In recent years, long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have garnered increasing attention as vital components in biological regulation. At Creative Biolabs, we reveal the potential roles of lncRNAs by precisely targeting those that exhibit differential expression under specific conditions.
What Are LncRNAs?
LncRNAs constitute a unique category of RNA molecules, characterized by their extended length of exceeding 200 nucleotides. Rather than encoding proteins, lncRNAs play pivotal roles in a series of cellular processes. For instance, lncRNAs facilitate the regulation of gene transcription by enlisting chromatin-modifying enzymes. Furthermore, they are capable of forming stable, higher-order structures, thereby engaging in diverse processes such as protein synthesis, cellular growth, and cellular differentiation.
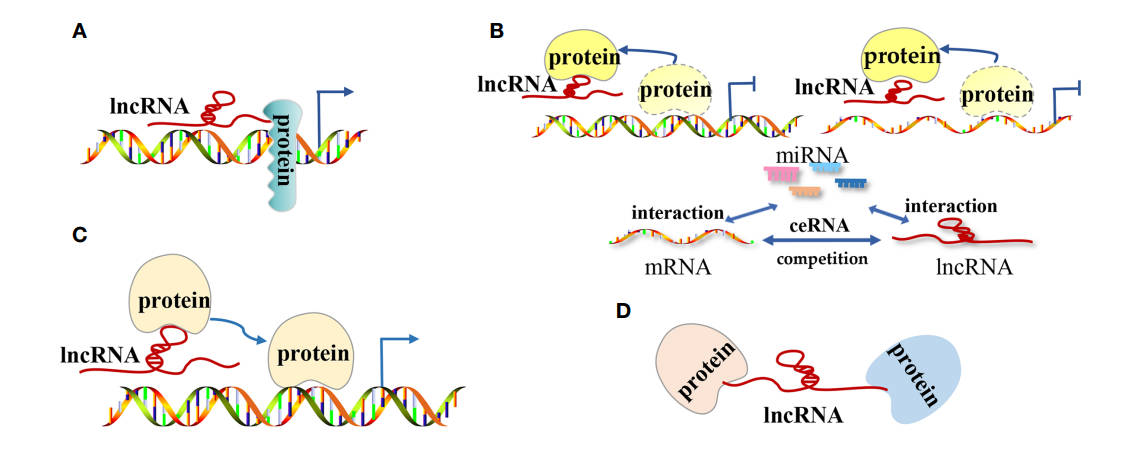 Fig.1 The modes of action of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in tumors.1
Fig.1 The modes of action of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in tumors.1
Core Features
- Comprehensive Analysis
LncRNA sequencing provides a comprehensive view of the lncRNA landscape within a biological sample.
- High Resolution
It offers high-resolution mapping of lncRNA transcripts, allowing for precise identification and characterization of these molecules.
- Discovery of Novel lncRNAs
The technique facilitates the discovery of novel lncRNA species that may have previously been unannotated or overlooked.
- Expression Profiling
LncRNA sequencing facilitates the generation of detailed expression profiles for lncRNAs across various tissues, developmental stages, and disease conditions.
- Integration with Other Data
The results from lncRNA sequencing can be integrated with other genomic, transcriptomic, and proteomic data to gain a more holistic understanding of gene regulation.
- Scalability
LncRNA sequencing is scalable and can be adapted to analyze large numbers of samples, making it suitable for high-throughput studies.
Detailed Workflow
The detailed workflow of LncRNA sequencing involves several crucial steps:

Applications
- Gene Regulation Studies
LncRNA sequencing is used to investigate the changes in lncRNA expression across different cell types, tissues, or developmental stages, shedding light on their roles in gene regulation.
- Disease Association Studies
By comparing lncRNA expression data between disease patients and normal controls, researchers can identify lncRNAs associated with specific diseases, contributing to a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms.
- Drug Development
Insights into the roles of lncRNAs in disease can facilitate the development of therapeutic strategies targeting lncRNAs, such as using them as drug targets or regulatory modulators.
- Cancer Research
LncRNA sequencing has broad applications in revealing the expression changes, regulatory networks, and functions of lncRNAs in cancer development and progression.
- Biomarker Discovery
Some lncRNAs show significant expression changes in specific disease states, making them potential biomarkers for disease diagnosis and monitoring.
FAQs
Q: How can LncRNA sequencing results be validated?
A: Validation can be performed using techniques such as qRT-PCR, northern blotting, or RNA-FISH to confirm the presence and expression levels of identified lncRNAs.
Q: What are some potential applications of lncRNA sequencing?
A: Applications include studying the roles of lncRNAs in disease development, identifying novel therapeutic targets, and developing diagnostic and prognostic tools based on lncRNA expression profiles.
Q: What are the requirements for lncRNA sequencing samples?
A: For lncRNA sequencing, RNA samples must meet specific quality and quantity criteria to ensure accurate and reliable sequencing results. The RNA concentration should be at least 100 ng/μL, with a total amount of at least 3 μg.
LncRNA sequencing is a powerful tool for studying the expression and functions of long non-coding RNAs. Contact our team for customized solutions for lncRNA sequencing.
Reference
- Gao, Na, et al. "Long non-coding RNAs: the regulatory mechanisms, research strategies, and future directions in cancers." Frontiers in oncology 10 (2020): 598817. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.