Microfluidic technologies serve an essential role in the field of cancer research as well as progressing personalized medicine. By providing high-quality and customized solutions and services with our state-of-the-art Microfluidic platforms, Creative Biolabs is a reliable partner for cancer diagnosis based on Microfluidic technology to support your specific diagnosis requirements effectively.
Cancer Diagnosis based on Microfluidics
Since cancer becomes the most common cause of death globally, early diagnosis is the most important cancer issue. Thus, low-cost and point-of-care diagnosis tools and technologies are desperately needed to enable cancer management and reduce mortality rates. Microfluidic technology holds great promise in cancer diagnosis and serves as an emerging tool for understanding cancer biology. Inherently, Microfluidic platforms are suitable for analyzing possible cancer biomarkers in whole blood, including cell-free DNA, miRNA, proteins, exosomes, and circulating tumor cells (CTCs) to monitor cancers. For example:
(1) CTCs can be separated from whole blood using several Microfluidic techniques.
(2) Cell-free DNA can also be detected by Microfluidic digital PCR or electrochemical biosensors.
(3) Exosomes can be captured and analyzed using immunoaffinity approaches based on Microfluidic.
(4) Multiple protein biomarkers can be quantitated by digital or analog immunoassays.
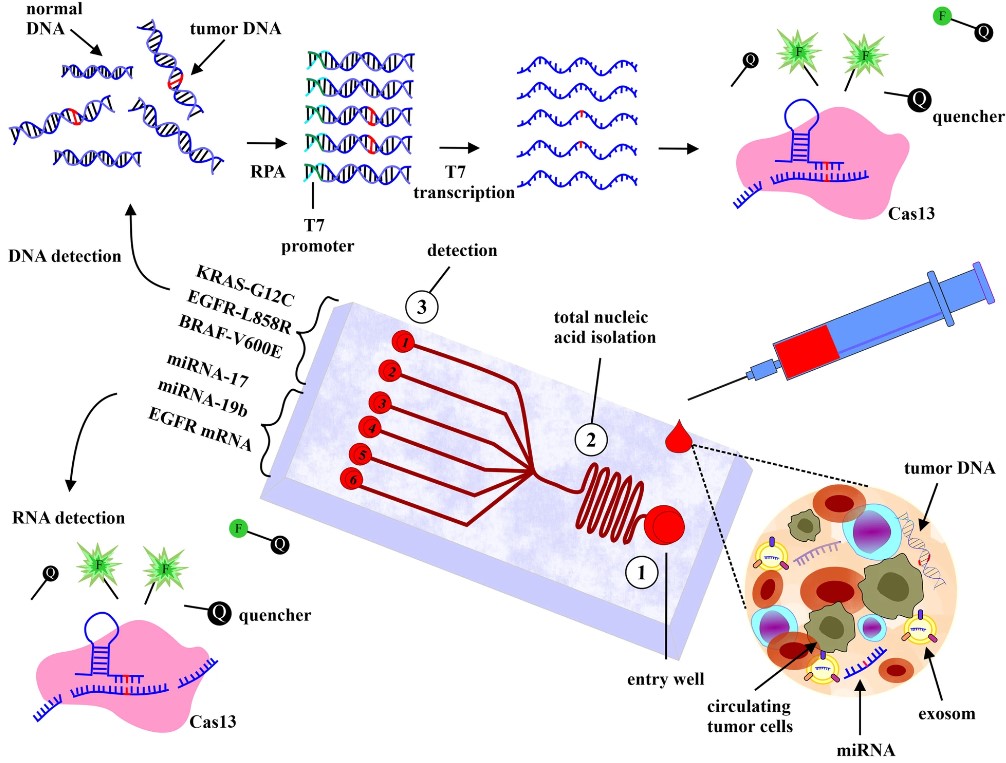 Fig.1 Cancer diagnosis based on microfluidics.1, 2
Fig.1 Cancer diagnosis based on microfluidics.1, 2
Advantages of Cancer Diagnosis based on Microfluidics
The development of early cancer diagnostic protocols using Microfluidic technology is considered a promising avenue to decrease mortality from cancer and improve outcomes. Microfluidic technology offers a non-invasive alternative for cancer diagnosis and disease management due to its high sensitivity, high throughput, less material-consumption, low cost, and precise liquid controlling capabilities. These characteristics make the designed Microfluidic platform a promising tool in separating and analyzing circulating tumor biomarkers for point-of-care (POC) diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring.
Our Cancer Diagnosis Services
Creative Biolabs is a leading diagnostic service company with a robust and standardized Microfluidic platform supporting cancer diagnosis. To meet the needs of your specific projects, Creative Biolabs now offers a series of custom cancer diagnosis services as follows:
- Nucleic acid detection based on Microfluidics
- Protein detection based on Microfluidics
- Integrated approach for multiplexed protein and DNA analysis
- Single cell analysis based on Microfluidics
Based on our robust and standardized diagnosis platform and Microfluidic technology, Creative Biolabs is a global leading diagnostic service company. Our specialized scientist team provides tailored services and full technical support to all of our customers. Please feel free to contact us for more details, and we will find the best solution for your needs.
Published Data
1. Microfluidics for Outpatient Ovarian Cancer Immune Monitoring
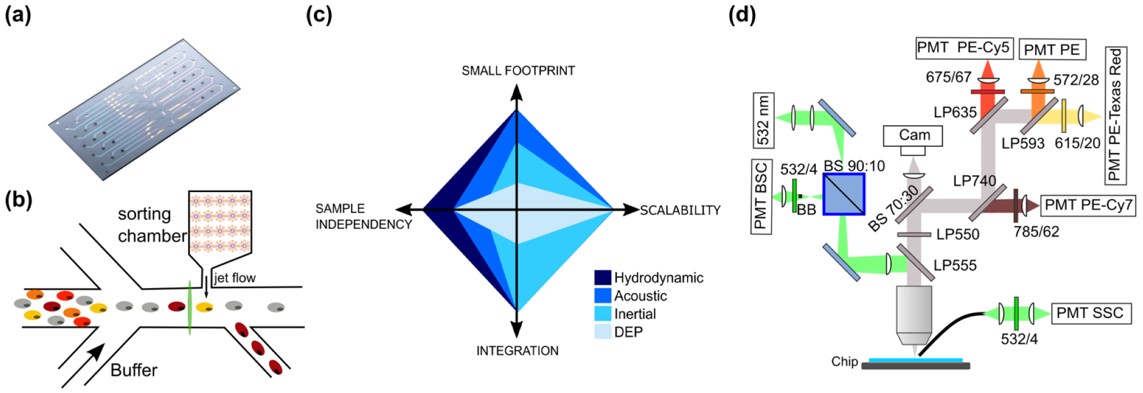 Fig.2 Description of the chip cytometer setup.3,2
Fig.2 Description of the chip cytometer setup.3,2
In this study, researchers developed a disposable microfluidic chip designed for immune readout with high sensitivity, aiming to guide diagnostic decisions for the patient. As a proof of concept, they compared the chip’s fluidics module to a conventional flow cytometer using a basic immune panel, including CD8, CD45, PD1, and a live/dead marker. Using peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 15 ovarian cancer patients at different treatment stages, the chip achieved a 99% correlation for detecting CD8+PD1+ T cells relative to CD45+ white blood cells. With further system development, including the integration of photonic illumination, this microfluidic chip could facilitate immune monitoring in outpatient settings, providing rapid data collection without requiring highly specialized personnel.
2. Digital Microfluidics for Drug Screening in Cancer Precision Medicine
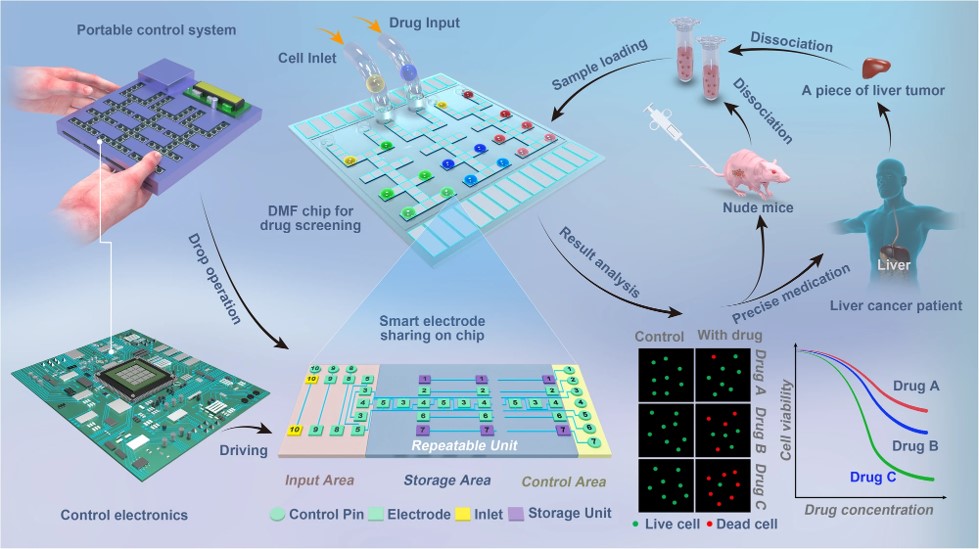 Fig.3 Schematic of drug screening on digital microfluidics.4.2
Fig.3 Schematic of drug screening on digital microfluidics.4.2
In this study, researchers engineered a digital microfluidic system for drug screening with primary tumor cells, establishing a framework for precision medicine. The system, featuring smart control logic, increased throughput while minimizing the device's footprint, allowing for parallel screening of three drugs on a 4 × 4 cm² chip within a device measuring 23 × 16 × 3.5 cm³. By validating this approach in an MDA-MB-231 breast cancer xenograft mouse model and patient liver cancer samples, they demonstrated tumor suppression in mice and patients who received drugs identified as effective through screening of primary tumor cells. Drugs deemed ineffective on-chip showed similar results to control groups. The effective drug’s consistency with gene exome sequencing of individual tumors further validated the protocol, highlighting its potential for advancing precision medicine for cancer and other diseases.
References
- Bargahi, Nasrin, et al. "Recent advances for cancer detection and treatment by microfluidic technology, review and update." Biological Procedures Online 24.1 (2022): 1-20.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Libbrecht, Sarah, et al. "A Microfluidics Approach for Ovarian Cancer Immune Monitoring in an Outpatient Setting." Cells 13.1 (2023): 7.
- Zhai, Jiao, et al. "Drug screening on digital microfluidics for cancer precision medicine." Nature Communications 15.1 (2024): 4363.
For Research Use Only.