Adipose Tissue Exosome Research and Application
Overview Services Features FAQs
In the past, studies mainly focused on body fluid-derived or cell culture supernatant-derived exosomes, and as the research progresses and the level of research increases, adipose tissue-derived exosomes are receiving more and more attention. Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive services for the isolation, identification, histological profiling, and functional modification of adipose tissue exosomes.
Overview
-
As the largest secretory organ of the organism, adipose tissue can participate in regulating the physiological and pathological processes of proximal and distal tissues/organs by releasing cytokines, hormones, and exosomes. Exosomes as significant messengers of intercellular communication are a hot spot in adipose tissue research.
-
Human adipose tissue is classified according to specific storage areas, structural organization, cell size, and biological function: white adipose tissue (including visceral white adipose tissue, subcutaneous white adipose tissue), brown adipose tissue, and beige adipose tissue. In contrast to visceral adipose tissue, subcutaneous white adipose tissue, and brown adipose tissue are capable of promoting metabolism. Adipose tissue contains adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells that can differentiate into a variety of cells, and adipose tissue grafts developed on this basis are widely used as candidates for physiological studies and human reconstructive surgery. Adipose exosomes are important members of the exosome family, secreted from adipocytes, and have been shown to play major roles in tissue regeneration, oxidative stress, immune regulation, and many other aspects.
-
Adipose tissue exosomes are not only capable of intercellular delivery within tissues, but also of circulating and localizing to distal organs to perform their functions. Changes in their cargo composition can reflect the normal or disease state of the body and can be studied as disease markers such as morbid obesity. In addition, similar to other types of exosomes, adipose tissue exosomes are engineered to facilitate the investigation of functional mechanisms and their application as therapeutic vectors.
Services for Adipose Tissue Exosome Research
At Adipose Tissue Exosome Research and Application, we specialize in facilitating cutting-edge research in the field of adipose-derived exosomes. Our services encompass the isolation, characterization, and analysis of exosomes from various adipose tissue sources. We offer comprehensive consultations for experimental design and the development of customized protocols suited to your specific research objectives. We aim to accelerate your discoveries and enhance the understanding of adipose tissue exosome biology.
Adipose Tissue Exosomes
-
Adipose Tissue Exosomes as Biomarkers
White adipose tissue exosomes have been identified as potential markers for obesity and its comorbidities. Researchers extracted exosomes from obese and lean individuals, analyzing their overall characteristics and protein profiles through characterization and mass spectrometry. They found that half of the proteins were identical between visceral and subcutaneous fat exosomes, but obese visceral adipose tissue exosomes were enriched with obesity-related adipokines. Functional classification revealed that these exosomes had increased proteins associated with inflammation and insulin resistance, such as TGF-β1 and CAVN1. Further SWATH analysis identified candidate molecular markers of morbid obesity, highlighting decreased syntenin 1 and increased TGF-β1 and mimecan, aiding in clinical quantification and diagnosis.
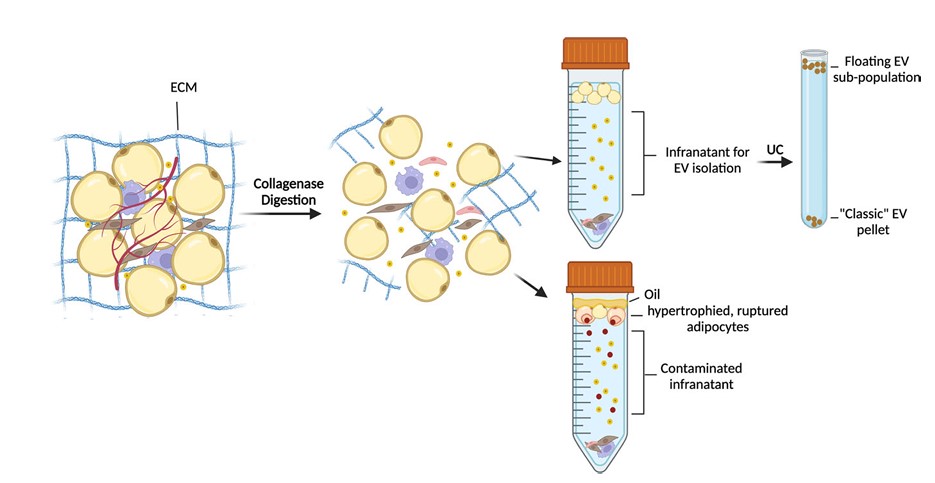 Fig.1 Challenges of EV isolation from adipose tissue.1
Fig.1 Challenges of EV isolation from adipose tissue.1
-
Adipose Tissue Exosomes Involved in Intercellular Communication
The key to studying the function of adipose tissue exosome-mediated intercellular communication is to verify the presence of shared cell membrane components between the two cell types and the exosomes delivering proteins within them. After several weeks of transplantation of adipose tissue labeled with cell membranes into the host fat pad, detection of fluorescently labeled signals in adipocytes at the transplantation site allows analysis of the exchange of membrane components between adipocytes and other cell types in the tissue. Before the co-cultivation of adipocytes with other cells, knockdown of target genes in recipient cells, detection of target protein signals in recipient cells, as well as setting up an exosome biogenesis inhibitor as a negative control, allows in vitro analysis of intercellular molecular transfer based on exosome mechanisms. The isolated adipose tissue exosomes were then profiled for density, morphology, particle size, vesicle markers, mass spectrometry, and target protein assays to dissect exosome components associated with signal transduction potential.
-
Adipose Tissue Exosomes Localize Distal Organ Regulation
Adipose tissue exosomes are linked to increased disease risk by regulating distal organs. Studies show that exosomes from adipose tissue in high-fat diets deliver pro-inflammatory miRNAs to the gut, worsening colitis. In vivo tracing of exosomes injected into mice revealed accumulation in the intestinal lamina propria, demonstrating tissue transfer. When lean mice received exosomes from high-fat diet mice, colitis worsened due to enriched miR-155 promoting M1 macrophage polarization. Modifying these exosomes to carry a miR-155 inhibitor and delivering them to high-fat diet mice significantly reduced colitis severity induced by dextran sodium sulfate.
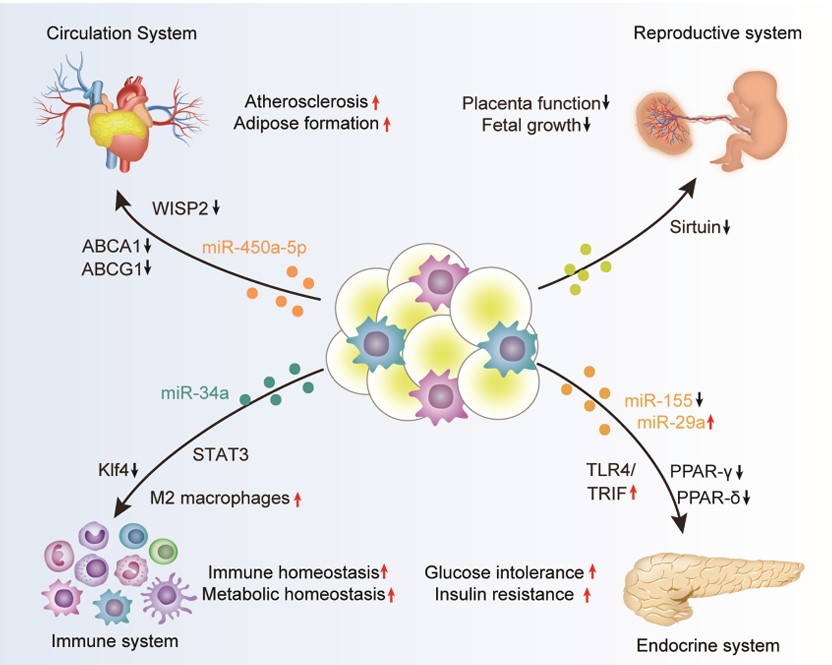 Fig.2 Adipose tissue-derived exosomes in the regulation of biological processes.2
Fig.2 Adipose tissue-derived exosomes in the regulation of biological processes.2
Creative Biolabs provides research services for multi-directional profiling and multi-domain applications of adipose tissue exosomes, helping clients to advance projects related to adipose tissue exosomes. Please contact us to discuss your project.
FAQs
Q: How can I optimize the isolation process of adipose tissue exosomes for my specific experiment?
A: We recommend tailoring the isolation protocol to your tissue source and intended downstream applications. Factors such as the choice of isolation method (ultracentrifugation, precipitation, etc.), buffer composition, and temperature can significantly affect yield and purity.
Q: What methods are most effective for characterizing exosomal cargo?
A: Depending on your research goals, we suggest employing a combination of techniques such as mass spectrometry for proteomic analysis, and qPCR or NGS for RNA profiling. Each method offers distinct advantages, and integrating multiple approaches will provide a comprehensive understanding of exosomal content.
Q: How can I ensure the reproducibility of my exosomal study?
A: To enhance reproducibility, we advise maintaining strict consistency in sample handling and processing parameters. Documenting all variables, including tissue source, isolation methods, and storage conditions, is essential.
Q: Can you provide guidance on the potential use of exosomal content in biomarker discovery?
A: Yes, we can assist in identifying and validating potential biomarkers present in adipose-derived exosomes. Our expertise in data analysis and bioinformatics allows us to suggest robust statistical methods and highlight relevant pathways, facilitating your biomarker discovery efforts.
Q: What are some common challenges researchers face when working with adipose tissue exosomes?
A: Common challenges include achieving high purity and yield during exosome isolation, maintaining the stability of isolated exosomes, and accurately characterizing their heterogeneous populations.
References
-
Crewe, Clair. "The challenges of interrogating adipose tissue extracellular vesicle functions in physiology." Communications Biology 5.1 (2022): 581. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
-
Liu, Yunnan, et al. "Multifaceted roles of adipose tissue-derived exosomes in physiological and pathological conditions." Frontiers in Physiology 12 (2021): 669429. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Challenges of EV isolation from adipose tissue.1
Fig.1 Challenges of EV isolation from adipose tissue.1
 Fig.2 Adipose tissue-derived exosomes in the regulation of biological processes.2
Fig.2 Adipose tissue-derived exosomes in the regulation of biological processes.2









