Placental Tissue Exosome Research and Application
Overview Services Features FAQs
Creative Biolabs provides research services on the placental tissue exosomes, providing clients with insights for exploring the causes of pregnancy complications and finding new biomarkers.
Placental Tissue Exosome Overview
-
Placental exosomes establish an interactive dialogue between fetal and maternal cells and exert immunosuppressive effects through multiple mechanisms, which are closely related to the physiological and pathological processes of pregnancy. Placental tissue exosomes mediate the regulation of the maternal pregnancy environment, particularly based on intercellular communication that facilitates embryo implantation. Various placental component cells secrete placental exosomes, such as syncytial trophoblasts, cytotrophoblasts, extravillous trophoblasts, and placental vascular endothelial cells, among which syncytial trophoblasts covered with placental villi are the major producing ones.
-
Placental alkaline phosphatase is located on the outer side of the exosome membrane and is a specific marker that distinguishes placental exosomes. Placental exosomes do not express classical MHC molecules outside the membrane, but rather express non-classical MHC-related molecules. It was also shown that the expression of HLA-G (human leukocyte antigen) was limited to the extravillous trophectoderm, which invades the maternal metaphase, while the syncytial trophectoderm was completely free of HLA-G. Exosomes originating from the syncytial trophectoderm do not activate NK cells due to the absence of HLA-G molecules. In addition to cytoskeletal proteins, vesicle transport proteins, macrophage inhibitory factors, and human cytomegalovirus protein UL16 binding proteins, the proteins located in the vesicles of placental exosomes express the pro-apoptotic molecules FasL and TRAIL, the endosomal sorting complex-associated protein Alix and the multivesicular vesicle protein TSG101, which are required for the transport of cellular regulatory factors (TGF-β and PD-L1) etc.
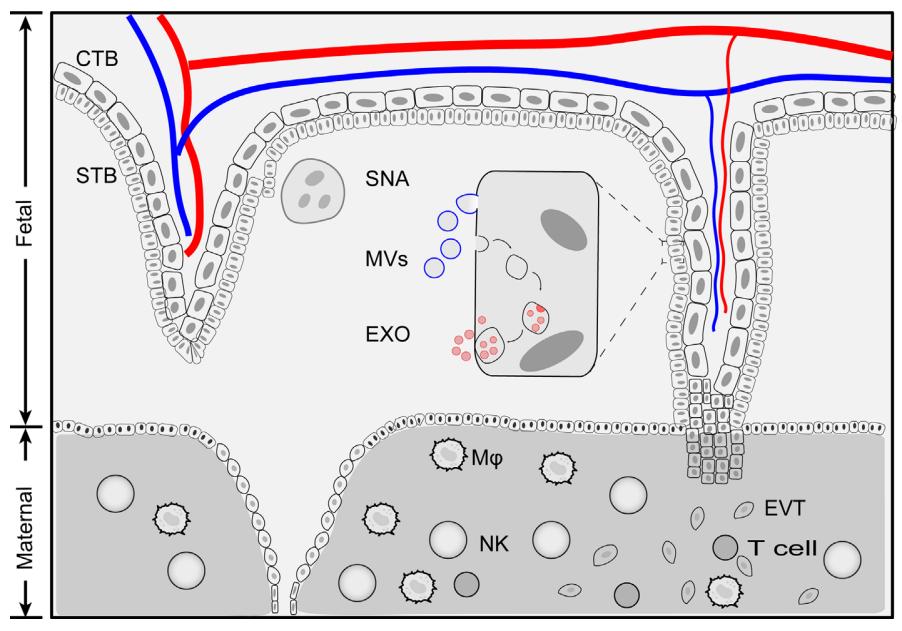 Fig.1 Placenta tissue extracellular vesicles. 1, 3
Fig.1 Placenta tissue extracellular vesicles. 1, 3
What We Offer
Our expertise lies in offering all-inclusive services specifically designed to investigate and make use of exosomes that are extracted from placental tissue. Our offerings include exosome isolation and characterization, advanced analytical techniques to explore their molecular composition and support in designing experiments focused on placental exosome functionality. We collaborate with researchers to facilitate innovative studies that leverage placental exosomes for understanding cellular communication, biomarker discovery, and potential applications in regenerative medicine.
Placental Tissue Exosome
-
Involvement in Physiological Pregnancy
Placental exosomes maintain pregnancy by participating in vascular remodeling and down-regulating the immune response. On the one hand, vascular smooth muscle cell migration experiments have revealed that exosomes released from extravillous trophoblasts can participate in spiral artery remodeling by promoting vascular smooth muscle cell migration, which is required for the formation of low resistance circulation in the uteroplacental. The placental syncytial trophoblast cells derived exosomes were detected by real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR and ISH to release placenta-specific miRNAs into the maternal circulation. miR-155 could regulate vascular remodeling and its function. It contributes to the maintenance of pregnancy by providing good conditions. On the other hand, placental exosomes establish maternal-fetal immune tolerance by mediating the apoptosis of immune cells. It was found that syncytial trophoblast cells released exosomes carrying membrane bioactive FasL and TRAIL molecules, which inhibited the CD3-ζ chain and JAK3 and contributed to Th1 apoptosis. In addition, placental exosomes carry NKG2D ligands, which can downregulate NK cell activity by binding to receptors, thereby weakening maternal immune-killing toxicity.
-
Involvement in Pathological Pregnancy
Abnormal changes in the contents of placental exosomes can lead to placental dysfunction and cause many obstetric disorders such as preeclampsia and GDM (gestational diabetes mellitus). The increase in the number, level, and function of placental exosomes may lead to an imbalance in the maternal immune system, thus triggering eclampsia. Proteomic analysis revealed that the expression of functional proteins such as syncytium 2 protein, matrix metalloproteinase 2, and matrix metalloproteinase 9 in the placental exosomes of preeclampsia pathology were significantly different from that of normal pregnancy. GDM is a prevalent metabolic condition that occurs during pregnancy. Hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and hypoxia are the main pathological changes associated with it. These adverse internal environmental factors can adversely affect maternal-fetal blood flow exchange by affecting trophoblast exosomes, resulting in adverse pregnancy outcomes such as preterm delivery, fetal distress, and fetal death. Longitudinal assays observed higher concentrations of placental exosomes in the plasma of GDM patients than in normal pregnant women matched for gestational weeks. Meanwhile, miRNA sequencing revealed an increased abundance of miR-518a-5p, miR-518b, miR-518c, miR-518e, miR-520c-3p, and miR-525-525-5p in placental exosomes in GDM compared with normal women, which may serve as a predictive biomarker for GDM.
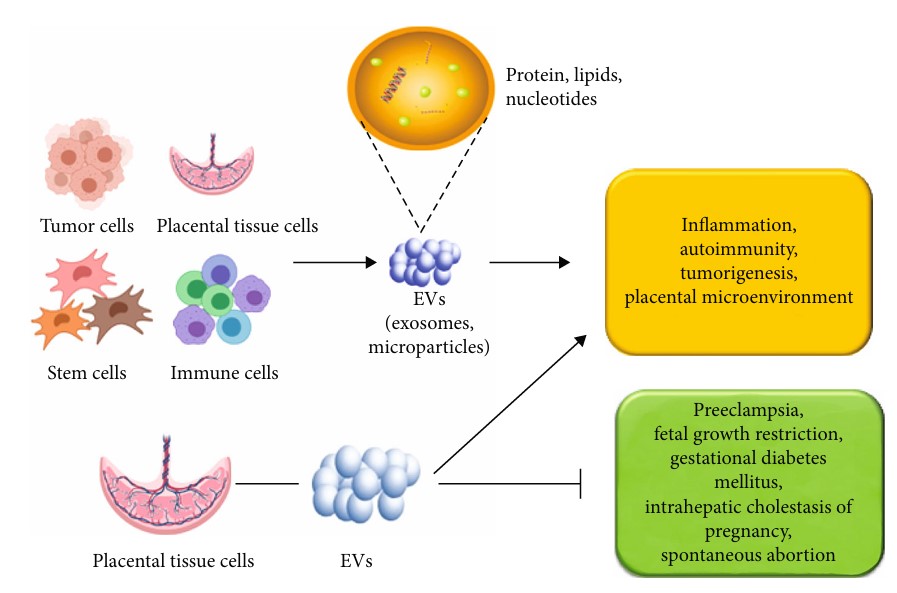 Fig. 2 Role of EVs in placenta and pregnancy disorders.2, 3
Fig. 2 Role of EVs in placenta and pregnancy disorders.2, 3
Creative Biolabs provides high-quality services for the characterization, omics profiling, and functional mechanisms of placental tissue exosomes. Please contact us to learn more.
FAQs
Q: Which specific methods do you apply to the isolation and validation of exosomes?
A: We utilize a combination of ultracentrifugation, size-exclusion chromatography, and immunoaffinity capture methods for robust isolation of exosomes. Characterization is performed using NTA, electron microscopy, and WB to confirm exosome purity and identify surface markers.
Q: How can researchers integrate your services into their existing projects?
A: Researchers can easily integrate our services by collaborating with us on specific aspects of their projects, such as exosome isolation, characterization, or functional assays. Additionally, we provide advice on study design and experimental procedures that are customized to meet your unique research goals.
Q: What unique features do placental exosomes have that set them apart from exosomes from other tissues?
A: Placental exosomes are known for their unique protein and RNA cargo, which reflects their role in maternal-fetal communication. They often contain specific growth factors, cytokines, and miRNAs that can provide insights into developmental processes and immune responses unique to pregnancy.
Q: Are there any limitations in the type of studies that can be conducted using placental exosomes?
A: While placental exosomes can provide a wealth of information, studies must be designed carefully to account for variables such as gestational age, maternal health, and environmental factors, which could influence exosome composition and functionality.
References
-
Bai, Kunfeng, et al. "Placenta-derived exosomes as a modulator in maternal immune tolerance during pregnancy." Frontiers in immunology 12 (2021): 671093.
-
Wang, Zengfang, et al. "Role of extracellular vesicles in placental inflammation and local immune balance." Mediators of Inflammation 2021 (2021).
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by revising the title.
For Research Use Only. Cannot be used by patients.
Related Services:

 Fig.1 Placenta tissue extracellular vesicles. 1, 3
Fig.1 Placenta tissue extracellular vesicles. 1, 3
 Fig. 2 Role of EVs in placenta and pregnancy disorders.2, 3
Fig. 2 Role of EVs in placenta and pregnancy disorders.2, 3









