Introduction of GPR22
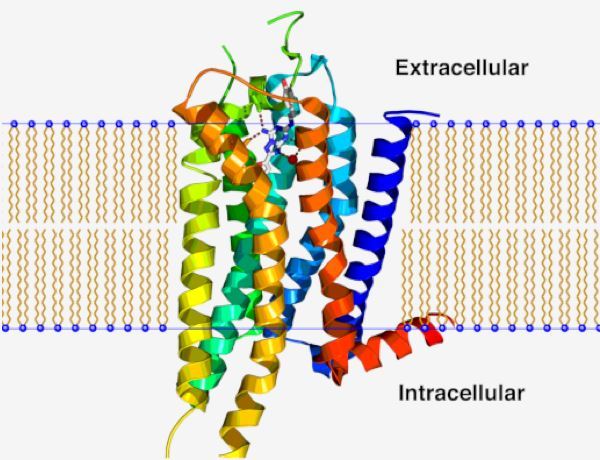
GPR22 is encoded by the GPR22 gene. It belongs to the G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family whose membranes are crucial molecular sensors for many vital physiological processes. GPR22 is an orphan GPCRs and belongs to the class A rhodopsin-like GPCRs subfamily. GPR22 possess seven transmembrane alpha helices and its endogenous ligand remains unidentified so far. Meanwhile, GPR22 is discovered by searching a database with similar expressed sequence tags together with three other human GPCR genes, GPR21, GPR23, and GPR20.
| Basic Information of GPR22 | |
| Protein Name | Probable G-protein coupled receptor 22 |
| Gene Name | GPR22 |
| Aliases | NA |
| Organism | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| UniProt ID | Q99680 |
| Transmembrane Times | 7 |
| Length (aa) | 433 |
| Sequence | MCFSPILEINMQSESNITVRDDIDDINTNMYQPLSYPLSFQVSLTGFLMLEIVLGLGSNLTVLVLYCMKSNLINSVSNIITMNLHVLDVIICVGCIPLTIVILLLSLESNTALICCFHEACVSFASVSTAINVFAITLDRYDISVKPANRILTMGRAVMLMISIWIFSFFSFLIPFIEVNFFSLQSGNTWENKTLLCVSTNEYYTELGMYYHLLVQIPIFFFTVVVMLITYTKILQALNIRIGTRFSTGQKKKARKKKTISLTTQHEATDMSQSSGGRNVVFGVRTSVSVIIALRRAVKRHRERRERQKRVFRMSLLIISTFLLCWTPISVLNTTILCLGPSDLLVKLRLCFLVMAYGTTIFHPLLYAFTRQKFQKVLKSKMKKRVVSIVEADPLPNNAVIHNSWIDPKRNKKITFEDSEIREKCLVPQVVTD |
Function of GPR22 Membrane Protein
GPR22 expresses in several human brain regions, such as the cerebellum, cerebral cortex, and amygdala according to the RNA expression analysis. The activation of GPR22 leads to the inhibition of adenylyl cyclase, a decreased production of cAMP and a decreased PKA activity in HEK-293 cells. GPR22 plays an important role in osteoarthritis (OA) in a genome wide association study because GPR22 is present in human OA cartilage but not in healthy tissue. Overexpression of GPR22 accelerates chondrocyte hypertrophy and can be antagonized by AG-041R, which is a novel stimulator of chondrogenesis. GPR22 is genetically and functionally linked to human OA and may be a potential therapeutic target. GPR22 knockout mice have an increased risk to functional cardiac decompensation following aortic banding even though it has no any notable phenotype. However, the biological function of GPR22 remains poorly studied and its role in the disease process is still discussed.
Application of GPR22 Membrane Protein in Literature
This article reports that expression pattern of GPR22 and GRP162 in heart, aorta, brain, and kidney of diabetic rats, suggesting that GPR22 and GPR162 may be involved in the development of diabetes complications.
This article shows that knocking down the expression of GPR22 using morpholino leads to the defective left-right axis formation in the zebrafish embryo. The overexpression of GPR22 results in the changes of cilia length and structure in zebrafish.
Authors in this group apply the genetic screening method to reveal that GPR22 may contribute to the pathology of juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
This article describes the expression pattern and possible physiological function of GPR22. The GPR22 null mice show increased susceptibility to functional decompensation following aortic banding even though have no obvious effect on normal heart structure or function in the mice model.
This article focuses on evaluating the biological function of orphan class-A G protein coupled receptors in the cAMP signaling pathway. It shows that GPR22 can inhibit the CRE-mediated gene expression in GPR22 transiently expressed CHO-K1 cells.
GPR22 Preparation Options
To obtain the soluble and functional target protein, the versatile Magic™ membrane protein production platform in Creative Biolabs enables many flexible options, from which you can always find a better match for your particular project. Aided by our versatile Magic™ anti-membrane protein antibody discovery platform, we also provide customized anti-GPR22 antibody development services.
As a leading customer service provider in the field of membrane protein as well as a forward-looking research organization, Creative Biolabs has accumulated a wealth of experience by successfully accomplishing numerous challenging projects including generation of many functional membrane proteins for our worldwide customers. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.