Heart Tissue Exosome Research & Application
Introduction Research and Direction Services FAQs
Beyond the Bloodstream: The Imperative for Heart Tissue-derived Exosome Research
The human heart is a remarkable organ, performing its critical function without pause. Yet, as the pace of modern life accelerates, the incidence of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) is rising globally, affecting a younger demographic than ever before. To address this growing health crisis, a deeper, more nuanced understanding of cardiac pathology at the cellular level is essential.
In this context, exosomes have emerged as key mediators of intercellular communication, representing a paradigm shift in our comprehension of biological signaling. Once dismissed as "cellular garbage bags," these sophisticated biological nanocarriers are now known to carry a diverse cargo of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, including microRNAs (miRNAs), between cells. This transfer effectively reprograms the behavior and gene expression of recipient cells, influencing a wide range of physiological and pathological processes.
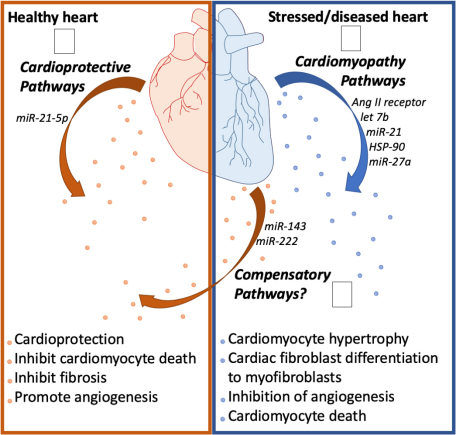 Fig.2 Cardiac health affects exosome biology.1
Fig.2 Cardiac health affects exosome biology.1
The complex cellular landscape of the heart relies on this intricate communication network. However, a majority of the research to date has focused on circulating exosomes derived from blood or serum, an approach that presents significant limitations for cardiac research. The fundamental challenges are:
Lack of Tissue Specificity
Blood-derived exosomes are a composite mixture sourced from every tissue and organ in the body. This makes it exceedingly difficult to pinpoint specific signals originating from the heart.
Inadequate for Local Communication
Circulating exosomes fail to reflect the dynamic, localized communication that occurs within the confined space of the cardiac tissue microenvironment, a process that is critical for understanding disease progression.
This complexity has driven a critical re-evaluation of research methodologies, moving beyond the systemic to the local. Evidence compellingly demonstrates that an exosome's cargo is strictly influenced by the physiological or pathological state of its parental cell and the local microenvironment. This highlights a foundational principle:
The specific stress or disease state of the heart directly modifies the content of the secreted exosomes.
Consequently, analyzing exosomes directly from cardiac tissues provides a clearer, higher-fidelity signal that is indispensable for both accurate diagnostics and meaningful mechanistic research. Creative Biolabs has long recognized this crucial distinction and has pioneered a comprehensive platform for the extraction and analysis of tissue-specific exosomes, addressing this core scientific necessity.
Discover how we can help accelerate your heart tissue exosome research. Request a consultation.
Groundbreaking Insights and Future Directions from Heart Tissue Exosome Research
|
Disease/Physiological Process
|
Research Findings & Mechanism of Action
|
Potential Application/Significance
|
|
Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (MIRI)
|
Cardiac exosomes induced by myocardial ischemia-reperfusion (IR), enriched with miR-155-5p, activate macrophages and polarize them towards the M1 phenotype, promoting an inflammatory response.
|
Inhibiting exosome release could be a promising therapeutic strategy to mitigate MIRI.
|
|
Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
|
Exosomes isolated from the epicardial fat (eFat) of AF patients carry distinct pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic signatures. These vesicles promote atrial fibrosis and alter the electrical properties of cardiomyocytes.
|
Offers a new perspective on the link between epicardial fat and AF, providing novel diagnostic and therapeutic targets.
|
|
Myocardial Infarction (MI)
|
A transient but significant increase in cardiac exosomes occurs in myocardial tissue after MI. These exosomes, primarily from cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells, regulate the local inflammatory response by being taken up by monocytes and influencing cytokine release.
|
Targeting these exosomes could be a strategy to modulate inflammation in the early stages following an MI.
|
|
Diabetic Cardiovascular Complications
|
Exercise-induced cardiomyocyte-derived exosomes (cardiosomes) contain specific miRNAs, such as miR-29b and miR-455, which downregulate Matrix Metalloprotease 9 (MMP9), preventing the extracellular matrix remodeling and fibrosis associated with diabetic hearts.
|
Provides a molecular explanation for the benefits of exercise in diabetic patients.
|
|
Cardiac Regeneration and Tissue Repair
|
Exosomes isolated from human heart explant tissue (left ventricular endocardium) promote endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis, improve wound healing, and enhance the recellularization of decellularized heart valves.
|
Highlights the potential of using human heart-derived exosomes for regenerative medicine applications.
|
|
Neonatal Heart Regeneration
|
Exosomes from regenerating neonatal heart tissue have stronger pro-proliferative and anti-apoptotic properties than exosomes from non-regenerating adult hearts. The protein Wdr75 was identified as a key regulator.
|
Provides a powerful model for developing regenerative therapies for adult heart diseases.
|
See how our services can empower your project. Book a consultation today.
Our Expertise and Services
Creative Biolabs has always focused on the latest research results of exosomes and has successfully isolated high-quality exosomes from multiple tissues. We can provide customers with:

-
Tissue exosome extraction services.
-
Exosome identification services via particle size analysis, morphological observation and other identification services.
-
Body fluid exosome and tissue exosome combined research service.
-
Tissue exosome and individual cell combined transcriptomics and proteomics research services.
-
Tissue exosome in vivo and in vitro function research services.
These technologies can help customers better explore the potential of exosomes based on the data of tissue exosomes.
We are confident that the next major breakthroughs in cardiovascular medicine will come from a better understanding of tissue exosomes. If you have a research idea, a key molecule you'd like to investigate, or a specific disease model you want to explore, don't hesitate to contact us. Let's work together to push the boundaries of science and develop the next generation of diagnostics and therapies for heart diseases.
FAQs
Q: Why is heart tissue exosome research more challenging than working with blood-derived exosomes?
A: The primary challenge stems from the fundamental differences in sample matrix. Blood is a liquid medium from which exosomes are relatively easier to isolate, despite the challenge of separating vesicles from various tissues. Heart tissue, in contrast, is a dense, heterogeneous solid matrix with a low abundance of exosomes in its interstitial fluid. This makes the initial extraction and subsequent purification from co-precipitated matrix components exceptionally difficult. However, while challenging, this approach is necessary to gain the high specificity and mechanistic insight that blood exosomes cannot provide, as it enables the direct analysis of cellular communication within the microenvironment itself.
Q: What are the key quality control measures for Creative Biolabs' exosome services?
A: The company maintains a rigorous quality control process to ensure data integrity and reproducibility. After isolation, all exosome samples are validated for size distribution and concentration using multiple, complementary technologies such as NTA and TRPS. This dual-platform approach ensures high-accuracy and single-particle resolution. The identity of the exosomes is further confirmed by verifying the presence of canonical exosome surface markers (e.g., CD9, CD63, CD81) using nano flow cytometry. For multi-omics studies, a minimum of three biological replicates is recommended to ensure statistical significance and data robustness.
Q: How can Creative Biolabs' services accelerate our research timeline?
A: By providing a comprehensive, one-stop platform that covers every step of the research workflow—from initial tissue processing to final functional validation—Creative Biolabs eliminates the need for researchers to invest in expensive equipment, optimize complex protocols, and train specialized personnel. This allows clients to bypass technical hurdles and logistical bottlenecks, enabling them to focus their expertise on hypothesis testing and data interpretation. By outsourcing these demanding processes to a professional team with decades of experience, the research timeline can be significantly accelerated.
Ready to take your research to the next level? Connect with us now.
Reference
-
Patil, Mallikarjun, et al. "The art of intercellular wireless communications: exosomes in heart disease and therapy." Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 7 (2019): 315. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2019.00315. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.2 Cardiac health affects exosome biology.1
Fig.2 Cardiac health affects exosome biology.1










