Introduction of GPR161
GPR161 was originally isolated from fetal brain and was later renamed GPR161 as a member of the GPCR superfamily that is commonly used by cells to sense and respond to their environment. GPR161 belongs to class A rhodopsin family, and following a large-scale phylogenetic analysis, the human GPR161 was assigned to the δ group of the RHODOPSIN family within the purine receptor cluster that includes several known receptors which bind such diverse ligands as nucleotides, leukotrienes, and thrombin.
| Basic Information of GPR161 | |
| Protein Name | G-protein coupled receptor 161 |
| Gene Name | GPR161 |
| Aliases | G-protein coupled receptor RE2 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| UniProt ID | Q8N6U8 |
| Transmembrane Times | 7 |
| Length (aa) | 529 |
| Sequence | MSLNSSLSCRKELSNLTEEEGGEGGVIITQFIAIIVITIFVCLGNLVIVVTLYKKSYLLTLSNKFVFSLTLSNFLLSVLVLPFVVTSSIRREWIFGVVWCNFSALLYLLISSASMLTLGVIAIDRYYAVLYPMVYPMKITGNRAVMALVYIWLHSLIGCLPPLFGWSSVEFDEFKWMCVAAWHREPGYTAFWQIWCALFPFLVMLVCYGFIFRVARVKARKVHCGTVVIVEEDAQRTGRKNSSTSTSSSGSRRNAFQGVVYSANQCKALITILVVLGAFMVTWGPYMVVIASEALWGKSSVSPSLETWATWLSFASAVCHPLIYGLWNKTVRKELLGMCFGDRYYREPFVQRQRTSRLFSISNRITDLGLSPHLTALMAGGQPLGHSSSTGDTGFSCSQDSGTDMMLLEDYTSDDNPPSHCTCPPKRRSSVTFEDEVEQIKEAAKNSILHVKAEVHKSLDSYAASLAKAIEAEAKINLFGEEALPGVLVTARTVPGGGFGGRRGSRTLVSQRLQLQSIEEGDVLAAEQR |
Function of GPR161 Membrane Protein
GPR161 is the key negative regulator of Shh signaling, which promotes the processing of GLI3 into GLI3R during neural tube development. GPR161 is recruited by the IFT-A complex and TULP3 to primary cilia, it functions as a regulator of the PKA-dependent basal repression machinery in Shh signaling by increasing cAMP levels, leading to promote the PKA-dependent processing of GLI3 into GLI3R and repress the Shh signaling. Furthermore, GPR161 displays restricted expression to the lateral neural folds, developing lens, retina, limb, and CNS. In presence of SHH, GPR161 is removed from primary cilia and is internalized into recycling endosomes, preventing its activity and allowing activation of the Shh signaling. Besides, A C-terminal truncation (deletion) mutation in GPR161 causes congenital cataracts and neural tube defects in the vacuolated lens (vl) mouse mutant. These previous studies identified GPR161 as a new receptor-ligand mediated pathway necessary for neural tube closure and lens development.
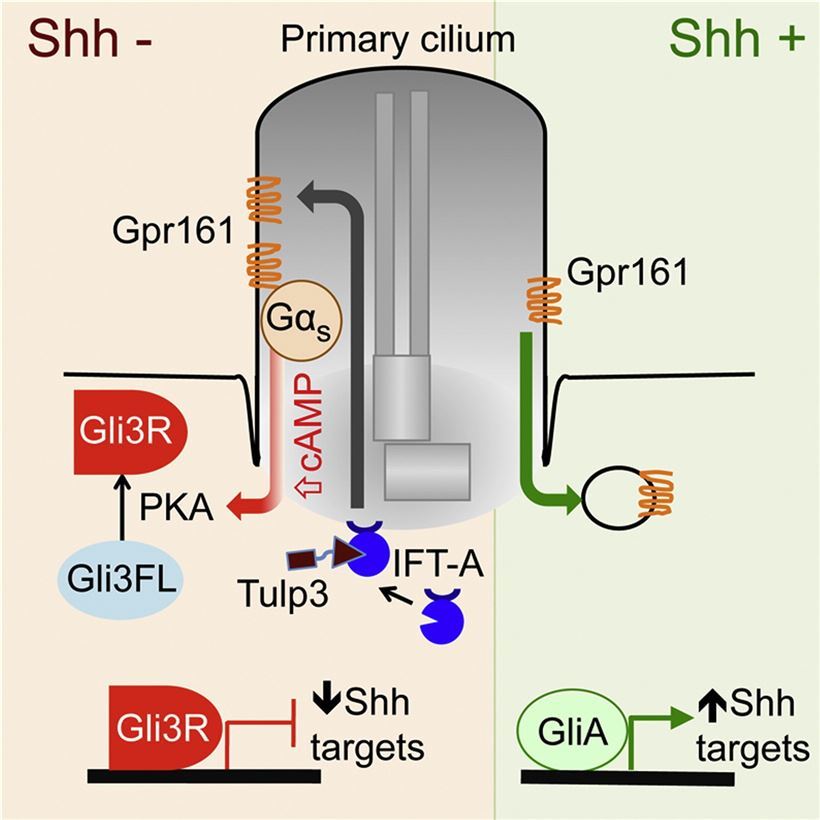 Fig.1 Basal activity of Gpr161 results in increased cAMP levels.
Fig.1 Basal activity of Gpr161 results in increased cAMP levels.
Application of GPR161 Membrane Protein in Literature
This article describes that G-protein-coupled receptor 161 localizes to primary cilia in a Tulp3/IFT-A-dependent manner. Complete loss of GPR161 in mouse causes midgestation lethality and increased Shh signaling in the neural tube, phenocopying Tulp3/IFT-A mutants. Constitutive GPR161 activity increases cAMP levels and represses Shh signaling by determining the processing of Gli3 to its repressor form
This study uses a deletion mutation in GPR161 to reveal that the cloning of the vl locus has identified a previously uncharacterized GPCR-ligand pathway necessary for neural fold fusion and lens development, providing insight into the molecular regulation of these developmental processes, and reveal that GPR161 interacts with a genetic modifier, Foxe3, to regulate lens development.
This article identifies the orphan GPCR, GPR161, as an important regulator and a potential drug target for TNBC. GPR161 forms a signaling complex with the scaffold proteins β-arrestin 2 and Ile Gln motif containing GTPase Activating Protein 1, a regulator of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 and E-cadherin. Consistently, GPR161 amplified breast tumors and cells overexpressing GPR161 activate mammalian target of rapamycin signaling and decrease Ile Gln motif containing GTPase Activating Protein 1 phosphorylation.
This study demonstrates the Modifier of the vacuolated lens (vl) congenic rescues the GPR161(vl)-associated lethality and NTDs but not cataracts.
This article proposes that GPR161 is itself an AKAP and that the cAMP-sensing GPR161: PKA complex acts as cilium-compartmentalized signalosome, a concept that now needs to be considered in the analyzing, interpreting, and pharmaceutical targeting of PKA-associated functions.
GPR161 Preparation Options
To obtain the soluble and functional target protein, the versatile Magic™ membrane protein production platform in Creative Biolabs enables many flexible options, from which you can always find a better match for your particular project. Aided by our versatile Magic™ anti-membrane protein antibody discovery platform, we also provide customized anti-GPR161 antibody development services.
As a forward-looking research institute as well as a leading customer service provider in the field of membrane protein, Creative Biolabs has won good reputation among our worldwide customers for successfully accomplishing numerous challenging projects including generation of many functional membrane proteins. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.