Muscle Tissue Exosome Research and Application
Overview Services Features FAQs
Past research has shown that muscle tissue-derived exosomes are biologically important in many ways and are a key component in maintaining normal organismal physiological function. Creative Biolabs summarizes exosome research and applications related to muscle tissue, providing valuable insights into their potential functions and mechanisms.
Overview
Exosomes can be secreted by muscle tissue cells, including various types of muscle cells (e.g. cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle) and muscle-associated cells (e.g. vascular endothelial cells and red blood cells). Multiple functions and mechanisms have been investigated for muscle tissue exosomes. Muscle tissue exosomes function by releasing biologically active molecules such as miRNAs and proteins that affect the physiological state of the recipient cells and remodel the extracellular matrix.
Our Services
We offer comprehensive research services focused on muscle tissue exosomes, including isolation, characterization, and functional analysis. Our expertise allows us to provide tailored solutions for studying the role of exosomes in muscle physiology, disease mechanisms, and potential applications. We employ cutting-edge methods to guarantee the best possible outcomes for your study requirements.
Muscle Tissue Exosomes
-
Regulating Metabolic Processes
Exosomes may have a role in the control of muscle metabolism. Exosomes isolated from trained mouse muscle underwent altered miRNA profiles compared to normal mice, including a significant increase in miR-133a and miR-133b. Importantly, it exhibited improved glucose tolerance. This mainly resulted from the altered miRNA targeting down-regulation of insulin-regulated transcription FoxO1 (factor forkhead box O1) expression in the liver. Also, treatment of exosomes with exogenous transfected miR-133b mimics and FoxO1-specific siRNA confirmed the altered metabolic effects of this signaling pathway in mice. These data demonstrate the impact of exercise on the miRNA profile of muscle tissue exosomes, which improves the organism's metabolic profile and prolongs survival.
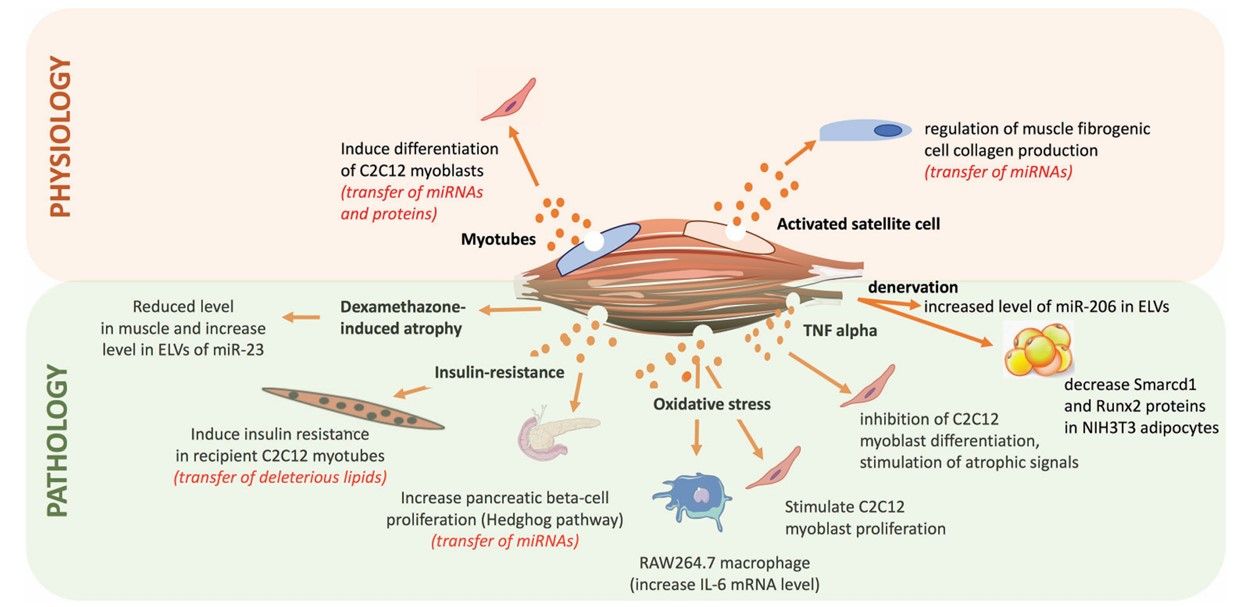 Fig. 1 Summary of the roles of exosome-like vesicles released from skeletal muscle cells.1, 3
Fig. 1 Summary of the roles of exosome-like vesicles released from skeletal muscle cells.1, 3
-
Promotes Muscle Development, Osteogenic Differentiation, and Adipose Homeostasis
Muscle tissue exosomes also play a regulatory role in muscle, bone, and adipose tissue homeostasis. For example, during the development of myotubes to myoblasts, myotubular exosomes are more abundant in muscle contraction-associated proteins, including myotonic dystrophy protein-associated glycoprotein 1, lipoprotein Cy, and titin, compared to myoblast exosomes. This targets the down-regulation of Cyclin-D1 and up-regulation of Myogenin protein expression to inhibit myoblast proliferation and promote their differentiation. Meanwhile, skeletal muscle exosomes regulate muscle development by secreting insulin growth factor and platelet growth factor AA. In addition, muscle also achieves mutual regulation with bone employing muscle tissue exosomes in an endocrine manner. By miRNA-seq of exosomes and quantifying gene expression after osteogenic differentiation, myoblast-derived exosomes were screened to induce osteogenic differentiation by acting on osteoblasts and delivering the key molecule miR-27a-3p. Skeletal muscle exosomes were also shown to act on adipose and adipose stem cells to maintain homeostasis.
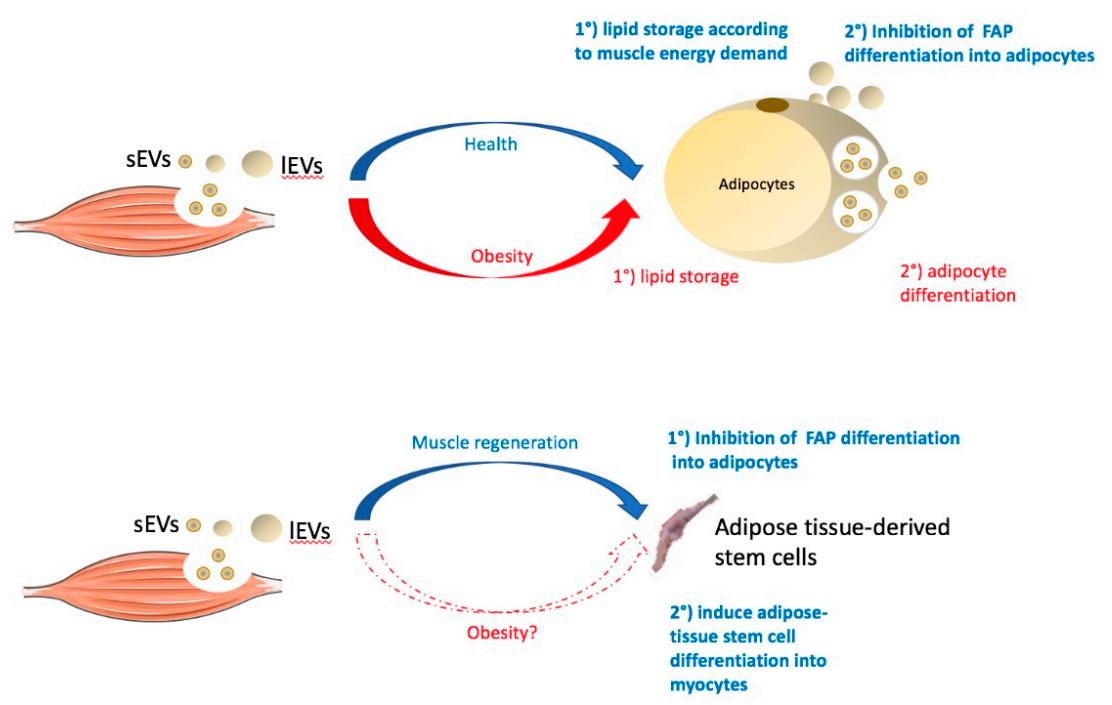 Fig.2 Role of skeletal muscle exosomes on adipose homeostasis.2, 3
Fig.2 Role of skeletal muscle exosomes on adipose homeostasis.2, 3
-
Muscle Tissue Repair and Regeneration
Muscle tissue-derived exosomes also have great therapeutic potential in the field of regenerative medicine as cell-free therapies for muscle injury. HGF (hepatocyte growth factor), a powerful catalyst for muscle stem cell activation and translocation to damaged sites, has been identified in exosomes from differentiating skeletal muscle cells, able to act in a dose-dependent manner in muscle repair and synergize with various myogenic factors such as FGF2, IGF1, and TGF-β. Meanwhile, exosomes released from muscle precursor cells contain miR-206, which promotes collagen synthesis in muscle fibroblasts and remodeling of the extracellular environment in muscle tissue by inhibiting Rrbp1 (ribosome binding protein 1).
-
Muscle Contraction Markers
Muscle tissue exosomes can likewise be studied as liquid biopsies and screening markers. Researchers explored the contents of human myometrial tissue exosomes, subjected them to quantitative liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and miRNA sequencing, and analyzed them in combination with a database, which revealed that GJA1 (gap junction protein) and SLC39A14 (solute carrier family 39 member 14) can be used as novel biomarkers for clinical detection of myometrial contraction.
Multifunctional muscle tissue exosomes have been shown to play a key role in regulating the onset and progression of a variety of diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, muscle atrophy, neurological disorders, etc. Creative Biolabs provides services for muscle tissue exosome research and applications to help explore their functions and mechanisms and deepen the understanding of their regulatory roles. Please contact us with your interest.
FAQs
Q: What are muscle tissue exosomes?
A: Muscle tissue exosomes are small extracellular vesicles released from muscle cells, playing crucial roles in cell communication, metabolic regulation, and muscle health.
Q: Can you help with functional studies of exosomes?
A: Yes, we offer services to assess the biological functions of muscle tissue exosomes, including their effects on muscle cell proliferation, differentiation, and communication.
Q: What sample volumes do you require?
A: Please get in touch with us with your research needs and sample details, and we will assess the required sample volume accordingly.
Q: How long does the process take?
A: The timeline varies depending on the specific services requested, but we generally provide results within 8-12 weeks after sample receipt.
Q: Do you offer custom research solutions?
A: Absolutely! Since every research project is different, we tailor our solutions to your particular requirements.
References
-
Rome, Sophie, et al. "Skeletal muscle-released extracellular vesicles: state of the art." Frontiers in Physiology 10 (2019): 929.
-
Rome, Sophie. "Muscle and adipose tissue communicate with extracellular vesicles." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23.13 (2022): 7052.
-
Under open access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig. 1 Summary of the roles of exosome-like vesicles released from skeletal muscle cells.1, 3
Fig. 1 Summary of the roles of exosome-like vesicles released from skeletal muscle cells.1, 3
 Fig.2 Role of skeletal muscle exosomes on adipose homeostasis.2, 3
Fig.2 Role of skeletal muscle exosomes on adipose homeostasis.2, 3









