Virulence Factors
As a leading service provider in the field of biological research and drug discovery, Creative Biolabs is fully competent and dedicated to providing antifungal drug discovery services. With the comprehensive advanced drug discovery platform, we provide our clients with antifungal drug discovery package service including target identification and validation, Hit identification, Hit to lead, Lead optimization, and IND enabling to meet the novel drug discovery goals.
Our scientists had explored the potential and well-recognized targets and are committed to being your best partner in target identification and validation. Here we introduced about the virulence factors which show potential as targets for the development of novel antifungal drugs.
Targets of Virulence Factors
To treat localized or systemic fungal diseases, the current popular drugs comprise several groups, such as polyenes, allylamines, azoles, flucytosine, and griseofulvin. However, in consideration of drug resistance in fungi, we are indeed in need of developing new antifungal therapeutics. In recent years, virulence factors had been discovered and characterized, and targeting virulence factors had been postulated as a new paradigm for antifungals. Virulence factors produced by the fungus are necessary for causing disease in the host and refer to the degree of pathogenicity. They are important in the ability to grow at physiological temperature and pH.
Advantages of Virulence Factors as Therapeutic Targets
Virulence factors have opened up a novel and exciting area of drug discovery because of the following potential advantages:
- Expanding the repertoire of pharmacological targets
- Preserving the host endogenous microbiome
- Generating antimicrobials with novel mechanisms of action
- Exerting less selective pressure, which may result in reducing resistance
Virulence Factors in Fungi
Here are various types of virulence factors of clinically important fungi.
Filamentation means anomalous growth which results in elongation rather than division. It’s a survival strategy to protect fungi from medical drugs taken from the host. Biofilms are microbial communities which are essential to be attached to solid surfaces. The filamentation and biofilm formation play the functional role in human health. Both of them are functional for fungal pathogenicity and resistance, hence, they can be potential therapeutic targets to treat fungal diseases.
As a second messenger in fungi, calcium plays an important role in various patterns of signaling pathways and has functional role in cell survival. In addition, calcium-calcineurin signaling pathway is critically determinant to fungal resistance to antifungal drugs. It has been reported that various channels, transporters, pumps, and other proteins or enzymes involved in this signaling pathway show potential as therapeutic targets for the development of antifungal drugs.
Heat shock protein 90-calcineurin pathway is an important virulence factor which can be targeted at different levels. Hsp90 is necessary for fungal survival and is closely related to the activity of calcineurin in stress responses and cell wall repair mechanisms. It has been reported that targeting Hsp90-calcineurin pathway can be a novel therapeutic strategy to treat fungal diseases.
Lysine deacetylases are also known as histone deacetylases (HDACs). For fungal infection, transcription levels are obviously affected for both pathogens and hosts as the major mechanism of gene regulation. And the transcription is highly regulated by post-translational modification of histones including acetylation and others. It has been reported that inhibition of histone deacetylases is able to reduce fungal infections. Therefore, histone deacetylases can be considered as a potential target for the development of novel antifungal therapeutic strategies.
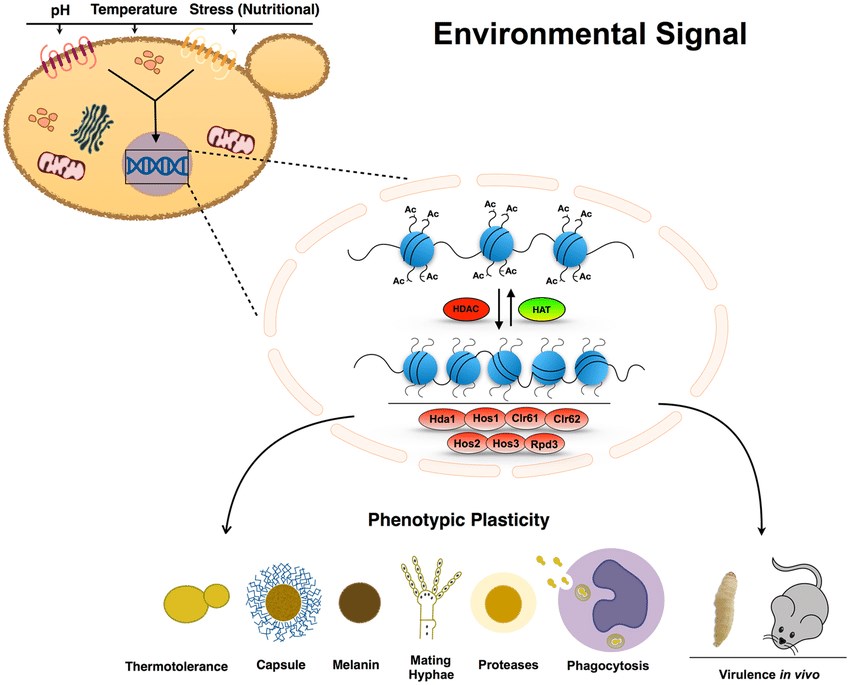 Fig.1 Model for HDAC regulation of the main virulence phenotypes in C. neoformans.1
Fig.1 Model for HDAC regulation of the main virulence phenotypes in C. neoformans.1
Fungal virulence factors are promising new potential drug targets. For future novel drug development, inhibitors can be the most possible agents to target virulence factors. Empowered by so many potential antifungal targets, Creative Biolabs offers our clients with various antifungal drug discovery services to meet your basic drug discovery research and development. We’re committed to being your best companion and facilitate and maximize the success of your projects. Please contact us for more details or a detailed quote.
Reference
- Brandão, F.; et al. HDAC genes play distinct and redundant roles in Cryptococcus neoformans virulence. Sci Rep. 2018, 8(1): 5209. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
