- Home
- ADC Development
- Antibody Discovery for ADC Development
- Tumor Surface Protein Specific Antibody Discovery
- Anti-CD200 Antibody Discovery
Anti-CD200 Antibody Discovery Service
Equipped with state-of-the-art research and manufacturing facilities, Creative Biolabs is dedicated to helping our clients design and prepare antibodies with high affinity and good specificity to promote the development of your projects. CD200 is a molecule with potent immunosuppressive functions through interaction with its receptor, CD200R. With over a decade of experience in monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) preparation and modification, experts at Creative Biolabs can provide customers with customized services against CD200.
CD200
CD200, a type-I transmembrane glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF), is overexpressed in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) patients and exerts its immunosuppressive function in fetal rejection, autoimmune disease, and transplant tolerance. Based on the structure of CD200, with a prominent extracellular V + C domain, a small transmembrane domain with no signaling motifs and no docking sites for adapter signaling molecules, along with a short cytoplasmic tail lacking signaling motifs, it had been prevailing dogma that signaling by CD200 occurred through engagement of its extracellular V + C region with an inhibitory receptor (CD200R) present on other cells. CD200 is one such molecule whose expression on lymphoma cells has been shown to dampen their killing by cytotoxic lymphocytes in vitro.
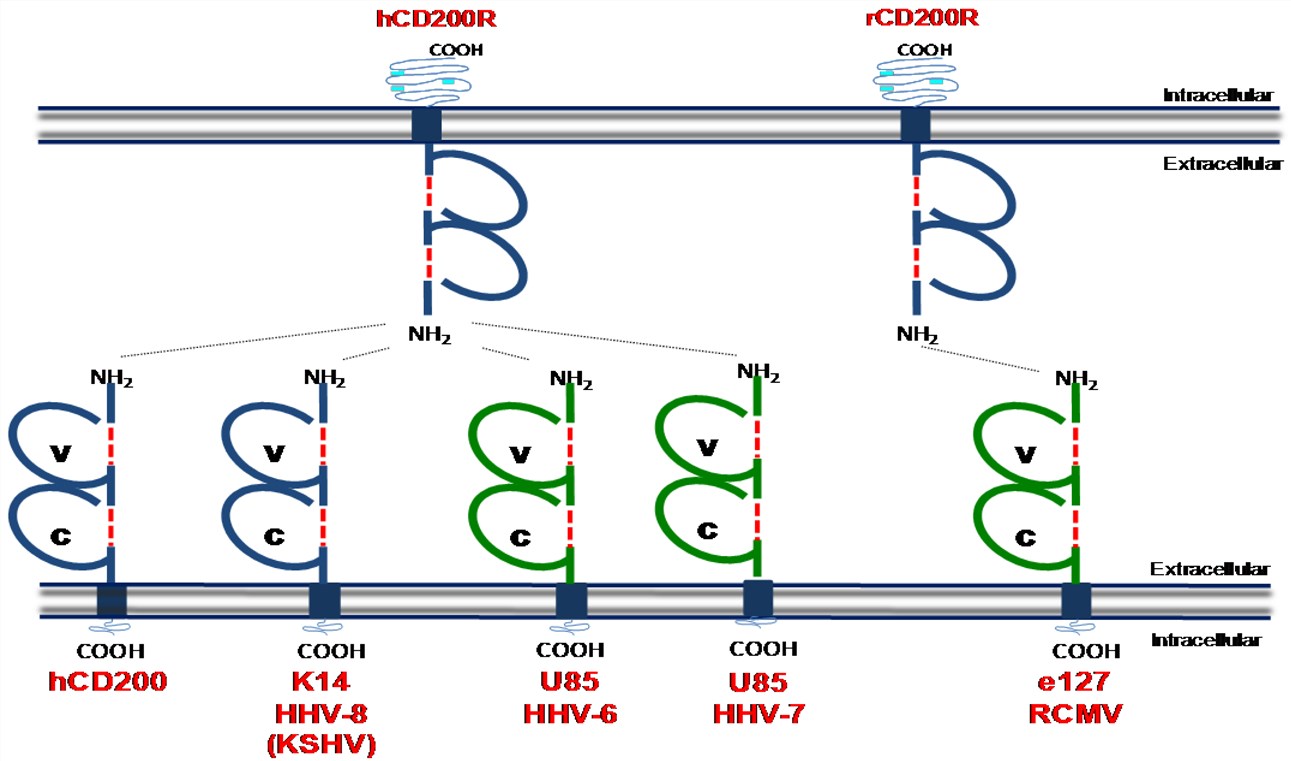 Fig.1 Determined structures of cellular CD200 and CD200 homologues encoded by human and rat herpesviruses.1,2
Fig.1 Determined structures of cellular CD200 and CD200 homologues encoded by human and rat herpesviruses.1,2
Ectodomain Shedding
CD200 shedding occurs in CD200-expressing cells of epithelial and lymphocyte origin, under both resting and activated conditions. The functionally active soluble CD200 extracellular moiety (sCD200) may be generated from the cell surface by mechanisms of ectodomain cleavage by a disintegrin and metalloprotease (ADAM) and matrix metalloproteases (MMPs) family of proteases. ADAM28 plays an extremely important role in the constitutive shedding of CD200. The exact cleavage site(s) on CD200 remains to be elucidated. sCD200 acts as an immunosuppressant following binding to and signaling through, its cognate receptor CD200R expressed on target cells. The interaction between sCD200 and CD200R is critical for the downstream consequences of the CD200: CD200R axis of immunoregulation. Cleavage of the intracellular cytoplasmic tail (CD200C-tail) from the membrane region of CD200 leads to nuclear translocation and DNA binding of the CD200C-tail. Subsequently, there occurs an altered expression of a limited number of genes, many of which are transcription factors (TFs) known to be associated with the regulation of cell proliferation. Studies have proved that sCD200 increased growth and survival of CLL cells.
Antibody Strategies Against CD200
Creative Biolabs could provide new strategies which focus on the sCD200 to promote the development of innovative cancer treatments. Although the exact site(s) of proteolytic shedding remains to be unclear, antibodies could also be exploited to improve the current disease situation. Since the membrane-localized CD200 seems to be so short, the extracellular V + C region of CD200 could be regarded as targets to develop antibodies to neutralize itself, thereby preventing interaction with CD200R and any possible active sCD200-induced activity beneficial to tumor development.
Creative Biolabs provides customized antibody development services against tumor surface protein shedding from cells by advanced technology platform to help your projects. With novel technology platform and professional experiment services, Creative Biolabs gets ready to provide you with the best antibody services. Please feel free to contact us for more details.
References
- Stack, Gabrielle, Maria A. Stacey, and Ian R. Humphreys. "Herpesvirus exploitation of host immune inhibitory pathways." Viruses 4.8 (2012): 1182-1201.
- Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. NOT FOR CLINICAL USE.

Online Inquiry
Welcome! For price inquiries, please feel free to contact us through the form on the left side. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
