Binary Kernel Discrimination
Binary kernel discrimination (BKD), a machine-learning technique, is applied for a virtual screening tool in drug-discovery programs. It is used to rank a set of test compounds in order of likely activity and identify the potential active compounds. Employing this technique, Creative Biolabs is honored to provide the best and all-round solutions for the identification of potential active drugs in a short time, promoting your project success.
Introduction of Binary Kernel Discrimination
BKD is a machine-learning approach that has been applied to identifying potential active compounds in leading-discovery programs. It uses a training set of compounds with known structural and qualitative activity data to generate a model. The model can then be used to rank another set of compounds in order of possible activity. In BKD the molecule is represented as 2D fragment bit-string. It consists of three components firstly structural representation section, secondly, similarity searching section using different coefficients, and thirdly section with different weighting schemes for lead compounds. It can be applied to a very large file of 2D fingerprints and also applicable to different pharmaceutical databases.

- Kernel Function
The bellowing shows a kernel function suggested by Aitchison and Aitkin.
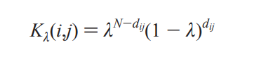
dij is the squared euclidean distance between a pair of compounds i and j represented by binary fingerprints. λ is a smoothing parameter to be determined. n is the length of the binary fingerprints. The kernel function is used in kernel density estimators to estimate the likelihood that a compound is active or not.
- Scoring Function
The bellowing shows a scoring function which is the ratio of the sum of the kernel functions computed with all the training set actives and the sum of the kernel functions computed with all the training set inactives, suggested by Harper et al. (1999).
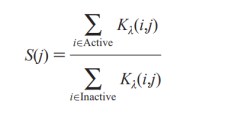
The optimum value of λ is determined from the training set by computing scores for each training set compound using a number of different values of λ between 0.5 and 1.0. And the optimum λ is considered to be the result of the lowest sum of ranks for the training set actives.
What Can We Do?
Creative Biolabs has organized an excellent expert team that has rich expertise in application of binary kernel discrimination for virtual screening in drug discovery programs. According to your special purposes, we can customize the optimal virtual screening strategy to accelerate the process of drug discovery. Leveraging binary kernel discrimination methods, we can analyze the dis-similarities between a single test set compound and the training set compounds to generate a score suggesting the likelihood of that test set compound being active, thereby selecting and identifying optimal active compounds.
If you are interested in our services of drug discovery based on binary kernel discrimination, please do not hesitate to contact us.
For Research Use Only.
