Aptamers are synthetic RNA or DNA oligonucleotide ligands with a huge potential for therapeutic applications. A vast number of disease-related targets have been used to identify antagonistic, agonistic, and inhibitory aptamers. Armed with a deeper understanding of aptamer structure, target interactions, and pharmacokinetics, Creative Biolabs strongly believes that we are competent to catch up to the preclinical market to offer diverse therapeutic aptamer candidates to promote your drug research project.
Introduction to Therapeutic Aptamers
Aptamers are a class of potential therapeutic agents due to their synthetic nucleic acid-based nature, their selective and high affinity interaction with target antigens. Therapeutic aptamers are either selected in vitro by using purified proteins, whole cells, tissue or directly in vivo using suitable model systems. Depending on the desired function, the systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX) conditions can be adjusted accordingly. For therapeutic applications, aptamers are normally in competition with antibodies and small molecules. As Table 1 shown, aptamers targeting different antigens have been developed with obvious therapeutic applications.
Table 1. Aptamers to partial targets of therapeutic interest.
| Target | Therapeutic applications | Target | Therapeutic applications |
| α-thrombin | Prevent thrombosis | FGF2 | Prevent angiogenesis |
| HIV-1 Rev | Inhibit viral replication | IgE | Prevent allergies |
| VEGF | Prevent neovascularization | Tenascin C | Prevent tumour development |
| PDGF | Prevent tumor development | αvβ3 integrin | Prevent tumour development |
| l-Selectin | Modulate inflammation | PSMA | Treat progressive malignant prostate disease |
| Interferon-γ | Modulate inflammation and immune response | U1A | Modulate gene regulation |
| Neutrophil elastase | Modulate inflammation | GNRH1 | Prevent tumour development |
| P-selectin | Inhibit viral adhesion | E2F transcription factor | Prevent tumour development |
| Acetylcholine receptor | Control neurotransmission | Neurotensin 1 | Prevent viral infection |
Aptamer Improvement for Translating into Clinical Candidates
Having worked on adapters for many years with rich experience and sound strategies, Creative Biolabs makes full use of advantages to overcome current challenges such as short half-life in vivo, immunogenicity, and entrapment in cellular organelles. Similar to monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), aptamers can theoretically be used therapeutically in any disease for which extracellular blockade of protein-protein interactions is required. At Creative Biolabs, aptamers can be addressed to intracellular targets, membrane components, or circulating molecules. They can also be used as drug-delivery agents to cells of interest.
On the other hand, wild-type aptamers are too susceptible to nuclease-mediated degradation to be useful for most therapeutic applications. Therefore, chemical modification is necessary to obtain a promising candidate.
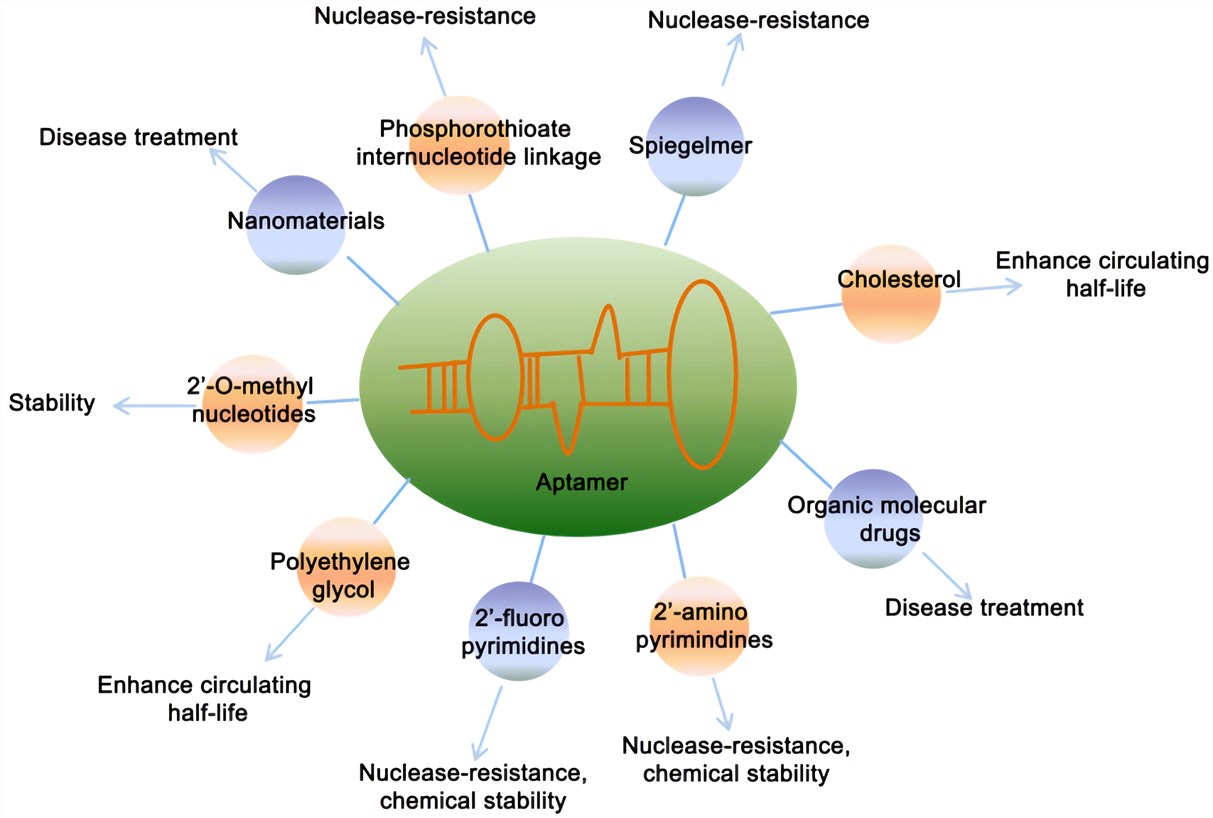 Fig.1 Chemical modification of aptamers.1,4
Fig.1 Chemical modification of aptamers.1,4
Modifications for Protecting Aptamers from Being Degraded by Nuclease
- 3’-3’and 5’-5’ Capping
- 2′-Substitutions and phosphodiester linkage
- Unnatural nucleotides incorporation
- Modifications with D-/L-Isonucleoside
- Nuclease-resistant circular aptamers development
Long-Acting Modifications of Aptamers
- 5′-End with cholesterol
- 5′-End PEGylation
- 5’-End-Dialkyl lipid modification
- Serum albumin carrier
Benefits of our Therapeutic Aptamers Agents
Aptamers constitute a new class of oligonucleotides that have gained therapeutic importance. At Creative Biolabs, aptamers could be truncated to reduce synthesis costs, modified at the sugars and capped at their termini to increase nuclease resistance, and conjugated to polyethylene glycol or another entity to reduce renal filtration rates. If you are interested in our therapeutic aptamer agent development to support your research projects, please feel free to contact us.
Published Data
1. DNA Aptamers Targeting DEK for Inflammatory Arthritis Therapy
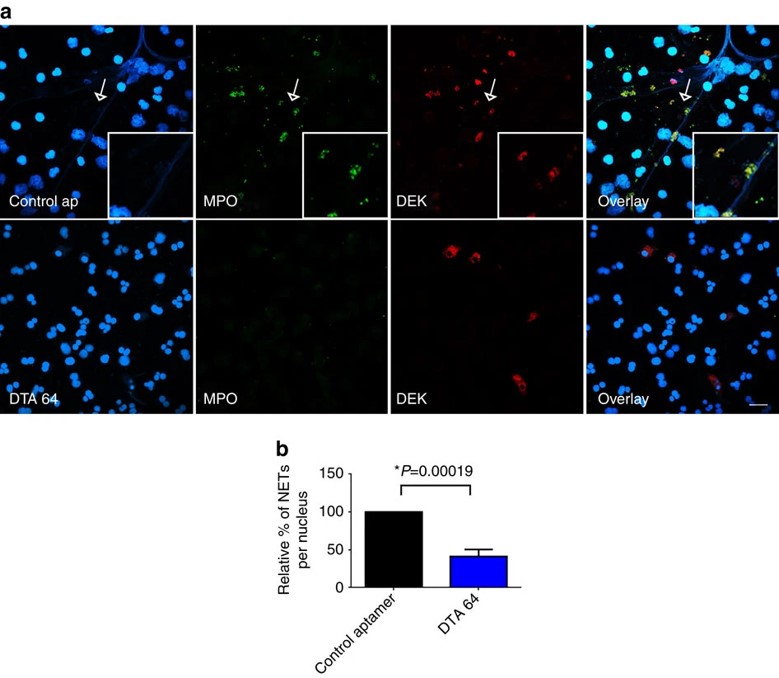 Fig.2 Fewer NET structures and retention of intracellular DEK in neutrophils treated with anti-DEK aptamer.2,4
Fig.2 Fewer NET structures and retention of intracellular DEK in neutrophils treated with anti-DEK aptamer.2,4
Innovative therapies are required to effectively treat chronic inflammatory diseases. The nuclear chromatin protein DEK, a secreted chemoattractant found in high levels in the synovia of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) patients, plays a key role in arthritis development. In this study, researchers showed that DEK was essential for arthritis progression in mouse models, making it a promising target for aptamer-based therapy. Genetic depletion of DEK or treatment with DEK-targeted aptamers significantly reduced joint inflammation and inhibited neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation. DEK was detected in NETs from JIA patient synovial neutrophils, and DEK-targeted aptamers reduced NET formation. These findings suggested that anti-DEK aptamers could be effective for treating JIA and other arthritis types.
2. A Neutralizing Aptamer Targeting FGF2 for Bone Disease and Bone Cancer Pain Therapy
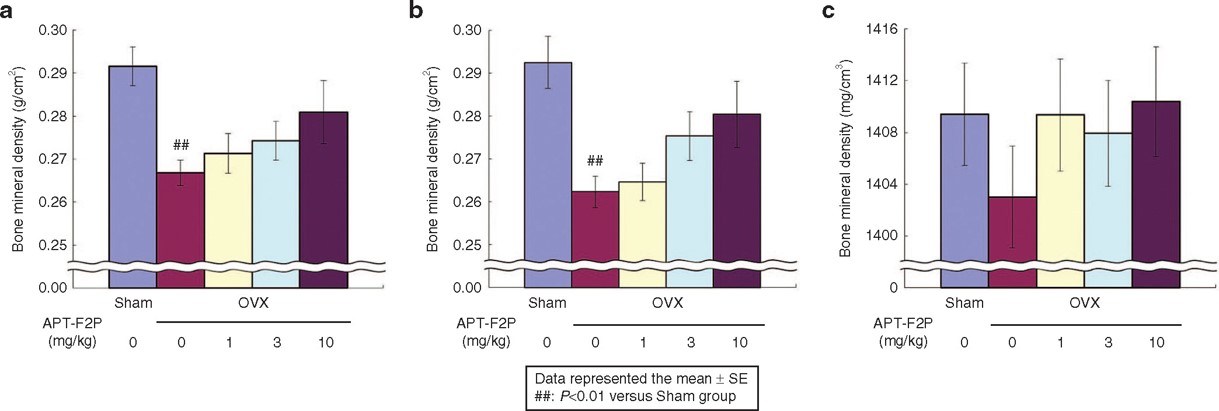 Fig.3 Blockade of bone density loss in ovariectomized rats by anti-FGF2 aptamer.3,4
Fig.3 Blockade of bone density loss in ovariectomized rats by anti-FGF2 aptamer.3,4
Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) is vital for bone remodeling and the advancement of various diseases. However, the therapeutic potential of FGF2 antagonists in treating bone diseases remains unexplored. In this study, a novel RNA aptamer specific to human FGF2 was generated and characterized both in vitro and in vivo. The anti-FGF2 aptamer effectively prevented FGF2 from binding to its four cellular receptors, inhibited downstream signaling, reversed the inhibition of osteoblast differentiation caused by FGF2. A PEGylated version of the anti-FGF2 aptamer also effectively prevented bone damage in mouse and rat models of osteoporosis and arthritis. Additionally, treatment with this aptamer provided significant analgesic effects, comparable to common anesthetics, in a mouse model of bone cancer pain. These findings demonstrated the dual therapeutic potential of the anti-FGF2 aptamer for treating bone diseases and pain, offering a promising treatment strategy.
References
- Han, Jing, et al. "Application and development of aptamer in cancer: from clinical diagnosis to cancer therapy." Journal of Cancer 11.23 (2020): 6902.
- Mor-Vaknin, Nirit, et al. "DEK-targeting DNA aptamers as therapeutics for inflammatory arthritis." Nature communications 8.1 (2017): 14252.
- Jin, Ling, et al. "Dual therapeutic action of a neutralizing anti-FGF2 aptamer in bone disease and bone cancer pain." Molecular Therapy 24.11 (2016): 1974-1986.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.