Besides, the chelating agents are equipped with a chemically reactive functional group for attachment to the sdAb, which can occur in several ways. Then, random conjugation can be performed via the free ε-amino-group on sdAb lysines or site-specific conjugation can be performed via cysteine, glycan, or enzyme-mediated conjugation. Site-specific or amino acid coordinating sequences such as His tag-mediated labeling has the advantage that antigen binding activity of the sdAb is usually unaffected. When lysine residues involved in random conjugation are located outside the antigen-binding loops, no interference with antigen binding should be expected either. Creative Biolabs provides customized sdAb-based diagnostic tools development services for worldwide clients.
Chelators for Radiometal-antibody Imaging
Metallic radioisotopes are incorporated into an sdAb via a chelator. Many factors influence the choice of a metallic radioisotope, including the imaging modality, the availability of the radioisotope itself, and matching of the half-life of the radioisotope to the pharmacokinetics of the vector. The chelator binds the radiometal, and the resulting radiometal-chelator complex will ideally possess both high thermodynamic and kinetic stability. This high stability is essential to ensure that the radiometal remains bound to the antibody in vivo. Table 1 shows the commonly used imaging radiometals.
Table 1 Decay properties for radiometals commonly used in PET and SPECT imaging. (Morais, 2018)
Attaching Chelators to Antibody
In chelator-antibody conjugation reactions, the antibody and chelator contain complementary reactive functional groups for attachment to each other. Significant efforts over the last decade have resulted in new site-selective conjugation methods for attaching chelators and fluorescent molecules to antibodies. Such an approach uses complementary pairs of functional groups that react chemo-selectively with each other. It involves appending one functional group to the chelator, and the other to the protein, followed by reaction between the two motifs. Click chemistry is one such approach.
Site-selective Conjugation for Radiometal-labelled Antibodies Generation
- Site-directed Modification of Cysteine
The most widely employed method of conjugating sdAbs via cysteines involves a Michael addition reaction of a thiol with a maleimide to form a succinimidyl thioether adduct. However, maleimide conjugates suffer from instability: the thioether can undergo a retro-Michael reaction, converting back to the starting maleimide and thiol. The maleimide motif, still attached to its payload, reacts with endogenous molecules containing bioavailable thiols, such as glutathione and albumin. In radionuclide imaging, this can potentially result in accumulation of radioactivity at off-target sites, decreasing image contrast, sensitivity and the ability to quantify protein biodistribution. Recent years, several new cysteine-reactive reagents that provide enhanced conjugate stability have been developed, such as methylsulfonyl phenyloxadiazole derivatives bearing DFO and DTPA chelators.
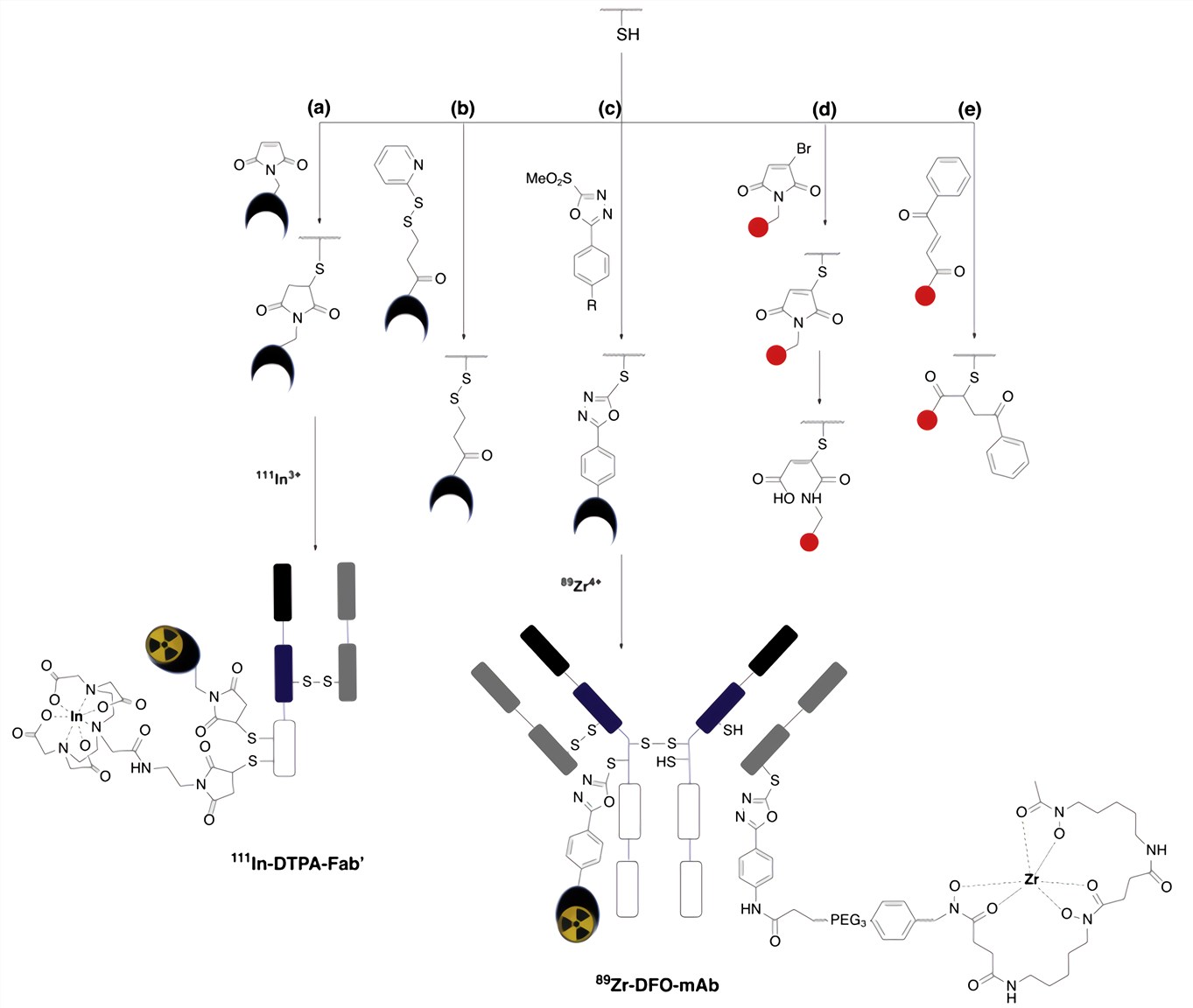 Fig.1 Thiol-reactive chemical agents.1
Fig.1 Thiol-reactive chemical agents.1
- Site-directed Modification of the Glycan Region
Glycan-based modification chemistry has been critically important in the clinical development of molecular imaging with sdAbs in nuclear medicine. The first FDA-approved imaging radio-immunoconjugate specifically incorporated 111In into the anti-TAG72 antibody via a DTPA chelator at the glycan region. Another FDA-approved antibody imaging agent, similarly incorporates a DTPA chelator using glycan technology. The mostly widely used two strategies are Reaction with oxidised hexose groups, Enzymatic modification of glycans.
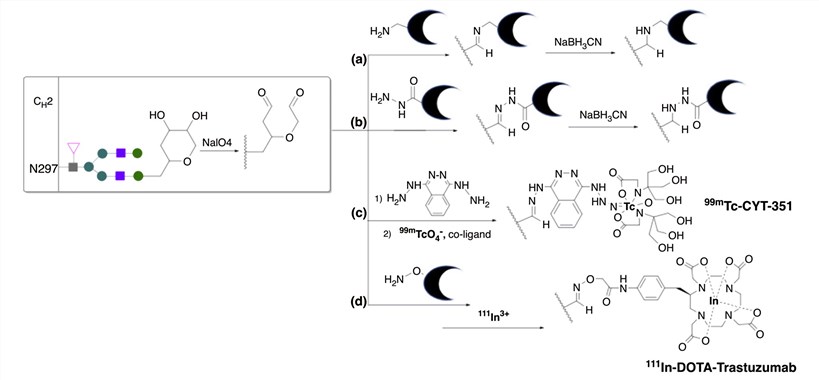 Fig. 2 Site-specific chelator attachment through oxidation of antibody glycans.1
Fig. 2 Site-specific chelator attachment through oxidation of antibody glycans.1
- Enzyme-mediated Conjugation
Enzyme-mediated conjugation makes use of an enzyme that recognizes two complementary motifs on the targeting sdAb and the cargo-containing compound. Using these two complementary motifs, the enzyme catalyzes covalent attachment of the targeting antibody/protein to the cargo. The use of transglutaminase are examples of this method.
- Incorporation of Sequences of Amino Acids
SdAb can bind to metal ions via amino acid side chains, carboxylate groups of C-ter, amine groups of N-ter, and N atoms of amide groups. Particular sequences of amino acids, containing several metal-binding ligands, enable direct radiometal complexation by the protein, without the requirement of a synthetic chelator. In such cases, the radiometal-binding amino acid sequence is simply engineered into the protein at the desired location. The hexahistidine sequence has been prevalently applied to incorporate the SPECT/PET isotope. Besides, several low molecular weight 99mTc radiotracers, including 99mTc-labelled compounds used in renal imaging and 99mTc-labelled peptides that target cell surface receptors, make use of deprotonated amide groups of a peptide backbone in combination with deprotonated thiols to coordinate 99mTcV. Peptide sequences incorporating these features can be engineered into sdAbs for efficient binding of the 99mTcVO3+ motif.
Reference
- Morais, Mauricio, and Michelle T. Ma. "Site-specific chelator-antibody conjugation for PET and SPECT imaging with radiometals." Drug Discovery Today: Technologies 30 (2018): 91-104. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.