Polyclonal and monoclonal in vitro diagnostic (IVD) antibodies are widely used in immunoassays and diagnostic kits such as sandwich ELISA, Western Blot, Immunofluorescence, Immunocytochemistry, and Immunohistochemistry for the diagnosis of a variety of diseases. With many years of experience in the field of IVD antibody development, Creative Biolabs is proud to offer the most comprehensive and reliable IVD antibody development services targeting different serum proteins, bacterial antigens, and other markers.
Introduction of Streptococcus
Streptococcus is a genus of spherical Gram-positive bacteria. They are generally classified into three groups based on their hemolytic properties: alpha-hemolytic, beta-hemolytic species, and gamma-hemolytic species. Different species are responsible for different diseases. The most important groups implicated in the respiratory infections are the Streptococcus pneumoniae (S. pneumonia) and group A Streptococcus (GAS). S. pneumoniae is a leading cause of bacterial pneumonia while GAS (also known as S. pyogenes) is responsible for group A streptococcal infections, including streptococcal pharyngitis (strep throat) and impetigo.
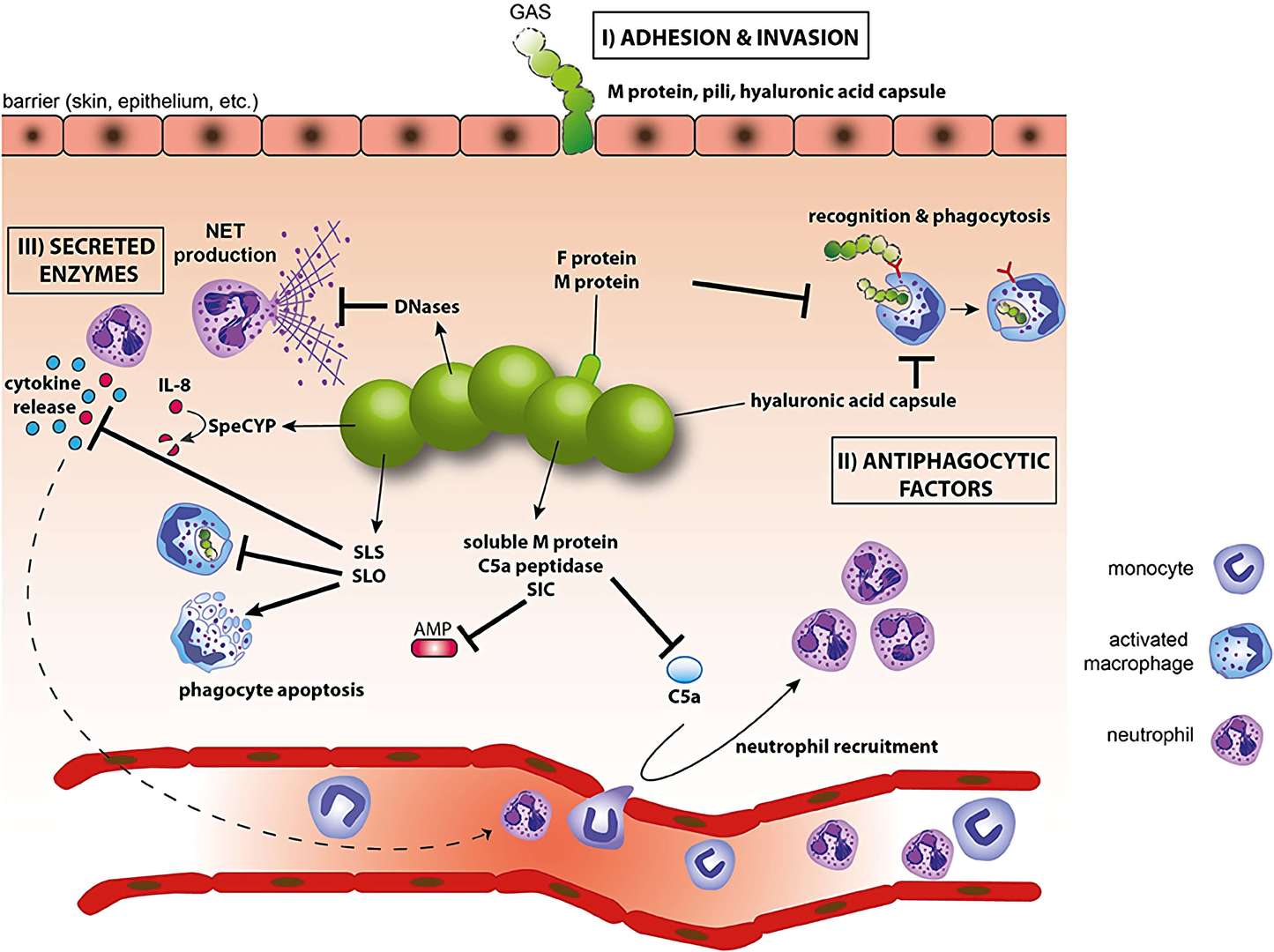 Fig.1 Evasion of innate immunity by GAS. (Fieber, C., 2014)
Fig.1 Evasion of innate immunity by GAS. (Fieber, C., 2014)
Laboratory Diagnosis of S. pneumoniae
The gold standard diagnostic method of S. pneumoniae is still culture, but good-quality samples are not always available. Specimens collected should be plated onto a sheep blood agar for culturing for morphology characterization. Other diagnostic tests that are inexpensive and easy to use without extensive training are also developed, such as an immunochromatographic test that detects the C polysaccharide cell wall antigen, common to all strains of S. pneumoniae, in urine. Besides, nucleic acid amplification tests, such as PCR, are important diagnostic tools for S. pneumoniae.
Laboratory Diagnosis of GAS
Today, laboratory diagnosis of GAS infections still largely relies on culturing bacteria from clinical specimens. For detection, the material is most often cultured on blood agar plates, which facilitates the primary screening of beta-hemolytic colonies. Subsequent confirmation of suspicious colonies as S. pyogenes can be achieved by several easy, rapidly performed laboratory tests such as Lancefield antigen determination, the PYR test (used to distinguish S. pyogenes from other β-hemolytic streptococci with a similar morphology), antibiotic resistance testing (using penicillin), and direct antigen detection. The Lancefield antigens are presented on the streptococcal surfaces which can be determined through the use of specific antibodies. Likewise, rapid antigen tests are based on the antigen-antibody interaction. During the past two decades, numerous commercially available immunoassays with varying specificity have been developed.
Correlation of Streptococcus and Food & Water
Water and food are essential to life, but many people do not have access to clean and safe drinking water and food. Even worse, many people die of waterborne and foodborne bacterial infections. Studies have suggested that various bacteria including Coliform, Escherichia coli, Streptococcus, Thiobacillus spp, are associated with food and water pollution which result in increased health risks to persons exposed to the pollutions and nutrient loss. Streptococcus agalactiae, also known as group B Streptococcus (GBS), colonizes the digestive and urinary tracts of approximately one-third of the human population. In addition to the cause of bovine mastitis and invasive disease in fish, it is also a well-known cause of severe infections in neonates, the elderly, and the immunocompromised. Most importantly, it has been used as an important biological parameter for the monitor of food & water pollution.
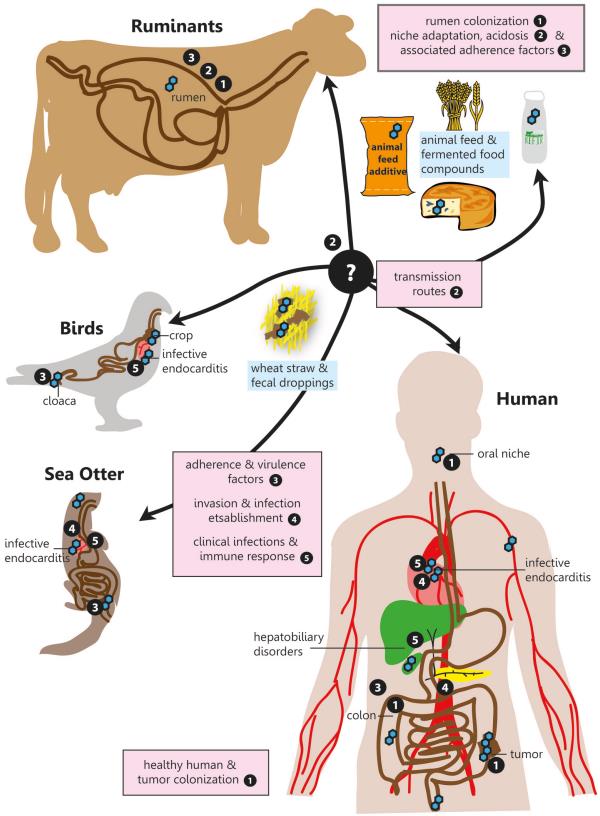 Fig.2 The infection road of Streptococcus bovis/Streptococcus equinus complex (SBSEC).2
Fig.2 The infection road of Streptococcus bovis/Streptococcus equinus complex (SBSEC).2
With the rapid evolvement of IVD market, antibodies with high sensitivity and low cross-reactivity are becoming increasingly important for the in vitro diagnosis of bacterial and viral infections, and they can provide important information for both of their diagnosis and treatment. Creative Biolabs has been focusing on this field and we provide customized IVD antibody development services to help promote the brilliant IVD researches of our clients. Contact us to discuss your requirements.
References
- Fieber, Christina, and Pavel Kovarik. "Responses of innate immune cells to group A Streptococcus." Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology 4 (2014): 140. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Jans, Christoph, and Annemarie Boleij. "The road to infection: host-microbe interactions defining the pathogenicity of Streptococcus bovis/Streptococcus equinus complex members." Frontiers in microbiology 9 (2018): 341264. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.