 Advanced Isolation Methodologies for Brain Tissue Exosomes
Advanced Isolation Methodologies for Brain Tissue Exosomes
Extracting exosomes directly from brain tissue presents significant challenges due to the tissue's complex structure and dense extracellular matrix, requiring careful avoidance of contamination from free or damaged cells. Creative Biolabs provides brain tissue exosome isolation services and products to help our customers solve this problem. Isolated exosomes are complemented by detailed downstream protocols for the characterization and analysis of isolation method, utilizing techniques such as nanotrack analysis, electron microscopy, and western blotting, as well as other advanced technologies.
 Brain Exosomes in Neurological Disorders: Key Findings
Brain Exosomes in Neurological Disorders: Key Findings
Brain tissue exosomes are increasingly recognized for their active roles in the pathogenesis of various neurological conditions, serving as both indicators and potential mediators of disease progression.
-
Alzheimer's Disease (AD): Brain-derived exosomes in AD show greater proteomic changes than brain tissue, with elevated t-tau, p-tau, and PRDX1/6 levels. Cell type-specific brain-derived exosomes markers are also increased.
-
Parkinson's Disease (PD): Advanced isolation enables consistent analysis of brain EV subtypes under PD-related pathological conditions.
-
Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy (SAE): In SAE models, 101 exosomal miRNAs are differentially expressed; four miRNAs correlate across brain, CSF, and plasma, indicating potential as biomarkers.
-
Stress-Driven Pathology: Chronic stress increases brain exosome release, linked to memory and mood deficits, suggesting a role in stress-related brain disorders.
 Brain Exosomes as Biomarkers
Brain Exosomes as Biomarkers
Brain-derived exosomes are a promising source for novel biomarkers reflecting the status of the brain.
-
Tetraspanin Heterogeneity: Exosomes from serum, plasma, CSF, and brain tissue show distinct tetraspanin (CD9, CD63, CD81) profiles depending on the sample source. Brain exosomes resemble those in CSF but differ from blood, aiding biomarker development for brain disorders.
-
Disease Monitoring: Brain EV proteins related to AD may support disease tracking. CNS-specific surface markers also offer potential for peripheral brain-derived exosomes capture as a non-invasive brain health assessment.
-
Early Diagnostics: Correlating brain and peripheral exosomal miRNA profiles, as seen in SAE models, may enable early detection of neurological diseases through minimally invasive assays.
Direction: The Future of Brain Exosome Applications
The burgeoning field of brain tissue exosome research points towards several transformative applications:
Exploring Exosome-Based Disease Mechanisms
Brain tissue exosomes offer an unparalleled opportunity to dissect the intricate molecular mechanisms underlying neurological diseases. By analyzing the specific proteins, nucleic acids (including miRNAs), and lipids encapsulated within these exosomes, researchers can identify key signaling pathways, cellular interactions, and pathological processes that drive disease progression.
Precision Liquid Biopsy for Brain Diseases
By leveraging the unique molecular signatures within brain tissue exosomes, we can find highly specific and non-invasive liquid biopsy markers for early diagnosis, disease staging, and monitoring therapeutic responses in neurological disorders. This will move beyond general systemic indicators to pinpoint disease activity at its source within the brain.
Creative Biolabs' Expertise and Services
At Creative Biolabs, we are at the forefront of brain tissue exosome research, leveraging over two decades of experience in molecular and cell biology. Our team of leading experts is dedicated to translating cutting-edge discoveries into tangible solutions for neurological health. We understand the unique complexities of working with brain tissue and have developed specialized platforms to support every stage of your research.
We offer a comprehensive, one-stop suite of services tailored specifically for brain tissue exosome research:
Isolation
Characterization
Profiling Services
In Vitro and In Vivo
We employ advanced and optimized methods to ensure high-quality, pure, and intact exosome preparations from brain tissue.
Our state-of-the-art techniques, such as Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), Nanoflow cytometry, and Western Blotting, provide precise insights into exosome size, morphology, and surface markers (e.g., CD9, CD63, CD81, TSG101).
We provide robust experimental systems, including advanced animal models and exosome labeling technologies, to evaluate the mechanistic pathways of brain tissue exosomes in vivo and in vitro.
We invite you to contact us to discuss your specific research ideas. Our professional scientific team is eager to collaborate with you to explore the mysteries of brain tissue exosomes.
FAQs
Q: How do brain tissue exosomes offer more specific insights compared to exosomes from blood or CSF?
A: Brain tissue exosomes are primarily secreted by cells within the local brain microenvironment, meaning their cargo directly reflects the specific pathological changes occurring in that particular brain region. In contrast, exosomes from blood are a mixed population from various tissues throughout the body, and even CSF exosomes, while closer to the brain, may not fully represent specific subregional changes due to the brain's complex compartmentalization. This makes tissue exosomes uniquely authentic and exclusive for localized brain disease research.
Q: What are the main methods for isolating exosomes directly from brain tissue?
A: Isolating exosomes from brain tissue is challenging due to its complex structure. We employ optimized method, enzymatic digestion, to collect released exosomes. This method is carefully selected and optimized to ensure high purity and integrity of the isolated exosomes.
Q: How can Creative Biolabs assist with my brain tissue exosome research?
A: We offer comprehensive, end-to-end services, from initial brain tissue exosome isolation and meticulous characterization (including proteomic, RNA, lipidomic, and metabolomic profiling) to rigorous in vitro and in vivo functional studies. Our expertise and state-of-the-art platforms are designed to provide precise insights and accelerate your project from discovery to validation.
Reference
-
Natale, Francesca et al. "Dual role of brain-derived extracellular vesicles in dementia-related neurodegenerative disorders: cargo of disease spreading signals and diagnostic-therapeutic molecules." Translational neurodegeneration vol. 11,1 50. 27 Nov. 2022, doi:10.1186/s40035-022-00326-w. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

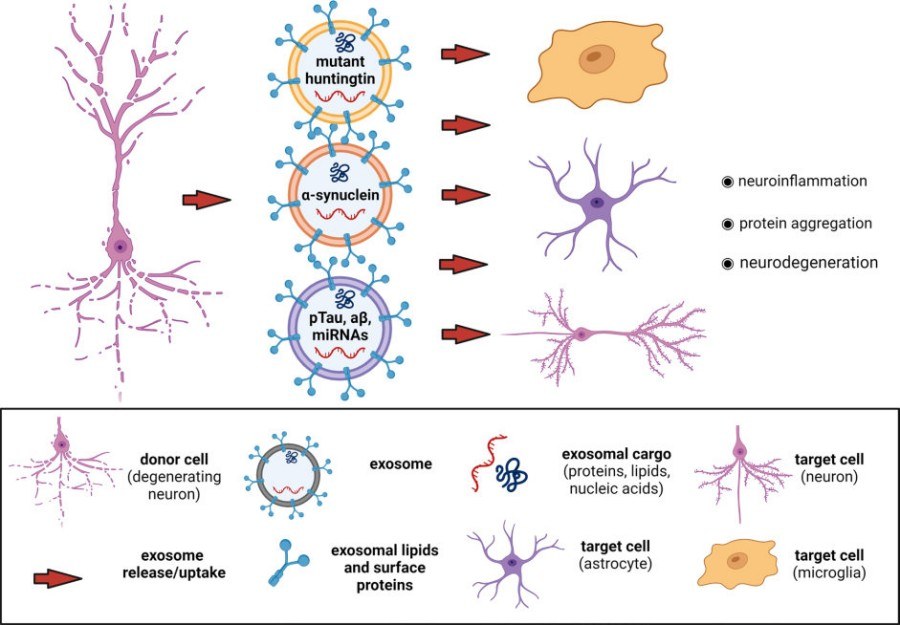 Fig.1 Role of brain-derived exosomes in the spreading of pathology in neurodegenerative diseases.1
Fig.1 Role of brain-derived exosomes in the spreading of pathology in neurodegenerative diseases.1









